Maximum memory for 32 discharge system. RAM and Windows system. Maximum amount of RAM in Windows
How much memory can use a 32 bit operating system
First a bit of theory.
The simplest element of information - bit. It is a minimal unit of information and can take a value of 0 or 1. Byte, it consists of 8 bits. Since bit can take 2 values, then 2 8 \u003d 256 byte values \u200b\u200bare obtained.
Now consider addressing the memory. Any computer has RAM (RAM) - the address space required for storing the data used in this moment. For information from RAM, the processor must select the address of the desired bit, which is stored in one of the memory chips, and then read it. This process is called memory addressing. One of the properties of the computer architecture is the number of bits used in addressing the memory.
32 Bit OS to address memory use 2 32 bits, which is 4294967296 bits or 4 gigabytes (GB). This means that the maximum amount of memory to which the 32 bit operating system may apply, is 4 GB. However, even this amount to use fully we will not succeed, since the components of the operating system and the device require a dedicated address space within the first 32 bits (4 GB) random access memory. For example, a video card with 512 MB of memory will require synchronization of this memory with operational, which will reduce the available capacity by 512 MB.
Thus, the total amount of memory available in a 32-bit Windows OS is usually 3.25-3.75 GB, depending on the iron used.
Some versions of Windows support the feature called Physical Address Extension (PAE), Allowing to use more than 4 GB of memory thanks to a special redirection technology. This technology allows the processor to work not with a 32-bit, but with a 36-bit addressing, theoretically expanding addresses available to it to 2 36 \u003d 68719476736 bytes (64 GB). At the same time, the address space itself remains 32-bit, that is, equal to 4 GB, but due to the changed display of physical memory, it becomes possible to use a greater volume.
According to the official information of Microsoft, the PAE mode can be used in the following 32-bit operating systemsoh:
- Microsoft Windows. Server 2000 Enterprise / Datacenter Edition
- Microsoft. Windows Server 2003 ENTERPRISE / DATACENTER EDITION
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 ENTERPRISE / DATACENTER EDITION
The Server 2008 PAE is enabled by default if the Data Execution Prevention technology is enabled on the server on the hardware level), or the server has the ability to hot-add memory (Hot-Add Memory). Otherwise, the PAE must be enabled forced using BCDEDIT, the following command:
BCDEDIT / SET [(ID)] PAE ForceEnabled
To enable PAE in Server 2000 \\ 2003, you must specify the key in the boot.ini file / PAE.. Here is an example of a boot.ini file containing the PAE key:
Timeout \u003d 30.
Default \u003d Multi (0) Disk (0) RDisk (0) Partition (2) \\ Windows
multi (0) Disk (0) RDISK (0) Partition (2) \\ Windows \u003d "Windows Server 2003, Enterprise" / FastDetect / PAE
It is worth noting that the ability to use the PAE mode for client OS has been implemented in the second service pack to Windows XP. However, in the process of testing, it turned out that when using this mode occurs a large number of failure The fact is that the drivers of some devices, mainly such as audio and video, are rigidly programmed to work with memory addresses within 4GB. They cut all the addresses above this volume, which causes damage to the contents of memory with all concomitant consequences. Since, as a rule, the servers do not use such devices, then with server systems similar problems did not arise.
In connection with the identified disadvantages, it was decided to remove from 32-bit client systems the ability to work with over 4GB memory, although it is theoretically possible. Therefore, in the client OS family of Windows this technology Although being present, however, it is not activated at the kernel level, and the attempt to use it will not lead to anything.
Summing up I will say that if there is a need for memory more than 4GB, then the best option is to use a 64 bit OS, because in it a memory limit is up to 192 GB for desktop and 2 TB for server OS.
Hello dear blog readers www.Syt. Should immediately admit that in spite of the fact that I professionally engage in various aspects of IT for many years, until recently, such a question as maximum size random access memory in client computers with 32-bit operating systems, I was absolutely not interested.
However, probably, like the vast majority of other IT specialists and ordinary users of computers. Basically, it was necessary to solve conventional daily tasks, such as the selection of the type of memory for one or another motherboard, choosing the size and number of planks, the diagnosis of failures and many other of the same kind.
It is understandable. IN server systems The maximum amount of RAM has always exceeded our real needs and financial capabilities, and in conventional computers for the time being, no problem, as it were, was not.
She appeared, or rather to say, manifested himself, after the real dimensions of RAM installed in client computers crossed the line of approximately 3 gigabytes. In the context of this topic, we will be called more equal to this or greater memory.
For the first time I really faced a big memory problem when a laptop with 4 GB of RAM and Windows 7 Professional X86 got into my hands. I wanted to find out what. Namely, - where "disappeared" part installed memory And is it possible to return it anyhow? After all, the volume of available physical memory most directly affects the speed of the system.
The topic was surprisingly multifaceted and extremely interesting, even though the new one would definitely call it - the earliest of the publications used by me to search for answers to the questions raised, dates back to 2006.
Almost all of the publications found by me on this topic were distinguished either with ultra blockonicity to a simple state of fact, or were devoted to some one side of the problem. We needed a generalization and systematization with "laying on the shelves" that I tried to do. The result was a cycle of five interrelated articles.
Today's article is the first, and its name "Large Memory Secrets in 32-bit operating systems" can be safely attributed to the entire cycle. I am very advised to familiarize yourself with this cycle not only to those who work with 32-bit operating systems, but also those who have already switched to 64-bit OS. Believe me, you will greatly begin to understand your computer.
At first breath, due to the fact that the mathematical limit for the 32-bit address bus is 4 GB and it is such a maximum size that Microsoft is officially declared as supported in Windows X86 client versions, named above ~ 3 GB may seem strange. However, as soon it becomes clear, there is nothing strange in this, and Microsoft is slightly misleading.
Maximum RAM size, which support 32-bit systems
Today we will deal with the question: can 32-bit systems work with physical memory more than 4 GB In principle, and if so, how.
The main thing is that it is necessary to do at the very beginning, it is clearly divided by three concepts among themselves:
- Processor properties;
- 32-bit operating system;
- 32-bit application (program)
The last two are very often mixed in one pile, which in this case, do not do it. Let's start in order and afar - we will make a short historical excursion.
CPU
Let us turn to the table of the main characteristics of the processors (almost written x86, which would be a mistake - this system team first appeared at the 8086 processor)\u003e
This table is needed in order to visually show the fact that the target tire bit does not always coincide with the discharge of the processor architecture.
To begin with, pay attention to 16-bit processors. If they had a 16-bit targeted tire, the maximum size of the physical memory available to them would be only 64 KB (2 in the 16th degree equal to 65536). However, Intel 8086 could work with memory up to 1 MB, and 80286 is already up to 16 MB due to 20 and, accordingly, 24 bits of the address bus.
The Epoch of the IA-32 processors and 4 GB of RAM began with Intel 80386 in 1985. Over the next 10 years, IA-32 architecture processors have not had a physical ability to work with more than 4 GB memory.
 In 1995, a processor was presented Intel Pentium Pro.. Along with a completely new architecture of the kernel, this processor received a 36-bit address bus due to which it is not difficult to calculate, the maximum size of the physical memory available to it increased to 64 GB (37 discharges are used in modern 64-bit processors, which increases the limit of the addressable physical memory to 128 GB).
In 1995, a processor was presented Intel Pentium Pro.. Along with a completely new architecture of the kernel, this processor received a 36-bit address bus due to which it is not difficult to calculate, the maximum size of the physical memory available to it increased to 64 GB (37 discharges are used in modern 64-bit processors, which increases the limit of the addressable physical memory to 128 GB).
In addition, the processor was implemented by the "tricky" memory management mechanism, which displaced the physical memory located outside 4 GB, into 32-bit virtual memory in the range of 0-4 GB "deceiving" so 32-bit applications. Such a memory management mode of the X86 processor was called PAE (Physical Address Extension - Expansion of physical addresses).
Pentium Pro was positioned while the processor for servers and workstations. Indeed, to imagine in 1995 a desktop computer with a scope of RAM is not something more, and at least remotely approaching 4 GB, it was not easy. Memory was measured by megabytes then. And in our time, 4 GB of memory in the desktop computer or laptop is not needed. In addition, this processor was very expensive and had problems with speed when performing 16-bit applications at the time.
It can be said that such a solution was new for 32-bit processors, however, due to the fact that a previously similar practice was used everywhere in 16-bit processors, the revolutionary name is difficult to call it.
Since they spoke about the processors, we note that the first 64-bit X86 processor appeared not at Intel, but at its main competitor - AMD in 2003. By this time, Intel was already released in 2001, the 64-bit ITANIUM processor of a completely new IA-64 architecture is not compatible with X86. Including due to the latter, the processor has not received distribution on desktop computers. In 2003, the only version of Windows XP 64-bit Edition Version 2003 (ITANIUM 2) was made specifically for Itanium. The project was discontinued in 2005 as unnecessary.
Not all but the overwhelming majority of modern X86 processors for desktop computers are 64-bit and have support for PAE. Due to this, they not only can work with the memory of more than 4 GB, but also provide such an opportunity for 32-bit operating systems.
The easiest way to determine the support for the PAE mode processor was in Linux.. In Ubuntu, or in any of its numerous clones, you can dial in the terminal:
grep -Color \u003d Always -i PAE / PROC / CPUINFO
As a result, something like this should turn out.

32-bit operating systems
The first of the 32-bit Microsoft OS was Windows NT 3.1, released in 1993. It was intended for the corporate sector, that is, for servers and workstations. Two years later, in 1995, Windows 95 appeared - an operating system for desktop computers and laptops. Between the two events in 1994, version 1.0 of the Linux kernel was presented. The 32-bit architecture was so successful and "sufficient" that it is used everywhere until now for 2 decades already. The last 32-bit server operating system Microsoft has become Windows Server 2008. However, newest Windows 8 is still offered in two versions. Disputes about what is better - 32 or 64 do not stop today.
To implement additional capabilities of the mode of expansion of physical addresses, in addition to the availability of an appropriate processor and motherboard with an adequate chipset and the desired amount of diluted targeted lines, it is necessary Support PAE directly the operating system itself.
If you have a 32-bit Linux, then problems using the memory of more than 4 GB, most likely will not arise. In operating rooms linux systems PAE support appeared in 1999 in the kernel 2.3.23 and used since then without any restrictions.
It can be noted that, for example, popular Linux Mint. In general, comes today exclusively with the PAE core and requires its mandatory support to the processor. By the way, as in Windows 8. Not all is happy for this circumstance, as the processors are still preserved without support for PAE.
Let's see the table of the maximum supported size of physical memory, taken from article 2005 in MSDN.Microsoft.com, for Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003\u003e

As you can see from this table, the PAE mode is supported in all versions of Microsoft OS starting with Windows 2000. Size variations maximum memory In various versions of server operating systems, they are explained solely by their market positioning. microsoft.. Probably it is easier to explain their difference from each other. For us, the rows of the table, which directly suggests that in all versions of Windows XP, the total addressable space of physical memory is limited at 4 GB. It is artificially limited in the kernel, since PAE support is. What is the reason for such a limitation, not only in XP, but also in all subsequent desktop 32-bit versions of Windows, we will understand.
PAE mode can be turned on, can be turned off. Starting with Windows XP SP2 PAE turns on forced to ensure the work of the security technology DEP. Data Execution Prevention is to prevent data execution).
DEP is a technology that allows you to protect the operating system from a large class. malicious codewhich is initially embedded in the memory area allotted for data and is masked for data, and then tries to start out of it. DEP technology This making malicious code blocks. The technology is implemented both software and hardware. In the latter case, the processor marks individual memory pages as not containing an executable code by a changed senior bit in the address table PTE (Page Table Entry) virtual memoryAnd then intercepts and prevents starting the executable code from these pages.
Go to our last today.
32-bit applications
Due to the processor memory dispatcher, which exercises its distribution in PAE mode, regardless of the application of applications, and support such an operating system operation, 32-bit applications are separated from physical memory and do not have information about its real size. Each application, as the 32-bit address space is saved for them, only 4 GB of virtual memory is still available. In Windows, the needs of the application itself from these 4 GB are given exactly half, in Linu - 3 GB. In Windows, there is an opportunity to force 3 GB forcibly, but, in most cases, it is inappropriate.
It should be borne in mind that the inclusion of the PAE mode is by no means equivalent to the transition to a 64-bit system in which each application is allocated incomparably larger memory. If at the expense of PAE, try to directly satisfy the uncomfortable appetite of a certain modern application, for example, advanced computer Game, There will be nothing good. But if you need to simultaneously start multiple demanding applications, then the benefits of PAE will be straight. First of all, it concerns servers.
For example, the simultaneous work of two virtual machines is required, each of which is assigned to 2 GB of memory. What will happen without PAE - the second virtual machine is likely to simply not start, well, or the system will begin such an intensive exchange with the SWAP file that the process will go to the category "Step-by-step strategy" (running in front of say that in a real experiment with virtual machineswhich you can read in, SWAP did not help). With PAE included, subject to a sufficient amount of the physical RAM host machine, both virtual machines Will work safely. In fact, everything is somewhat more complicated, but, in general terms, so.
The disadvantages of the PAE usually include a possible reduction in system performance due to a reduction in memory access speeds associated with additional operations on switching displaced memory pages, and poor work Some device drivers in 36-bit address space.
On this until we stop and summarize:
- Almost all modern 32-bit operating systems can work with rapid memory of more than 4 GB. Such an opportunity appeared in 1995, thanks to the implementation of PAE technology in processors (Physical Address Extension - expansion of physical addresses);
- Despite the fact that PAE support allows you to use the physical memory of up to 64 (128) GB, the operation of the operating system kernel in this mode is completely not equivalent to the transition to the 64-bit OS. Applications continue to be performed in the 32-bit address space conventional for them, but if the installed physical memory exceeds 4 GB, the applications themselves can be simultaneously launched more;
- In the PAE mode, there may be a decrease in the speed of access to memory and problems with device drivers;
- In Microsoft Windows operating systems, the upper limit of the available physical memory is limited to the OS kernel level.
The last item of our today's conclusions we will examine in detail in.
Yes, I would like to praise the author, the article is really clear.
It's hard to really find, so much slag had to shock in the internet (((
Alexander, tell me whether I realized that if I launch any process on the disappeared Windows, well, let's say 3D MAX, then no more than 4 GB, even if I have 16?
Those. I can run 4 Max and each of them exit 4 GB of memory, but so that one occupied all 16 GB will not work.
Windows 7 (32).
Thanks in advance.
Thanks for the feedback. Yes, you all understood absolutely right. Each 32-bit process will operate with no more than 4 GB with memory. In fact, only half of 4 GB will be available directly. Another half will be left under systemic needs. In order to change this ratio to a new download section in the BCD, the "IncreaseUserVA 2500" string is added.
Ehhh, sorry.
It turns out that from the rearness of Windows is not going anywhere, to fully load the RAM ((((
Thank you for your prompt response.Dont be upset. As they say, whatever it would be, it's all for the better. If there is a lot of memory and there is a resource-intensive application, then x64 for anyone and better and more correct. In addition, because of the "curves" of the drivers, after removing 4 GB of restrictions in 32-bit Windows, unfortunately, there is still no guarantee of its stable operation.
I agree, it is, of course, a lot. However, it may be possible not to install absolutely all applications simultaneously, but as you need? On the home desktop, I usually install a new system on separate disk And for some time "new" and "old" exist in parallel. At work, I also forbade my employees of technical support to reinstall systems over, that is, to a disk with the "old" system. Moreover, this disc is some time (from a month to three) was kept in an inviolable state. Such an approach guaranteed the complete absence of data losses of any sense.
Hmmm, an interesting thought.
I just wanted a new screw to buy, here on him and round a new Windows.
Thanks again.
Several years have passed since the article "Four gigabytes of memory is written - an unattainable goal? ", And questions, why Windows does not see all four gigabytes, there is no less. The owners of 64-bit systems, which this problem, seemed to be added to the number of questions, and should not be touched. And it became clear that it's time to write a new article on the same topic. As before, it will be only about Windows operating systems, and in the main client, that is, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and the upcoming Windows 8. In some cases, several simplified descriptions of certain aspects will deliberately. This will provide an opportunity to focus on the subject of this article, without going into unnecessary details, in particular, the internal device of processors and microcircuits (chipset) for system boards. We recommend pre-read the article specified above, as not everything that said in it will be repeated here.
Although theoretically 32-bit system is available (without additional triggers) to 4 GB of physical memory, 32-bit client versions of Windows cannot use all this volume due to the fact that part of the addresses is used by computer devices. That part of RAM, whose addresses coincide with the addresses of devices, must be turned off to avoid the conflict between RAM and the memory of the corresponding device - for example, a video adapter.
Fig. 1. If the RAM in the addresses used by devices is not disabled, conflict occurs
RAM Fills the addresses, starting with zero, and devices, as a rule, are given addresses in the fourth gigabay. While the size of RAM does not exceed two or three gigabytes, conflicts do not occur. As soon as the upper limit of the installed memory enters the zone where the device addresses are located, a problem occurs: the same address is also a cell of the RAM, and the device memory cell (the same video adapter). In this case, the data record will result in distorting the image on the monitor and vice versa: change in image - to distort the memory content, that is software code or data (let's say, text in the document). So that the conflicts do not occur, the operating system has to abandon the use of that part of RAM, which overlaps with the addresses of devices.
In the mid-nineties of the last century, the PAE technology was developed for expanding the available volume of RAM, which increases the number of address lines from 32 to 36 - thereby the maximum RAM volume grew from 4 to 64 GB. This technology was originally intended for servers, but later appeared in client Windows XP. Some features of the implementation of this technology in modern memory controllers make it possible not only to use the PAE for its direct intended purpose, but also to "cross" memory to other addresses. Thus, a part of the memory that is not used for the sake of conflict prevention can be moved to senior addresses, for example, in the fifth gigabyte - and again become an affordable system.
In the discussion of the first article, a remark was expressed that it incorrect to identify the presence in the memory controller system board support for PAE - and the ability of the board to redirect memory; That it may well be things, not related to each other. However, practice shows that in the "hardware" for desktop systems These are interchangeable concepts. For example, Intel in the documentation for its G35 microcircuit's set, no word indicates the possibility (really existing) memory redirection, but emphasizes the support of RAE. And not supporting the PAE set i945 has no memory forwarding. FROM aMD processors64 I. last models Intel processors The situation is even easier: the memory controller is built into the processor, and support for PAE (and RAM of more than 4 GB) automatically implies forwarding support.

Fig. 2. Forwarding
The drawing is quite conditional, the redirection is not necessarily performed by the blocks by one gigabyte, the discreteness may be different and is determined by the memory controller (which, we recall, is either part of the system board equipment or part of the processor). The BIOS SETUP computer usually uses a configuration that allows or prohibiting redirection. It can have different names - for example, Memory Remap, Memory Hole, 64-bit OS and the like. Its name is best to find out in the manual for the motherboard. It should be noted that if a 32-bit system is used, then on some system boards, mostly enough old, redirection must be turned off - otherwise the volume of the available RAM can decrease.
By default, in Windows XP, the RAE mode was disabled, since there was no real need (we will remind that in 2001 the typical memory capacity of the desktop computer was 128-256 MB). However, if it is included, xp could use all four gigabytes of memory - provided, of course, that the motherboard would support the paradise. But, repeat, there was no real need to include this mode in those years. If desired, the reader may be installed for sample modern computer Windows XP or Windows XP SP1 (do it for work, of course, not worth it), enable PAE mode and make sure that the system is available four gigabytes of RAM.
In 2003, Microsoft began to develop the second phase package for Windows XP (released in 2004), since it became necessary to significantly reduce the number of vulnerabilities in the OS components. One way was to use data prevention (Data Execution Prevention, DEP) - a set of software and hardware technologies that allow you to perform additional memory content checks and in some cases prevent the launch of a malicious code. These checks are performed both on the program level and on the hardware (if there is an appropriate processor). AMD called this feature of the "Protection of Page Protection" (NO-Execute Page-Protection, NX), and Intel used the term "execution prohibition" (Execute Disable Bit, XD).
However, the use of such hardware protection requires the translating processor to the PAE mode, so Windows XP SP2 is detected suitable processor It began to include this default mode. And here "Microsoft" faced a rather serious problem: it turned out that not all drivers can work in PAE mode. Let's try to clarify this feature, not too deepening in the processor device and addressing mechanisms.
The so-called flat model of memory is used in Windows. Thirty-two drops of addresses provide an appeal to the size of four gigabytes. Thus, each cell of the RAM or the memory cell of another device corresponds to a certain address, and there can be no ambiguities here. The PAE mode enabled allows you to use 36 address discharges and increase the number of memory cells 16 times. But after all, the processor command system remains the same and can add only 4 billion (binary) bytes! And so to provide the ability to access any of the 64 billion bytes, indicating only 32 address discharge, the processor includes an additional stage of address translation (those who are interested in details may turn to special literature - for example, the book of Russian and Solomon " Internal organization Windows "). As a result, the 32-bit address in the program may indicate any of the bytes in the 36-bit space.
Applied programs This feature does not concern anything, they work in their own virtual addresses. But drivers that should refer to the real addresses of specific devices have to solve additional tasks. After all, a 32-bit address generated by this driver can be completely different after an additional stage of broadcast, and the command issued by the driver may, for example, instead of outputting the icon on the screen to change the value in one of the cells excel tables. And if any system data will be fastened, then before the emergency completion with the conclusion blue Screen hand to file. Therefore, for successful work in PAE mode, drivers must be written, taking into account the characteristics of this regime.
However, since it has historically developed so that until that time in client computers, the PAE was not used, some companies did not consider it necessary to maintain this mode in the drivers written by them. After all, the equipment they produced ( sound feesFor example), it was not intended for servers, and the drivers did not have the server version - so why not need to complicate these drivers? Moreover, for testing work in PAE mode, it was earlier required to install the server OS and use server equipment (System boards for desktop computers only relatively recently began to support PAE). So the developers of the drivers are easier and more profitable to simply forget about this PAE and ensure performance on regular client computers with ordinary personal, and not server OS.
And here with such drivers and problems arose in XP SP2. Although the number of firms whose drivers stopped working or even caused the collapse of the system, it turned out to be small, the number of devices issued by these firms was calculated by millions. Accordingly, the number of users who might after installing SP2 to get an unpleasant surprise was very significant. As a result, many users themselves will refuse to install this package, and they would have dealt with bad fame, which would affect other users. They, although without any good reason, would also refuse to install it.
And the need to improve the security of the XP company "Microsoft" felt very acute. However, reasoning on the topic, why we saw Windows XP SP2 and did not see something like Windows XP Second Edition, go beyond the scope of this article.
The main thing that interests us is that to ensure compatibility with poorly written drivers, the PAE functionality in SP2 for Windows XP was cut. And although this mode itself exists and, moreover, on computers with modern processors It turns on by default, it does not give any address space expansion, simply by passing the same addresses to the output that were submitted to the input. In fact, the system behaves like an ordinary 32-bit without PAE.
The same behavior was inherited by Windows Vista, and then moved to Windows 7 and the future Windows 8. Of course, 32-bit. The reason for which this behavior has not changed, remained the same: ensuring compatibility. Especially since the need to relegate the shares of the gigabyte disappeared: those who need large amounts of memory can use 64-bit versions of the OS.
Sometimes you can hear the question: if this circumcised PAE mode prevents the system to see all four gigabytes - so, maybe disable it at all, so as not to interfere, and voila, the system will be available 4 GB? Alas, will not be: this requires just the presence of PAE, with a complete one. The other is not so rarely asked as the question sounds like this: if the devices really interfere with the system to use all memory and reserve it under their needs, then why did they not reserve anything when there were two gigabytes of RAM in the computer?
Let's go back to the first drawing and consider the situation more. First of all, we note that you need to clearly distinguish between two concepts: the size of the address space and the volume of RAM. Mixing them together prevents understanding the essence of the question. Address space is a set of all existing (to which processor and other devices) of addresses can appeal. For the I386 family processors, this is 4 gigabytes as usual and 64 GB using PAE. In 64-bit systems, the size of the address space is 2 TB.
The size of the address space does not depend on the volume of RAM. Even if you pull out the entire RAM from the computer, the size of the address space will not change either on the iota.
The address space can be real in which the operating system itself works, and the virtual, which OS creates programs for working in it. But the features of memory use in Windows will be described in another article. Here we only note that you do not have any operating system and drivers to the real address space of the access program.
Consider how the address space is used in the computer. Immediately emphasize that its distribution is performed by the computer equipment ("iron") and the operating system in the general case cannot affect it. There is only one way: change the equipment settings using Plug & Play technology. They spoke a lot about her in the mid-90s of the last century, but now she is perceived as something of granted, and everything is increasing the number of people who did not even hear about her.
Using this technology, you can change in certain, the limits specified by the manufacturer, the limits of the memory address and the port number used by the device. This, in turn, makes it possible to avoid conflicts between devices that could occur if the computer had two devices configured to use the same addresses.
The basic program in the motherboard, often a generalized BIOS (although in fact the BIOS (basic I / O system) it is not) when the computer is turned on, the devices poll. It determines which address ranges each device can use, then it is trying to distribute memory so that no device prevents the other, and then informs devices to its solution. Devices set up their parameters according to these instructions, and you can start the OS boot.
Since we are talking about this, we note that in a number of systemics there are settings called "P & P OS". If this setting is turned off (NO), the system board performs addresses distribution for all devices. If it is enabled, the memory distribution is performed only for the devices required to download, and the operating system will be engaged in the setting of other devices. In the case of Windows XP and more new OS of this family this setting It is recommended to include because in most windows cases Perform the required setting at least not worse than BIOS.
Since with such self-configuration is distributed addresses Memory, it does not matter how much RAM is installed in the computer - the process will still flow equally.
When a number of RAM is inserted into the computer, then the address space is released from the bottom up, starting from the zero address and then towards an increase in addresses. Addresses of devices, on the contrary, stand out in the upper area (in the fourth gigabyte) in the direction of decreasing addresses, but not necessarily adjacent blocks - more often, on the contrary, non-negative. As soon as the zones of addresses allocated for RAM (on the one hand) and for devices (on the other side), contact, becomes possible to conflict addresses, and the amount of RAM used has to be limited.
Since the change in the address when configuring devices is performed with some step defined by the characteristics of the device specified by the manufacturer, the solid portion of addresses for devices cannot be obtained - unused gaps appear between the addresses of individual devices. Theoretically, these gaps could be used to access RAM, but this would complicate the operation of the operating system memory manager. According to this and other for Windows reasons Uses RAM to the first memory address occupied by the device. RAM, which is from this address and above will remain unused. Unless, of course, the memory controller does not organize forwarding.
Sometimes you ask the question: Is it possible to influence the address distribution to move all the devices in the address space as high as possible and make as much memory as possible an affordable system. In general, without interfering with the design or firmware of the devices themselves it is impossible. If the arms are still squeezed, and it's not a pity, you can try the following method: In the BIOS Setup, you enable the "PNP OS" setting (it may or not be called differently) so that the addresses for most devices distribute windows and then Reinstall drivers using edited files INF with remote areas Memory, which, in your opinion, are too low.
On the Internet you can find different tips that, supposedly, should give the system the opportunity to use all four gigabytes based on the forced inclusion of PAE. How to easily understand from the above, no winnings can give it, because it does not matter whether PAE is turned on automatically or forcibly - this mode works in both cases equally.
The question may also arise: what will happen if you install a video adapter with four gigabytes of memory. After all, then it turns out that the system will remain completely without RAM and will not work. In fact, nothing terrible will not happen: the video adapter has already been used for a long time of the address space of 256 MB, and access to all over the video screen memory is carried out through the window of this size. So more than 256 megabytes, the video adapter does not take away. Perhaps, in some models, the size of this window is doubled or even fourwise, but they have not come to the author in hand.
64 discharge
So, with 32-bit systems, we figured out. We now turn to 64-bit.
That's where it would seem that there should be no submarine stones. The system can use much more than four gigabytes, so, at first glance, it is enough to plug in the system board memory and install the system. But it turns out, not everything is so simple. First of all, we note that special equipment intended only for 64-bit systems will not be able to find (we are talking about ordinary PCs). Any motherboard, network card, video adapter, etc., operating in the 64-bit system, should work with the same success in 32-bit.
And this means that the addresses of devices must remain within the first four gigabytes. And it means that all restrictions imposed on the amount of memory available to the 32-bit system are applied and to 64-bit - of course, if the motherboard does not support redirection or if this redirection is disabled in the settings.
Do not support the redirection of motherboards on Intel chip sets to 945 inclusive. Next, of course, they won't call them, but computers on their base still exist and are used. So, on such fees and 64-bit, and 32-bit systems will be able to see the same amount of memory, and it will be less than 4 GB. Why less - described above.
With 64-bit AMD processors, the situation is easier: they have a memory controller for quite a long time built into the processor, and redirection is missing only in obsolete models. All processors for the 939-pin nest and more new support more than 4 GB and, accordingly, can redirect memory. The same applies to intel processors Core i3, i5, i7 families.
However, and here there may be a snag: if the system board does not contain additional address lines, it will not be possible to refer to the redirected memory. And some younger models of system boards for deposits are released just such, so it is necessary to watch a description of a particular system board.
And here we will be waiting for a surprise, similar to the one with which we face in a 32-bit system: Using the address space for the operation of devices can limit the amount of memory available to Windows.
For example, if a motherboard supports up to 8 GB of RAM (say, using the G35 chipset), and install all of these 8 GB, it will be used only ≈7-7.25 GB. The reason is as follows: 33 lines of the address are divorced on such a motherboard, which, from the manufacturer's point of view, it is quite logical - why complicate the design, if more than 8 GB does not support any equal? Therefore, even if the memory controller can cross the unused section of RAM into a ninth gigabyte, it will not be possible to contact him anyway. This will require a 34-bit address, which is physically not formed on a 33-bit system bus. In the same way on boards supporting 16 GB, Windows will be able to use ≈15-15.25 GB and so on.
With redirection, another little-known nuance is connected. Restricting the size of the memory performed in the MSConfig program (or appropriate download configuration settings) does not apply to the memory itself, but to the upper limit of the address of the memory used.

Fig. 3. This setting limits the top border of the addresses, and not the memory size
That is, if you specify this value of 4096 MB, then the memory located above this boundary (forwarded to the fifth gigabyte, for example), will not be used, and in fact the amount of memory will be limited to about three gigabytes. This feature is in some cases it is possible to use to diagnose whether forwarding works or not. For example, the author met the case when windows laptop Used 3.75 GB of four, and it was unclear: whether the redirection does not work, whether the memory is used for some needs. Installation of the flag and limiting the size of the memory with four gigabytes led to the fact that only 3.25 GB began to be used. From this we can conclude that the redirection worked, and a quarter of a gigabyte, therefore, was used for a video adapter or some other purposes.
Well, finally, it is worth saying that even when working forwarding and a 64-bit system, several dozen or even hundreds of megabytes can still be reserved for equipment. The reasons for such reservations are best found out from the manufacturer of the motherboard, but most often it can be assumed that it is used for the built-in video adapter or the RAID controller.
Most recently, a note was published on the blog, to help those who are going to update their computer or buy / collect new. Namely, it said how many RAM is a computer, depending on the tasks that are put on the front: how many RAM is needed?
The following note on the plan was an article on the support of various amounts of memory from the operating system - about the discharge of the operating system; The fact that not all memory volumes are supported by all versions of Windows. Special thanks to all readers who mentioned about the topic of discharge in the comments on the blog: After reading them, I realized that a short note on this topic was not enough. Need a detailed material on this topic.
That is why it was decided to write an article, (libez, if you wish) on this issue and place it here, on itexpertportal.com - in the archive of free training materials and articles on important computer literacy topics.
So, back to the main topic, to the discharge of operating systems and to support various amounts of memory. Initially will answer the question:
What is a bit at all?
Scientific definition: In the informatics of the discharge of electronic (in particular, peripheral), the device or tire is called the number of discharges (bits), simultaneously being processed by this device or transmitted by this bus. The term applicable K. compound parts Computing, peripheral or measuring devices: Computer data tires, processors, etc. The computence of the computer is called the discharge of its machine word. (Source - Wikipedia).
I think everything is simple and understandable. Bigness - the ability to simultaneously process some number of bits, if it is easier to speak.
In fact, everything is not so simple, and to highlight all this question and the "academic" - no article is enough. Therefore, we will not delve into the PC architecture course, and we will touch on the purely practical moments with which you have to face and that matter for us - users.
And then the amount of RAM?
There are two versions of the Windows operating system (at least yet - only two). It does not matter what we will take from modern and current systems: XP, Vista or 7.
All these systems exist in two versions - 32-bit and 64-bit. For example:
Windows 7 Ultimate 32-Bit (or x86 - equivalent notation)
Windows 7 Ultimate 64-bit (or x64 - equivalent notation)
Windows Vista Ultimate X86 (x86 -this is the designation of the 32-bit version)
Windows Visa Ultimate X64 (respectively - 64-bit version)
Architectural differences between 32 and 64-bit versions of Windows, of course, is. You can talk about them for a long time, but this is nothing, believe me. 🙂
The most important features and differences that directly relate to the user and with whom have to face:
1. The maximum amount of RAM.
2. The discharge of the operating system.
3. CPU bit.
Here we will talk about this more ...
The maximum amount of RAM.
A 32-bit operating system can add (i.e., can use, "see") not more than 4 GB of RAM. This is the most important difference, and most significant. If you are installed in your computer, say, 2 GB, then the 32-bit operating system works with this volume normally.
If you have 4 GB of memory and work under the control of a 32-bit OS, then it simply will not see such a volume. All that she can use is about 3.5 GB of 4 GB. The rest of the volume it cannot provide for working programs. Of course, if you install 8 GB of memory to a computer, say, and at the same time you will remain on the 32-bit system, it will also not see more than 3.5 GB from the entire set volume.
The 64-bit operating system can work with much greater memory - up to 192 GB (for Windows 7). Those. If you, let's, wanted to install 8 GB of memory, must necessarily switch to a 64-bit OS, otherwise you simply cannot use such a large available volume.
 We considered, you can say, "extremes", up to 2 GB and 8 GB and more. And what about the golden middle? What if you have already installed or do you plan to increase the amount of memory up to 4 GB? Do I need to go to a 64-bit OS in this case so that the computer can use not 3.3, and all 4 GB of memory?
We considered, you can say, "extremes", up to 2 GB and 8 GB and more. And what about the golden middle? What if you have already installed or do you plan to increase the amount of memory up to 4 GB? Do I need to go to a 64-bit OS in this case so that the computer can use not 3.3, and all 4 GB of memory?
Not everything is so simple ... 64-bit versions of the OS use noticeably more memory. All variables are no longer 32-bit, but 64-bit. This usually increases applications by 20-40%, which also leads to an appropriate increase in the amount of memory. On file formats such as music or video, it does not affect.
Install a 64-bit versionWindows To better use 4 GB of memory, it makes no sense, even if the 32-bit version recognizes only up to 3.5 GB of memory. The problem lies in the fact that you will receive missing memory, but immediately lose it for the reason that the 64-bit version requires more memory for itself. So the transition to 64 bits is relevant only with the memory of more volume: 6, 8 GB and more.
So, if you decide to establish a lot of memory, and here the 64-bit OS is needed for sure, then perhaps you are interested in the question:
What features 64-bit Windows Vista / 7 have?
Visually - no. Those. Outwardly, this is an ordinary OS, which does not stand out from the 32-bit option. You can define it belonging to a 64-bit architecture just entering the "System Properties" item in the control panel - the bit indicated there.
Technically - there are small differences. The first, in fact, that the 64-bit OS "sees" the large amounts of memory and can work with them. Second - it allows you to run 64-bit applications.
The 64-bit OS allows you to start and conventional 32-bit programs. With the familiar way, no settings are required for this. Everything as usual. Just in the 64-bit system there is a subsystem of performing 32-bit applications. Therefore, you can successfully install and work with both 32-bit and 64-bit applications.
Now there are few such x64 applications, although their number is constantly growing. This is especially true of resource-intensive programs - graphic and video recorders and so on. Those. All programs that are needed primarily by large amounts available for memory. For example, that some kind of video editor can use in more than 4 GB from available memory.
For example, Adobe has declared that modern ADOBE CS5 series applications will only 64-bit. This means that, say, Photoshop CS5, Dreamweaver CS5etc. will be able to start only on the 64-bit system. On a 32-bit OS, they simply do not start. Why?
Because 32-bit applications can work in the 64-bit OS, but not vice versa!
Next technical moment - 64-bit OS requires 64-bit drivers. As a rule, all modern (no older than two years) PC devices, laptops and peripherals have two versions of drivers - 32 and 64-bit on the supplied installation disk. Therefore, S. modern devices There will be no problems - as usual insert the drive with the driver to the drive and run the installation, the installer itself will determine the version of Windows and starts the corresponding bit of the driver.
If there is no disk or there is no 64-bit driver on it, you need to visit the official developer website specific deviceTo download such a driver. The same applies to outdated equipment.
Be sure to check for the presence of 64-bit versions of all necessary drivers Even before installing the 64-bit version of Windows!
CPU bit.
Where to take / how to define 64-bit applications?
64-bit software You can determine without difficulty. On packaging in system requirements, as a rule, it is indicated that this program 64-bit. It can be specified separately on the package.
If you acquire some other Internet, then belonging to 64-bit architecture is also indicated.
Here is an example: My licensed box version of Windows Vista Ultimate. Included two installation disk - 32 and 64-bit version of OS:


Do not pay attention to "English-language" in this case, simply OS was purchased in the United States.
But this is in this case - Vista Ultimate (only Ultimate) was so supplied, in two versions. As a rule, the same Windows, for example (or any other program) for sale OR 32-bit OR 64-bit, as indicated on the box, as I mentioned.
This difference and features of the 64-bit Windows operating systems, meaningful for the user end.
Otherwise, everything is exactly the same as on the familiar 32-bit Windows XP / Vista / 7.
In this article, we will deal with how to remove the limit of 4 GB of memory on 32 bit versions of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, and use the all-available RAM available on the computer.
Most windows users convinced that 32 bit Microsoft OS do not support more than 4 GB of RAM. Thus, the memory maximum available in Windows 8 / 8.1 x86 is 4 GB. And taking into account the fact that Windows reserves part of the memory for their needs and the needs of peripheral devices) most often for the video card), the end user for use is usually available about 3-3.5 GB of memory.
At first glance, everything is logical - the limit of the addressing for a 32-bit targeted tire is the same 4 GB. In all officials microsoft documents It is exactly this maximum memory size supported in all client versions of the X86 system. Although actually Microsoft misleads everyone.
What is PAE and why he need
PAE (Physical Address Extension - Extension of Physical Addressing) - This option X86 processor allowing it to access more than 4 GB of physical memory. We will not delve into the technical details of the PAE technology, simply note that this technology is supported by all processors and directly in OC Windows already quite a long time ago.
For example, a 32-bit version of Windows Server, running on the X86 processor, can use the PAE to access the entire system operational memory (up to 64 GB or up to 128 GB, depending on the generation of the processor).
Let's say more, support for PAE mode in the Windows kernel is available, still starting with Windows XP. Just by default the PAE is available only in server OS, and in the client Windows OS, this mode is also available, but is disabled.
Note. The PAE can only be used on 32-bit versions of Windows running on the X86 processors compatible with this mode.
PAE Mode Restrictions
- The PAE does not expand the virtual address space of each process. Each process running on the 32-bit system is still limited 4 GB of address space.
Council. PAE will not help increase the amount of memory available for a resource-intensive application (for example, a graphic or video editor). If such a need is available, it is better to go to a 64 discharge OS.
- When using PAE, it should be noted a small decrease in system performance by reducing the memory access rate caused by overhead to switch the displayed pages in memory
- Drivers of some devices cannot work correctly in the 36 bit address space.
So, it can be concluded that the upper limit of the available physical memory in 32-bit versions of Windows is limited to the OS kernel level. And if there is a software limit, it means that it can be circumvented! How to enable PAE mode in 32 Bit Windows 8.1 and use all available RAM.
Patch including PAE and allows you to use all RAM on Windows 8 / 8.1 x86
Enable PAE mode in Windows 8 (Windows 8.1) It will not work by standard tools (for this you have to manually edit the ntoskrnl.exe kernel file and redupping it). The easiest way to use the finished patch Patchpae2.which is written by the enthusiast Wen Jia Liu. You can download Patchpae2 patch. (the archive contains the patcher himself - patchpae2.exe, his source codes and necessary instructions).
Patch is a small utility command linewhich allows you to modify 32 bit kernel files versions of Windows In order to activate the PAE mode, which allows you to use more than 4 GB of RAM (up to 128 GB of memory).
PatchPae2 patch will work with the following OS:
- Windows Vista SP2.
- Windows 7 / Windows 7 SP1
- Windows 8 / Windows 8.1
Note. Before installing, a patch is needed to prevent conflicts. It is recommended to disable optimizers and RAM drivers. They can be activated after applying the patch and loading the system in PAE mode.
Installing PAE - Patch in Windows 8 / 8.1
Attention. This instruction can be used only for 32 bit versions of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, for the previous Microsoft OS, the procedure is slightly different! Be careful!

Note. At any time, the user, rebooting, can switch from the PAE mode to normal, or back in the boot menu.
Important! After installing the patch, you must be particularly attentive when installing Windows security updates. Because some windows updates Sometimes contain and updates for the kernel, after their installation, you need to update the PAE kernel: patchpae2.exe -type kernel -o ntoskrnx.exe ntoskrnl.exe
In addition, problems described and are also described.
Removal PAE Patches
To remove the PAE patch from the system, you need:
- Remove the appropriate entry from the boot menu (the easiest to do this with msconfig)
- Delete files ntoskrnx.exe. and WinLoadp.exe. in catalog % Windir% \\ System32.
No other changes in the patch system does not contribute.
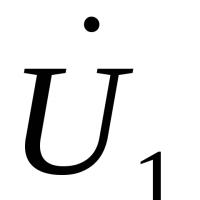 Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it
Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it Effective job search course search
Effective job search course search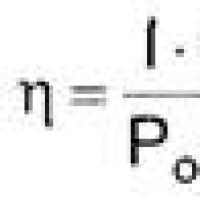 The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode
The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF
How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF Why the fired program window is long unfolded?
Why the fired program window is long unfolded? DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT
DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT What to do if the mouse cursor disappears
What to do if the mouse cursor disappears