Connector for connecting FDD. Solving the problem of connecting a floppy disk drive to a modern computer. Emulation using USB Flash
Connecting drives
Drive for flexible disks is installed in the computer case. To connect to a system board on which the FDD connector is always available (NGMD, a flexible magnetic disk drive), a 34-core flat cable is used.
Since in personal computers, two drives can be installed, followed by logic names A: and in:, then to task the name, the drive is used to connect the drive to the corresponding connector on the loop.
When working in MS-DOS and Windows, when one drive is in a computer, you can contact it and as to A:, and how to:. For example, you can copy files from the disk A: on the disk in:, changing discs using the operating system command:
Copy A: \\ File name in:
To connect to drives and system board Tra plumes with the same and symmetric 34-pin connectors are used. To not confuse them, it is necessary to pay attention to that the first wire in the loop is always red, and there are crossed wires between connectors for connecting drives from 10 to 16.
To connect the old drive for 5-inch flexible discs, sometimes on the loop next to the drives for drives A: and in: additional knife connectors are installed.
Note
When the flexible disk drive is wrongly connected, when the connector is inserted on the contrary, the drive indicator will constantly light up.
FDD B. Interface personal Computer simplest. In tab. Signals are given in the connector installed on the system board. For example, to move the heads to the next track, you need to use the STEP signal, the selection of the head number is made using the Side 1 signal, the start of the track is determined by the INDEX signal, etc. That is all the drive of the drive is assigned to the controller located on the system board or extension board . In the disk drive itself there are a power part for motor control and blocks responsible for working with analog signals. All odd conductors are grounded in the connector.
Signals in the System Board FDD connector
|
Contact |
Signal |
Contact |
Signal |
||
|
2 |
Reduce Write. |
20 |
Step. |
||
|
4 |
Reserved |
22 |
Write Data. |
||
|
6
|
Reserved |
24 |
Write Gate. |
||
|
8 |
Index. |
26 |
Track 0. |
||
|
10 |
Motor ON A. |
28 |
Write Protect. |
||
|
12 |
DRIVE SEL 1. |
30 |
Read Data. |
||
|
14 |
DRIVE SEL 0. |
The floppy disk is a wonderful thing and sometimes even necessary. I remember well how the saving boot discograph sometimes helped me when checking a computer or configuration software (for example, I am constantly for the test random access memory Used the MemTest program, which was recorded on a diskette). And in the Elder Times, this old format was the main source for storing and transferring data. It is a pity, but those times have already gone ... Now all people use flash drives for these purposes, and few people remember about the floppy disks. But, given the current point in time, I decided to tell in detail about one important problem, which is very relevant.
The usual diskette with a capacity of 1.44 MB once occupied an important place in computer history.
Many owners of modern computers have such a problem: there is such a situation when you need to copy some information from the floppy or is required to write something. Today, there is little such thing to do, but still ... Of course, it is not difficult to get a drive for 3.5-inch floppy disks now, it should be cheap (you can even get for free), but the user may face that there is no on his motherboard Connector for its connection. And about reading / write information you can forget. I myself encountered such a problem: I had to create a boot diskette, and there was no such possibilities. My computer turned out to be too modern to connect old devices, and the old one was inoperable. I wondered: "So how can you get the ability to connect the drive? How to be?" And as a result, I found several solutions to this problem.
Exterior drive
The most obvious way to get the opportunity to work with diskettes is a purchase. external drive. Many know that there is on sale USB-FDD drives. Of course, they are very easy to solve the problem with reading / recording such an old carrier on modern devicesEspecially on laptops, where at all any other way, except via USB, cannot be connected to a floppy drive. If the USB bridge is connected to the drive through a standard interface, both on 34-pin connectors, then theoretically connectivity is even a 5.25-inch drive.

External USB-FDD drive can solve the reading problem with a floppy disk, but the quality of such devices may be different
But there is one nuance. The fact is that finding a normal USB-FDD today is quite problematic, at least on sale you can find only Chinese-made drives. I do not argue that this device is capable of functioning normally and cannot spoil old media, but you yourself understand that the likelihood of fake or marriage is great. I believe that classic old floppy drives (not modern lots) will be much better work. You can, of course, try to develop an adapter for an external interface itself, but it is associated with great difficulties and the requirement of great experience and knowledge in developing such devices.
There is still such a device like Kryoflux. It allows you to connect any standard drive (5.25 and 3.5) to a computer via USB. Its price is quite high, but if you need to constantly copy information from a floppy disk - then this is the best option.
Controller
Another solution to the problem is to use a special controller. Well, if on the motherboard there is a place for an ISA controller (koi full full), and then everything will be fine. But where did you see modern fee With ISA-tire? Oddly enough, such fees are also there (IBASE MB970 is an example), but they are extremely rare and are intended for specific use (industrial computers, etc.), and the price of such boards will be far from low. Other options for FDD controllers, for example, for tires PCI I have not met (although I seem to see the photo of these boards on the Internet, but I'm not already remembered where), and I'm not found for PCI-E - generally incredible. And at what price such a thing will be sold? Therefore, the find of such a rare controller can be considered a big luck. I repeat, you can try it to develop it yourself.

IDE and FDD controller for the ISA bus. For a modern computer, he will not work: ISA is outdated in the past century
SuperDisk
There are several exotic but very effective method. It is suitable for almost anyone, even the most modern system. Of course, for this option, it is necessary to find some rare equipment, but, nevertheless, this method has the right to life. The main conditions for the implementation of the method is the presence of an IDE connector (in the absence of it or use the PCI IDE controller, or, if there are SATA connectors - cheap iDE-SATA adapter), and the presence of the LS-120 drive. I'll tell you what it is for the drive. LS-120, or SuperDisk - one of the planned "killers" floppy disks. The standard was developed by Iomega in 1995. This technology allowed to record and store data on special media With a capacity of 120 MB (later - and 240 MB) and was planned as replacing outdated floppy disk drives and diskettes. Sometimes he was called a floptic disk, because combined magnetic technology and optical recording. Connected to a computer via the IDE interface. After the spread of cheaper carriers, such as CD and DVD, this standard could not take care and outdated extremely quickly.

Drive LS-120. Supports both its non-standard floppy disks and usual on 720 KB and 1.4 MB. However, it is difficult to find

Drive LS-120 front. At first glance, it is practically no different from a regular drive
However, what was the SuperDisk chip? And the chip consisted that such a drive could read and record not only its non-standard carriers, but also classic floppy disks at 720 kb and 1.4 MB, which made it possible to use it as a standard floppy disk drive. It is a combination of reading / recording disks and connecting through the IDE interface allows you to work with outdated carriers even with the most modern hardware. By the way, I checked it on my computer with the maternal gigabyte board GA-H77-DS3H Rev.1.1 with intel processor Pentium G2030 and installed operating system Windows 7. By connecting the LS-120 to the computer via the adapter to the SATA connector, the system immediately began to install the drivers, and after that I could immediately start working with an ancient media information. Read from the carrier, which has already shouted for 30 years, on modern technique is an amazing feeling. The only thing: for proper work I recommend installing the jumper on the drive to the Master. Oh yeah, Superdisk also existed in an option for SCSI, LPT and USB interfaces.

The diskette is formatted on a modern computer using LS-120

Use SCSI? This is also an option. If we speak more specifically - you can find a floppy drive that will connect to SCSI directly or through the adapter fee. But where is where to find such a rare device? However, if you find such a way with the controller, then as a bonus you will also receive support for the connection. large number Additional devices due to the SCSI interface.

SCSI controller. Supports various devices: Hard drives, streamers, CD-ROM, scanners and ... Flops!
Second System Block (laptop)
Well, finally, the last option is the easiest. I don't need anything rare and expensive. Find yourself another one, the old system unit, which will already be normal drive support. This is the most efficient option for working with floppy disks. Transferring data from one computer to another can be implemented different ways: through local network, through a zero-modem cable (in the absence of network equipment Or with extremely ancient gland), through a USB flash drive (with USB) or CD, DVD Dawks. The only critical lack of such a method for some users is the need for a free space for the second system unit (although many of them can be somewhat). For those who cannot for any reason have two computers, only previous options will have to use. Although no, there is still hope to use old laptop with built-in FDD :)

Old system unit. He is ideal for working with old media
But what about 5.25-inch floppy disks?
If you need to read information not with an ordinary 3.5-inch floppy disk, but with an older and rare 5.25-inch, then it will already be more complicated. Here LS-120, of course, no longer helps, it does not fit in size :) However, all other options are suitable, although the most optimal one is to use the second system unit specifically for such purposes. And if someone wants to read something from the 8-inch "monster", then only one option comes to me: Assembling a special adapter and the organization of food for a huge floppy drive (if memory does not change me, the motors were fed like as at least 127 volts!). But in fact it is not so unrealistic, there would be a desire ... and a diskette with which you need to throw out valuable information.

5.25-inch drive. There are no special problems when connected ...

... well, and this is "Crank" without alterations you will not connect
Conclusion
Well, I want to complete the article on this, but I will say a few more words. Of course, any of these options will help any person to make a copy of data from old diskettes or continue to work with them if there are outdated equipment, where, except diskettes, no other means can transfer information. In general, I recommend using the old computer. This allows not only to fully work with floppy disks, but also allows you to some extent to maintain a computer history, as we thus find the use of old equipment and save it from oblivion. On the old computer, you can not only make copies of the diskette, and a lot of interesting things ...
Additional links:
English-speaking about reading data from disks in our time;
Website of the adapter board for connecting a 5.25-inch drive via USB, where it can be ordered from the USA.
Thanks for attention!
Text, Photos - Alexander Antsuhenya
Iron ghosts of the past - 2015
Additions or amendments to
To connect IDE devices on motherboards manufactured until 2005, there were two 40-pin connector ( fig. 13.32). Just below there is a 34-pin connector for connecting the FDD drive.
On all modern motherboards, the connectors have a plastic clip with a P-shaped neckline, which is the installation key. On the motherboards of outdated models, these connectors did not have a plastic closure, which often led to improper connecting connectors.
These 40-pin connectors are called IDEIH IDE2. Winchester should be connected to the IDE1 connector. The second IDE2 connector is usually connected by a CD or DVD drive.
Almost all the more or less new motherboards IDE1 port is blue (in fig. 13.32 it is dark).
If the ports do not differ in color, then marked on the motherboard: IDE1, IDE2.
For all hard disks The IDE interface is recommended to use the UDMA 80-core. In such a plume of the signal wires is 40, but each is separated from the adjacent additional wire, which has zero potential and is connected to the PC housing for lack of supply. It is allowed to use a 40-core loop, but hDD With this connection, it will not work with the maximum speed.
Fig. 13.32. Connectors for connecting IDE devices and FDD drives
The plumes are always painted in such a way as to highlight the first socket of the connector. In the 40-core loops, it is usually isolated in red (or red dotted).
80-residential loops can be painted in any colors, but the first wire will always be different in color. In addition, 80-core loops have multi-colored pads: the first shoe shoe, the second is black and the third is gray.
Between blue and black pads, the distance is greater than between black and gray. Similarly, a 40-core loop is also arranged, but all the pads on it are black.
The loop always connects to the connector on the motherboard with a long end or blue block. The Master device is connected by a black block, and the Slave device is gray.
On the system board, the slots are visible a cutout, eliminating the erroneous switching of the loop. All drives are the same cutout. Some models have a bilateral cutout.
In this case, it is necessary to just remember that the first needle of the connector is located next to the hard drive power connector (the same applies to CD and DVD drives).
On motherboards installed a special IDE connector without central contact. For such boards, special 80-cable cables with connectors without a central socket are available. If the motherboard is installed on the motherboard with all the contacts, and there is no central to the cable connector, you can make a hole in the desired location of the connector.
Until recently, the keys were not on all loops, and therefore they could be connected incorrectly. This is primarily refer to the 40-residential loops. If you connect the hard drive (CD drive) inverted the loop, the device will not work, but the system board or device does not cause damage.
If a keyless loop is used, then you should carefully examine the marking on the motherboard next to the connector - the number 1 must be applied near the first needle of the connector.
The CD drive is connected in the same way as the hard disk. This applies to all devices - CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD. To enhance the performance of the computer, it is desirable to connect the hard drive and CD drive to different IDE interface controllers.
In case of use of two optical drives, for example CD-RW and DVD, it is desirable to install them for one loop connected to IDE2. One device is installed in Master mode, Other - in Slave. Moreover, the writing drive is desirable to install in Master mode.
If two hard drives and one CD drive are used in the system, then the first (main) hard drive is connected by one loop to the first controller (IDE1) on the motherboard and the Master mode is installed on the hard drive. The second hard drive is connected by the same loop, but the Slave mode is installed on it.
The CD drive is connected by the second loop to the second IDE2 controller on the motherboard and is installed in the Master position. It turns out that two hard drives are installed on the first controller, and on the second only CD drive.
Installing one loop hard drive and CD drive is undesirable because if one of the devices supports more quick mode Data transfer than others, the connection with both devices will be made in the most slowly supported mode. For example, if you connect a hard disk with ATA-100 and CD-ROM support that supports only ATA-33 mode by one loop, the operation of the hard drive can be slow.
In fig. 13.33 The jumper is shown to connect the CD drive in Master mode. To the left there is an optional connector for connecting analog audio cable that connects to sound card To listen to audio CDs.
Fig. 13.33. CD drive connectors
Such a cable exists from the moment of the appearance of CD drives when these devices were used mainly to listen to the audio parts ( fig. 13.34).
Fig. 13.34. Analog audio cable for connecting a CD drive
The digital MPZ format currently existing today does not require connecting this cable, but it must be connected to the corresponding connector on the motherboard or sound card to listen to the audio sections. The sound cable connector has a specific shape and connectually impossible to connect it ( fig. 13.35).
Connecting power to IDE devices is performed through a standard 4-pin connector ( fig. 13.36). To eliminate the erroneous connection, the connector has a special key - one of the connector planes has special jokes on each side. Similar spaces are available on the IDE device connectors.
It should be noted that modern motherboards are manufactured only with one IDE connector, since with the implementation of the SATA interface, the need for it gradually disappears. Currently, IDE hard drives are removed from production and gradually transitions and DVD drives on the SATA interface. But, since the market will still be saturated with the IDE interface devices for a long time, this fact cannot be discharged.
Fig. 13.35. Connectors for connecting a CD drive
Fig. 13.36. IDE device connectors
To connect the FDD drive, a 34-core cable is used, which connects to the corresponding connector on the motherboard. In fig. 13.32 It is located below the IDE connectors.
The cable to the system board connects the same as the Ide device loop. When connecting a loop to the drive, you should pay attention to that the first contact at the FDD drive is not closer to the power connector, both on the IDE devices, and on the opposite side ( fig. 13.37).
There are two connector on the FDD drive cable. And on the first one with the "recess" of a small part of the loop. When the drive is connected to the "twisted" end, it is perceived by the system as a drive A, and to the second - as a drive V. We remind you that there are still magneto-optical drives that are connected by the same 34-pin loop.
If the loop is connected incorrectly, the green LED will constantly burn on the drive and the device will not work. In this case, the loop must be flipped over 180 °.
Fig. 13.37. Connect FDD drive
Above the interface connector is a 4-pin power connector. In fig. 13.38 Presented a connector for its connection.
The connector has a key, but when the drive is connected, it is necessary to be particularly attentive, since it is possible to incorrectly connect it, especially if these actions are made "blindly". In this case, a frequent error occurs the connector when connected to one direction or the other. This error can lead to fatal consequences - can burn the drive or even the power supply.
Motherboards supporting the Serial ATA interface (SATA) have additional connectors for the SATA interface ( fig. 13.39).
Fig. 13.38. Connector for connecting the power of the FDD drive
Fig. 13.39. SATA interface connectors
Only one device is connected to each connector. As already mentioned above, hard drives with sATA interface Do not have jumpers to determine the modes of operation.
Exterior interface sATA cable shown in Fig. 13.40.
For the power supply to the processor corresponds to a separate 4-pin ATX 12V connector (in Fig. 13.42, right).
Initially, this connector was called P4, since it was used to supply power only to Pentium 4. But in the future it was adapted for motherboards with the AMD processor. Then there appeared an 8-pin power connector to even more powerful. pentium-D processors And Pentium 4 on the Prescott kernel.
But today aMD processors And Intel is enough of the features of the 4-pin interface ( fig.
13.43). Most motherboards with an 8-pin nest will operate both from 8- and with 4-pin forks, since the connectors are compatible with each other.
Power connection to the system board
Fig. 13.42. System Board Power Connectors
Fig. 13.43. ATX 12V connectors
If the PC power supply does not have a 4-pin connector for powering the processor, then the power can be served from the standard power connector for IDE devices. There are system boards on which both variants of power connectors are installed to feed 12 V to the processor.
In fig. 13.44 shows such a layout of the connectors.
The latest modification of the ATX standard provides 24-pin forks that have previously met on server power units.
The main reason for the appearance of 24-pin connectors was to increase the current flow supplied to PCI-Express slots compared to the old standards. Although for the power of most modern cards, it is enough of the possibilities of a 20-pin connection, but developers provide further development of the standard and in connection with this power increase.
Fig. 13.44. Two options for power connectors to CPU
Most motherboards do not require the mandatory connection of all 24 contacts. In fig. 13.45 shows how the 20-pin plug is connected to a 24-pin connector.
Wide hook on the connector motherboard Allows you to connect both 20- and 24-pin forks.
Fig. 13.45. Connecting a 20-pin plug to a 24-pin connector
It should be noted that the remaining 4 free contact in no case cannot be used to connect the 4-pin CPU power connector! The decay of the remaining free contacts does not correspond to the 4-pin processor connector.
If already purchased powerful block Food with a 24-pin connector, then to supply the power to an old motherboard, you must use the adapter from 24 to 20 contacts. In fig.
13.46 shows appearance Such an adapter, and in fig. 13.47 - Adapter installed in the motherboard.
Installing the power connectors is fixed by a special latch ( fig. 13.45 and fig. 13.47). After the connector is inserted into the slot until it stops, a click that means fixing the connector in the nest.
Fig. 13.46. Power Adapter 24/20 ATH
Fig. 13.47. Power connection via adapter 24/220 ATX
The SA-400 interface is used to conjugate a drive with the Controllet. They are connected to the help of a 34-podium cable, in which even PRIOV are signaling, and odd - common. Total Intepplica Wait Press Matches Connecting to Controllet to four drives, Wait for IBM PC - up to two. In general, the drives are connected to the fullest dpugu, and the drive number (0..3) is set by the papes on the electronic circuit board; In the WPIANT for IBM PC, both drives have Nomep 1, but the cable help is connected, in which the selected signals (PROs 10-16) are moved between the two drives. Sometimes a contact 6 is removed on the drive of the drive, which is governing in this case by the mechanical key.
The data on the interface is transmitted in a sequential code in both directions (by different wires). Data transfer rate for a diskette of 1.44 MB is 500 kbps. Like the hard drive controller, the flexible disk controller in modern computers is installed on the system board (special extension boards were produced for old computers models).
The driver of the drive is enough and turns on the device selection signals (four dead, in the general case, two - in the WPIANT for IBM PC), starting the engine, heading the heads to one step, turn on the record, read / recorded data, as well as information signals from the drive - the beginning Shipping, pensioning heads to zero (outer) cash, signals from sensors, etc. All information encoding information, search for milking and sectoys, synchronicization, error crossing is performed by the Controllet.
Standal Flat Dials Type HD (High Density - high density) - 80 hundreds on each of the STOPON, 18 sects of 512 bytes on the cash. The compacted format is 82 or 84, up to 20 sects of 512 bytes, or up to 11 sects of 1024 bytes.
Connection:
To connect the drive there are two connectors: one for electrical power supply, and the other for data transmission and control signals. These connectors in the computer industry are standardized: To connect the power, a four-contact MATE-N-LOCK line connector of AMP large and small size is used, signal - 34-pin connectors. In 5¼ diskheads, a large power connector is used, while in most 3½ disk drives, a smaller connector is used to power.
The "oddity" of the signal cable is that lines 10-16 are cut and rearranged (twisted) between the drive connectors. This twisting the first and second position of the drive selection jumper and the engine power signals, and therefore, changes to opposite settings of the "DS" signal for a disk drive. Accordingly, all drives in the computer with this type of cable have jumpers installed in the same way, and setting up and installing drives (instead of the first and second, they are designated in the system as a and b) simplified. As a rule, the motherboard contains an integrated drive controller (as well as a separate controller board that existed in the earlier), which ensures the installation of a pair of drives.
When connecting the cables, it is necessary to consider their orientation, if the signal cable is incorrectly connected, the light bulb on the front panel of the drive will glow immediately after the power supply. In the case of improper orientation of the power cable on electronic circuit Drive control instead of 5V power 12 V, which is guaranteed to exit its failure. Given that the cost of repairing a piece board exceeds the wholesale cost of the drive itself, the repair of the drive is usually economically not appropriate.
Electrical connection Discovers

Interface for connecting 3½ "Flexible disk drive: a small-sized power connector and a connector for connecting a 34-pin signal cable.

Cables: left, right - signal.

"Strange" signal cable with a twist.

Pads for connecting 5¼ "(left in photo) and 3½" (right) Discovers are different. To connect to a 3½ "drive cable to a block for a 5¼" drive, a special adapter could be used.
Controller programming:
The controller of flexible disks, from the side of modern programming, looks sufficiently primitive - registers having a byte organization are reduced to a block of eight consistently located cells (only part of them is actually used).
| Address | Designation | Reading / writing | Purpose |
| 3F0 16. | - | - | Not used |
| 3F1 16. | - | - | Not used |
| 3F2 16. | Dor. | Reading / writing | Digital output register |
| 3F3 16. | TSR | Reading / writing | Ribbon Drive Drive Register |
| 3F4 16. | MSR. | Reading | Main register of status |
| 3F4 16. | DSr. | Record | Data speed selection register |
| 3F5 16. | Fifo. | Reading / writing | Data buffer register |
| 3F6 16. | - | - | Not used |
| 3F7 16. | Dir. | Reading | Digital input register |
| 3F7 16. | Ccr | Record | Configuration Management Register |
Practical work number 7
Despite the huge popularity of flash drives, optical disks Still in the go. Therefore, maternal manufacturers still provide support for CD / DVD drives. Today we want to tell you how to connect them to the system board.
How to connect a drive
Connecting drive optical disks It is performed as follows.
- Disconnect the computer, and, therefore, the motherboard from the mains.
- Remove both side covers system BlockTo access the motherboard.
- As a rule, before connecting to the "Mother", the drive will be required to be installed in the corresponding compartment in the system unit. Its approximate location is shown in the image below.

Install the tray drive out and secure it with screws or snaps (depends on the system unit).
- Next important moment - Connect to the board. In the article on the motherboard connectors, we casually affected the main ports for connecting memory devices. These are IDE (outdated, but still used) and SATA (the most modern and common). To determine what type you have a drive, take a look at the connection cord. Here it looks like a cable for SAAT:

And so - for ide:

By the way, floppy disk drives (magnetic diskettes) are connected only by IDE port.
- Connect the drive to the corresponding connector on the board. In the case of SATA, it looks like this:
In the case of IDE - so:
Then you should connect the power cable to the BP. In Sata-connector, this is a wider part of the shared cord, in the IDE - a separate wire block.
- Check whether you have connected the drive correctly, then return to the location of the system unit cover and turn on the computer.
- Most likely, your drive will not be immediately visible in the system. In order for the OS correctly to recognize it, the drive is required to activate in the BIOS. This will help you with an article below.
- Ready - CD / DVD drive will be fully ready for work.

As you can see, nothing complicated - if necessary, you can repeat the procedure on any other motherboard.
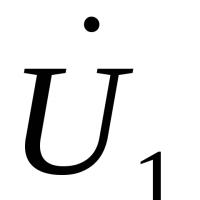 Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it
Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it Effective job search course search
Effective job search course search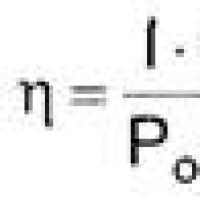 The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode
The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF
How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF Why the fired program window is long unfolded?
Why the fired program window is long unfolded? DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT
DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT What to do if the mouse cursor disappears
What to do if the mouse cursor disappears