Laser disks and drives. Principles of digital optical recording and playback of information from CDs Device and varieties of CDs The principle of recording data to an optical disk
 Optical disk - a collective name for media made in the form of disks, reading with optical radiation.
Optical disk - a collective name for media made in the form of disks, reading with optical radiation.
 History The first optical discs were developed at the turn of the 70s and 80s by the joint efforts of Sony and Phillips. &
History The first optical discs were developed at the turn of the 70s and 80s by the joint efforts of Sony and Phillips. &
 History CD (Compact Disc) mini. DISK (MD) DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) HD DVD & Blu-ray (BD) HVD (Holographic Versatile Disc)
History CD (Compact Disc) mini. DISK (MD) DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) HD DVD & Blu-ray (BD) HVD (Holographic Versatile Disc)
 The structure of the CD disk is usually flat, its base is made of polycarbonate, which causes a special layer, which serves to store information. - Diameter of a CD 120 mm. - Disc thickness 1, 2 mm.
The structure of the CD disk is usually flat, its base is made of polycarbonate, which causes a special layer, which serves to store information. - Diameter of a CD 120 mm. - Disc thickness 1, 2 mm.
 Single-written discs (CD-R). A single-writable disk consists of an active, reflective and protective layers, which are consistently applied to the base of polycarbonate.
Single-written discs (CD-R). A single-writable disk consists of an active, reflective and protective layers, which are consistently applied to the base of polycarbonate.
 The principle of recording CD-R During recording, a powerful laser beam heats small areas of the active layer. Under the influence of high temperature, the properties of the substance of the registering layer are changed at the heating site, as a result it ceases to skip light.
The principle of recording CD-R During recording, a powerful laser beam heats small areas of the active layer. Under the influence of high temperature, the properties of the substance of the registering layer are changed at the heating site, as a result it ceases to skip light.
 The principle of recording CD-R to restore the transparency of substances used as an active layer in cD-R discs, Impossible. You can damage the record applied to the active layer, you can only in one way - make transparent areas opaque.
The principle of recording CD-R to restore the transparency of substances used as an active layer in cD-R discs, Impossible. You can damage the record applied to the active layer, you can only in one way - make transparent areas opaque.
 Multiple-writable discs (CD-RW) difference of such discs from CD-R lies in the device of the recording layer. The intermediate layer of a special organic material can be either in amorphous or crystalline. Ray of recording laser
Multiple-writable discs (CD-RW) difference of such discs from CD-R lies in the device of the recording layer. The intermediate layer of a special organic material can be either in amorphous or crystalline. Ray of recording laser
 CD-RW Amorphous substances have a feature crystallized with time. No matter how we stored CD-RW, after a few years the record will be irretrievably lost. In addition, such discs can easily be erased by simply heating. !
CD-RW Amorphous substances have a feature crystallized with time. No matter how we stored CD-RW, after a few years the record will be irretrievably lost. In addition, such discs can easily be erased by simply heating. !
 DVD Disc Structure The DVD recording principle is not very different from the CD recording principle. The basis for recording and storing data on DVD-RAM and DVD-RW disks is the technology of changing the phase state of the substance. The layer structure of one half of the disk is shown in the figure.
DVD Disc Structure The DVD recording principle is not very different from the CD recording principle. The basis for recording and storing data on DVD-RAM and DVD-RW disks is the technology of changing the phase state of the substance. The layer structure of one half of the disk is shown in the figure.
 The principle of recording to a DVD record of amorphous regions is shown on this schedule. A short high-power laser pulse melts the recording material. Then it follows the cooling below the crystallization temperature. The result of cooling is to prevent the formation of crystallization centers. Thus, the growth of the crystalline phase does not occur, and the substance remains in amorphous state.
The principle of recording to a DVD record of amorphous regions is shown on this schedule. A short high-power laser pulse melts the recording material. Then it follows the cooling below the crystallization temperature. The result of cooling is to prevent the formation of crystallization centers. Thus, the growth of the crystalline phase does not occur, and the substance remains in amorphous state.
 Erasing from a DVD for erasing you need to return the substance into the crystalline state. Again, with a laser, the amorphous substance is heated to a temperature of T. Heating (or more precisely, annealing) continues for a time sufficient to restore the crystalline state of the substance. This time should be greater than the so-called crystallization time.
Erasing from a DVD for erasing you need to return the substance into the crystalline state. Again, with a laser, the amorphous substance is heated to a temperature of T. Heating (or more precisely, annealing) continues for a time sufficient to restore the crystalline state of the substance. This time should be greater than the so-called crystallization time.
 Recording DVDs When recording disks, a multi-digit record strategy is used. Each recorded label is formed by means of powerful laser pulses. . After each pulse, the melted material is cooled, forming an area with an amorphous phase.
Recording DVDs When recording disks, a multi-digit record strategy is used. Each recorded label is formed by means of powerful laser pulses. . After each pulse, the melted material is cooled, forming an area with an amorphous phase.
 Recording discs at home To record disks at home, you must have not only the recording CD drive, but also special software.
Recording discs at home To record disks at home, you must have not only the recording CD drive, but also special software.
 Recording a disk at home The process of recording one session is a single operation that cannot be interrupted, otherwise the disk will be corrupted.
Recording a disk at home The process of recording one session is a single operation that cannot be interrupted, otherwise the disk will be corrupted.
 Recording a disc at home before recording you need to form full list included in the session of the files; Subsequent addition of files to the disk is possible only in the form of additional sessions.
Recording a disc at home before recording you need to form full list included in the session of the files; Subsequent addition of files to the disk is possible only in the form of additional sessions.
 Recording a disc at home CD-ROM drives that do not support the multi-section record, read from the disk only the first TOC - respectively, with their help, you can read only the first session files.
Recording a disc at home CD-ROM drives that do not support the multi-section record, read from the disk only the first TOC - respectively, with their help, you can read only the first session files.
 Label technology. Flash Labelflash - technology that allows you to apply your drawings to recorded DVDs. It was represented by NEC in December 2005.
Label technology. Flash Labelflash - technology that allows you to apply your drawings to recorded DVDs. It was represented by NEC in December 2005.
 The principle of work Label. Flash to create a picture is used in a dye of a different type that provides greater contrast of the image.
The principle of work Label. Flash to create a picture is used in a dye of a different type that provides greater contrast of the image.
The CD and DVD disc reader consists of an engine rotating a CD, disc boot systems, an optical reading system and control device. All these components are placed in a single case, which is inserted into the five-liter compartment of the computer case. External CD-ROM drives, as well as DVD-ROMs are made in the form of a separate device.
In household devices, the engine must rotate the CD with a constant linear speed so that the reading speed of the information has not changed. Modern computer devices change the read speed depending on the quality of the disk used. On the axis of the engine there is a playground to which the disk is pressed. Disks rotate with significant speeds, which causes a sufficiently loud unpleasant noise. IN lately Work is underway to reduce the noise of high-speed drives.
There are several disk boot options. Most often the retractable tray is used, called Tray - Tray. With the help of a special engine, the tray leaves and removes inside after the desired CD put it
Devices for recording CDs outwardly almost do not differ from the reading devices. However, the laser used in the optical system can heat the sections of the workpiece so that in this place the recorder layer is tempted. Laser power during recording is about ten times more than when reading.
When recording a CD, the laser is turned on at high power. The laser moves along the track, recording the necessary information. It is impossible to interrupt this process. If the computer does not have time to transfer the next portion of information for recording, the process will be interrupted and the billet used is spoiled. To protect the interruption of information flow in modern devices, there is a buffer size of several megabytes. In addition, in many modern CD / DVD-RW models, a special technology is used that allows you to temporarily interrupt the recording and resume it after receiving the next portion of the data.
Billets for recording CDs have preliminary marking. It contains special labels and synchronization signals. Preliminary marking helps the laser movement on the desired trajectory. In addition, you can read some parameters of the workpiece used before recording. This will help you easier to configure the recording program. The signals are recorded with a reduced amplitude and subsequently overlap the recorded signal.
DVD-R and DVD + R formats
The DVD-R recording standard was developed in 1997 by the Japanese company Pioneer and a group of companies attached to it and included in DVDFORUM as the official specification of the recorded (subsequently rewritable) disks.
DVD-RW discs created on the basis of DVD-Rs, originally had a nuisance associated with the incompatibility of old drives with these new discs (the problem was the difference between the optical layer responsible for the "memorization of" information that had a smaller (compared to the carriers with a single recording and stamped discs) reflective ability). In the future, this problem was almost completely solved, although before, because of this, old DVD drives could not normally play new rewritable discs.
Since the development of DVD-R and DVD-RW standards, Sony, Philips and some other (as well as the price of a license to this technology were too high), then these manufacturers of recording drives and recording media were united in DVD + RWalliance (English), who developed in the middle of 2002 the DVD + R (W) standard, the cost of the license to which was lower.
Created alternative format, called DVD + R and DVD + RW, had another reflective layer material and a special markup that facilitates the positioning of the head (LPP, LandPre-Pits - pre-written petes between tracks containing addressing data and another service informationThese data allow dVD drive To record information in the desired disk spaces) - the main difference between such "plus" disks from "minus". Using this DVD + RW discs are capable of recording (on top of existing), as in a conventional cassette video recorder, excluding the tedious pre-erase of all contents (for DVD-RW first, it is necessary to completely erase the available entry).
In addition, during the use of rewritable "plus" disks, the number of errors is reduced, and the recording correctness increases, as a result of which the failure sector can easily overwrite, and not to wash and not write the entire disk. Therefore, if you intend to actively use the function of overwriting and record, it is better to choose a recorder that supports the "positive" format (for which most models are capable of now).
Modern discs most often fall into one of two categories - CD or DVD. Both categories are based on one principle of recording and at the same time differ from each other with the amount of information recorded on them and others. technical characteristics. The CD abbreviation is decrypted as Compact Disk - a compact disk, however, usually say "CD", the DVD abbreviation first meant Digital Video Disk - digital video disc, but later it has become decrypted as a digital versatile disk - digital universal disk.
What is the similarity and difference between CDs and DVD? The main and, perhaps, the only similarity is that they are laser. The information on them is recorded on the spiral track, like the usual vinyl recorder. At the same time, each bit of information on the track is stored as pit- small spots, or recesses on the working layer, and landov- smooth, untouched layer sections. When reading the laser beam enters drinks and lundes, after which it is reflected in the receiving device, which fixes the result of reading. The physical size of the disks themselves is the same - the diameter of the CD and DVD is 12 cm.
Note
The terms "Pete" and "Land" originated from English words Pit - "Deeperation", "Yamka", and Land - "Earth", "Soil". Both of these terms are firmly entered into computer literature, like many other words having an English-speaking origin.
The CD and DVD difference list is much more extensive.
The density of information record on DVD is significantly higher than on the CD. On DVD Petes is physically smaller in size, located closer to each other, like the neighboring rings of the spiral track. All this ultimately gives a significant gain in DVD density compared to CDs.
DVDs have several working layers, and CDs are always single-layer. DVD can have up to four working layers, two on each of the disk side. The more working layers, the greater the volume of the disk. The capacity of the standard CD is 700 MB, and the standard single-layer DVD can be written on home computer up to 4.7 GB. Wrapped at the DVD plant for an order of magnitude packed with CD - their volume reaches 8.5 GB.
The correction of errors that is present on both the CD and the DVD, in the latter is much higher.
All these differences lead to the fact that the CD reading and writing devices cannot read and write a DVD. On the contrary, modern DVD devices can record CDs.
CD and DVD are divided into many other categories.
Created at the factory for stamping with a matrix called discs only for readingand the designated CD-ROM and DVD-ROM (ROM means Read Only Memory - "read only").
Allowing to perform singlerecord from a computer drive. They are denoted by abbreviations CD-R, DVD-R, DVD + R (R means Writable - "recordable"). You can write data to the recordable discs or only once (if the "under the string" fill in the information disk), or in several receptions, or, as they say, the sessions, each time adding the information, until all the available disk space is filled. It is impossible to erase anything from the recordable disk.
Admitting multi-capacityoverwriting, which are designated CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD + RW (RW means Rewritable - "rewritable"), DVD-RAM. In everyday life, recorded and rewritable discs are often called "dwarves", or "blanks". Reworked discs allow you to record and erase information repeatedly. Manufacturers of rewritable discs are guaranteed from 1000 to 100,000 recording / erasing cycles.
A guarantee for reading data from CD-ROM is about 10 years, from recorded and rewritable discs - from 10 to 200 years, although in practice it is naturally not checked. Reworked discs are just more expensive than recorded, but serve very convenient and, most importantly, the replacement of the floppy disk.
Recently, a new generation of optical disks appeared on the market - Blu-Ray and HD DVD (High-Definition DVD - DVD high permissions).
Blu-ray disks (BD) received their name from the Blue word combination ("Blue") and Optical RAU ("Optical Light"). Blu-ray standard was developed by a group of companies for the production of consumer electronics and computers led by Sony.
The Blu-ray disc is used to record and store digital data, including high-definition video, with high density. The main difference of such discs from CD and DVD is a large storage capacity, as well as the use of a blue laser technology with a wavelength of only 405 μm, while in CD and DVD, a red laser is used with a wavelength of 780 μm and 650 μm, respectively. Due to this, it was possible to record data more tightly and, thus, significantly increase the capacity of the disk.
Blu-ray disk structural design is very different from the CD or DVD structure. Covering layer CD - 1.2 mm thick; A similar layer DVD is 0.6 mm. Blu-ray disc is covered with a layer of only 0.1 mm thick; Thanks to which the optimal distance is achieved between the data tracks and the optical system of devices for reading / write disks. The distance between the tracks on the surface of the Blu-ray disks is 0.32 μm. The blue laser is about 1/5 width of the red laser used in DVD. From here it follows that with the help of a blue laser, it is possible to increase the storage capacity of data by 500%.
The Blu-ray single-layer disk (BD) can store 33 GB of data, a two-layer disk can accommodate 54 GB - enough to write for approximately eight hours HD video. In addition, in the development of discs with a capacity of 100 GB and 200 GB using four and six layers, respectively.
HD DVD disk has the same basic structureAs a DVD, and much in common in production technology. The disk with a diameter of 120 mm consists of two glued bases with a thickness of 0.6 mm. The tracks on the HD DVD surface are formed in the process of molding molten polycarbonate on the metallic plate of the matrix. However, in comparison with the usual DVD, for HD DVD, it is necessary that the distance between the two tracks on the disk surface is less to achieve a higher record density (DVD - 0.74 microns, HD DVD is 0.4 microns).
Single-layer HD DVD has a capacity of 15 GB, two-layer - 30 GB. Toshiba also announced the release of a three-layer disk, which will store 45 GB of data.
Blu-ray and HD DVD formats are back compatible with DVD and both use the same video compression techniques: MPEG-2, Video Codec 1 (VC1, based on Windows Media 9) and H.264 / MPEG-4 AVC.
How CDs are recorded
As already mentioned, the information on CD and DVD is stored in the form of pita and lands. In the case of CD-ROM and DVD-ROM, petes are recesses in the working layer located along the spiral path. The entry on the CD-ROM and DVD-ROM is made by stamping on a special plastic - polycarbonate. The start of the recording is located near the center of the disk. When reading the disk, the laser beam moves along the helix from the center of the disk to its edge and at the same time it is different from the lands and peits. The reflected beam falls on the receiver, which registers the Pit-Land transitions as a logical unit, and the lack of transition is like logical zero. Thus, a sequence of units and zeros is read from the disk, which make up the binary information code - the basis of the basics of computer information.
Recording on disks, both recorded and overwritten, produced with a laser beam. Among the various layers forming a recordable and rewritable CD, there is a special working layer, which is recorded or, as they say, "burning" a laser beam. Reading information from recorded and rewritable disks occurs similarly to the CD-ROM and DVD-ROM disks, only the role of the pita play spets, scorched by a laser beam.
Most of the programs, video films and computer games are distributed to CD-ROM and DVD-ROM, since it is these discs that are manufactured in an industrial way. On the home computer you can create only recorded and rewritable discs using for this special reading and writing devices CD / DVD. The popularity of these devices is very large, and all modern personal computers are equipped with them.
CD recording modes
CD and DVDs can be recorded in three modes: TAO (Track-AT-Once - "Track (track) at a time"), SAO (Session-at-once - "Session (session) at a time") and DAO (disk- AT-ONCE - "Disc at a time"). I will explain what it means - when creating disks, the Nero program offers to choose one of these modes, and you should know what you get as a result.
Tao - disc is recorded in several passes, each time on one track. The minimum length of the recorded track - 300 blocks (600 KB for a typical CD with data). Maximum - 99 tracks on the disk. The laser during the record is turned on and off several times, so the recording device leaves a pair of blocks, called "output" and "accession" between the tracks.
SAO - disc is recorded for several sessions (sessions). At the same time, the gaps between the tracks are excluded, and at the same time, after each session, the disk remains "open" for subsequent sessions, which makes it possible to replenish it with new data. For example, you can replenish the music disc of audio recordings or enter new data portions to the archive disk.
DAO - the entire disc is recorded entirely at a time, it is possible to record many tracks. The record should not be interrupted, and after completion, the information cannot be added more to the disk - the disc is "closed" - is finalized.
In all these modes, with each session of computer or audio data on the corresponding part of the CD, three zones are created: LEAD-IN (Login), Program Area (data or programs) and LEAD-OUT (output). DVD each entry has the same structure - the LEAD-IN, Data Zone (data area) and the LEAD-OUT. Two-layer DVD has another Middle Zone (intermediate zone) between layers. The following information is located in the zones:
In LEAD-IN and LEAD-OUT - various service information;
Program Area and Data Zone are actually all the information that is on the disk in the form of audio, video, text, graphic and other data.
The LEAD-IN zone can be the starting part or the entire CD or DVD, or each session of the multisession CD. The LEAD-IN CD contains a table of contents called TOC table (Table of Content - "table of contents"). In particular, the time of the beginning of each audio track, the overall recording time is recorded for audio parts in TOC. In the DVD, the LEAD-IN zone contains information that describes the contents and type of disk.
The LEAD-OUT zone is the last part of the CD-ROM or one of the sessions of the multisession CD. In DVD it is placed immediately after the Data Zone data zone. This zone contains a special label - the end of the recording end identifier.
If you write a disk in DAO mode, that is, the entire disc is at it, then it will be the only LEAD-IN input zone, the only LEAD-OUT output zone and the only Data Zone data zone. If you write down the same disk several times in Tao or SAO modes, then several LEAD-IN and LEAD-OUT zones will be created on the disk, that is, such a disc will become a multisession.
Thus, choosing the recording mode in the program for a variety of sessions, you can repeatedly add to the information dial. If you choose a single recording mode, the disk will be finalized and nothing will be allowed to write anything. During the acquaintance with the Nero program, it will be described how to choose recording mode when creating your own disks.
1.2. Disc formats
So, you learned that optical CD / DVD contain information in the form of records that have a certain structure, or, as they say sometimes, format. The most diverse information can be recorded in the disk data zones. For most computers users, there are greatest interest to audio music, wheels with some kind of data and video with films. All helpful informationStored on the disks is written on them in a specific format so that playback devices (disc players) can correctly read and reproduce information, for example show you a movie on a DVD.
Attention!
We emphasize that there are disk formats and data formats on disks, although sometimes these terms are confused. One of the other should be clearly separated: the disk format, such as a DVD-ROM, is the format of the disc itself, its structure, determined by its manufacturing technology. A DVD-Video format is a disk data format. For example, DVD-Video can be made at the factory by dvdrom stamping or write on a home computer using DVD-R bilps, DVDRW and others using a CD / DVD drive. At the same time, the DVD-R disk is recorded in DVD-Video format.
Data recording formats on CD / DVD There are a great set. Now I will briefly describe the formats that you have to often encounter when creating your own CDs or DVDs.
All CDs lead their origin from the AUDIO CD format music disk, which defines the structure of digital records. music disks. CDs recorded in this format will be read on household players, so when recording music disks, you should select Audio CD format. With the advent of musical MP3 disks, the popularity of Audio CD has slightly decreased, but they are still widely represented on sale. The main characteristics of the Audio CD format are as follows.
The sound is written in a stereo format with a frequency of up to 44 kHz, which completely covers the entire frequency range, hearing by man.
At Audio CD, you can write no more than 99 sound tracks. This should be considered when writing to the Audio CD disk of music files from various sources.
Record AUDIO CD discs are better in DAO mode, which absolutely eliminates the likelihood of unpleasant clicks in pauses between the records characteristic of the Tao records. Rewrite the already ready-made Audio CD CD simply copying to ExplorerWindows will not work. For this, Nero provides special tools that will be told in this book.
The further development of the Audio CD format was SACD - Super Audio CD. By playback quality, these discs are higher than standard CDs. Conventional CD players are able to play hybrid discs Super Audio CD, which have two layers - one is made in the usual Audio CD format, the other in the Super Audio CD format.
The DVD also has AUDIO DVD format. The sound quality in it can be higher than that of the AUDIO CD discs, but even experts are often unable to distinguish the quality of Audio DVD from Super Audio CD. And the other formats do not enjoy wide popularity. Although AUDIO DVD disks come out, but not so large circulation as ordinary Audio CD.
CD Extra and Mixed-Mode
CD Extra (or Enhanced CD - Expanded Architecture CD) is a disk with two recording sessions. The first session contains sound data, such as musical, and the second session is arbitrary data. Ordinary household players supporting Audio CD format can read only the first session with sound data on the CD EXTRA.
Mixed-Mode CD - a mixed format disk on which both audio recordings and arbitrary computer data can be stored. At the same time, the first on the disk is a record with computer data, and the second and subsequent entries contain audio data. Therefore, household players cannot read such discs.
The first storage format for video data on CDs was Video CD (VSD). Such a disc stores video data in a compressed form determined by the MPEG-1 special format, and allows you to play video with a resolution of 352 x 240 for the NTSC and 352 x 280 system for PAL / SECAM. Video playback quality This discs do not have any comparison with DVD-Video, and to date, VIDEO CD format discs are outdated. Video CD can be read on the CD-interactive player (CD-I) and on all modern computer drives.
More high quality Video playback - something average between Video CVD and DVD-Video - have Super Video CD (SVCD) disks. Although the disks of this format are not very common, the Nero program allows them to be created.
MiniDVD format allows you to record files in DVDVideo format. The small capacitance of the CD allows you to place the video of the playback duration of not more than 15-20 minutes.
The most common video storage format is a DVD-Video. The disks of this format can be read on all DVD household players. Such discs can store some of the Hollywood blockbusters and contain a menu, sound tracks in several languages, subtitles, several shooting points at different angles.
Pretty interesting MPEG-4 video, the format of which is not yet recognized as the official disk format. The video film in MPEG-4 format is represented by the only file, often with the AVI extension, which can be recorded on any rewritable disk or postpone in CD-ROM format and further use as a medium of video data to play on the computer.
Official MPEG-4 discs are available for viewing on a computer. However, it can be said that both on TV, since there is currently little video cards that do not have video outputs on the TV. Thus, run the movie on the computer, and watch it on the TV.
Data CD / DVD Data CD
Data CD / DVD format is designed to store arbitrary information, that is, to record arbitrary files. Audio recording, video, archival data can be used as these files. As a rule, the disks of this format are used to work on a computer, however, some DVD players can read and play information on disks, such as play movies or music, display photo galleries. To make CD and DVD drives to read the data disk files, a table containing addresses of all files is written to the disk table contents. Using this table, the drive finds the start of the file on the disk path and read the information you need. Consider this technology.
1.3. File Systems CD and DVD
To play the disc or computer drive to read the information on the CD / DVD of most formats, a file system is created on the disks similar to the computer hard drives. The file system is a specific information added to the disk, with which the folder structure and files on the disk are formed. The file system also stores auxiliary information on the information on the disk. All this data file system provides the reading device so that it can access the files on the disk. In one form or another, the file system is present almost on any CD or DVD, with the exception of Audio CD.
File systems are different types. Briefly consider some of them.
For a CD-ROM, the standard file system is ISO 9660 with various modifications. For other CD file formats iSO system 9660 has various modifications. Without going into details, I would only like to note that the ISO 9660 file system first implied the following restrictions for folders and files:
In the file name, only capital letters, numbers and an underlining symbol can be used;
The length of the file name cannot be more than eight characters, the extension length is no more than three characters;
Depth of folders attachment, including root directory - no more than eight;
The name of the folder cannot be expansion.
Thus, the ISO 9660 file system was initially fully compatible with the MS-DOS operating system. In the future, it was allowed to increase the number of characters in the file name up to 32 or more. Therefore, when recording discs, you will currently do not have problems with files that have names consist of more than eight characters, which is often in operating system Windows.
An alternative ISO 9660 file system used for data disks is Joliet developed by Microsoft to provide support for long file names and encoding Unicode characters, which is important for international CD / DVD technologies. The Joliet file system allows file names up to 64 characters, the depth of the folder attachment is limited to eight, and the total length of the full track name must not exceed 255 characters, including spaces.
For all DVDs use UDF file system (Universal Disk Format - universal disk format). In accordance with UDF at the highest level of the hierarchy, the disk is a volume containing the following parts:
Video view in folder Video_ts.in which video data are located;
Audio view in the folder Audio_ts.in which audio data are located;
Data zone occupying the rest of the disc.
Video files must be located in the folder Video_ts.and have a VOB format (Video Object - a video object). Their size can not be more than 1 GB, and they must be recorded in the form of a continuous sequence. The file names should be no more than eight characters, the extension is from three characters. VOB format files may include not only video and audio data, but also auxiliary images, as well as data for navigating on a recorded video, allowing you to move through the DVD fragment menu.
Files that do not meet UDF requirements will not be read by household dVD playerThat is, you will not be able to view a DVD film on the household player if it is recorded on a disk with deviations from the above rules. Audio files must be in the folder Audio_ts.. The data zone may contain any folders stored recorded to the disk information. Maximum length Data File Name - no more than 255 characters.
Nero 8 Premium packet recording tools allow you to select the file system on the CD / DVD recordable, offering the optimal option when performing individual operations. As a rule, the default file system is optimal for solving most tasks, but in some cases it has to be installed manually.
1.4. Reading / write devices CD and DVD
Currently, there are devices that can only read CD and DVDs, but cannot record them, and devices that can read and write discs. The first type of devices is called CD-ROM drives or DVD-ROM. They are relatively cheap, but they are replaced by second-type devices, which are called CD and DVD drives and are already comparable for the price with CD-ROM and DVD-ROM drives.
In the factory conditions for the manufacture of CDs, special equipment, stamped CD-ROM format discs and DVD-ROMs are used. But in this case, the interest of CD and DVD recording devices are of interest, in the surroundings called "drives" (from the English. drive.- "Drive"), "drives", "cutters", "writs", "writs". In this book they will be called drives. They are implemented in the form of computer peripherals, both external and embedded in the system unit.
The most common CD-RW and DVD-RW drives are currently. In this case, the CD-RW drive can record CD-RW and CD-R. The DVDRW drive can usually record the following formats: CD-RW, CD-R, DVD-R, DVD-RW, DVD + R, DVD + RW / -RW. It is less supported by a DVD-RAM entry, although it is the most common format in domestic, non-computer devices. There are also combined drives, with COMBO marking - so they are usually marked in price lists and shop chambers. They can read DVD and record CD-R / -RW.
In general, the trend is such that not only CD-, but also DVD recording devices slowly, but steadily go into the past. To replace them, they are drivers Blu-ray with recording volume up to 25-50 GB, HD DVD with a 50 GB recording volume. In both drives, a laser generating the light of a blue spectrum is used for recording, which makes it possible to perform a more tight recording.
Speed \u200b\u200bcharacteristics of CD and DVD drives
The faster the disk rotates in the drive, the faster the data can be read from it, of course, taking into account some other factors. If there are no defects on the disk, it will be read at the maximum speed supported by the drive.
When writing a disc, the effect of rotational speed on speed is not so easy. On the one hand, a specific recording speed supports the disk workpiece itself. At a higher speed, write the disk cannot, therefore the drive supporting the drive will not be able to record discs faster than it allows the workpiece. For this reason, the recording speed on the same drive will be different for recorded and rewritable CD and DVD. Usually rewritable discs are recorded at a slower speed than recorded. Thus, the speeds are only two:
The speed of reading data from the disk - depends on the drive;
The data recording speed on the disk depends on both the drive and the disc itself.
Consider these characteristics separately.
Drive speed
Often, on the front panel of the CD drive, you can find the inscription like 52x - this means that the maximum reading speed of CDs is 52. Under this, in turn, it is understood that the speed of rotation of the disk and, as a result, the data reading speed from the disk equal to 52 units. What are these units?
For once the speed of the CD denoted as 1x, the read speed of 150 KB / s is adopted. Thus, the ten-speed drive should read data at a speed of 1500 KB / s, and 50-speed - almost 15 MB / C - which is usually not available in practice.
For a DVD, a single speed of 1x is not at all the same as for CDs, and is equal to 1380 KB / C, and for a new Blu-ray format coming to replace the speed of 1x is 300 KB / s.
Attention!
In pursuit of speed, the manufacturers sometimes forget about reliability, and then the disc who spinned to the exhaust speed will fly into the drive on small pieces. The drive in this case is also most likely to be spoiled.
Sometimes 54-speed drives are also found. But it should be noted that high speeds are also increased noise, especially when the manufacturer did not take care of proper sound insulation. For this problem there is a solution - a forced decrease in the speed of the disk rotation. For this you need to:
The drive itself maintained a reduction in speed;
There was a program that allows you to set the desired speed.
With the first not everything is so smooth, as I would like. Separate drives contain almost no a full range of Speeds from the first to the last, others - only a maximum. Based on the practice, you can recommend drives from ASUSTEK (on the actuator panel is more often written by ASUS) that support labor range Speed \u200b\u200b- from 4 to a maximum with a step in two speeds. In addition, there are good drives from the company NEC in a step of four speeds. But some models of drives support only the maximum speed and work very noisy. Take this feature when choosing a new drive.
Disc speeds
Often discs are marked with the values \u200b\u200bof the recording speeds that they support. For example, 2-10x is written on the disk - this means that the disc can be recorded with the maximum speed of 10x, and the minimum - 2x. It would seem what is the problem? However, it is. Some CDs have a relatively high rewriting speed. Some not such old CD-RW drives cannot overwrite discs at high speeds. If so, then the disk will stay with you with a dead cargo "to the best time" until you buy a new drive that supports high speeds. Carefully choose discs for writing, relate them to your drive. The Nero 8 program includes a disk speed reducing utility, and work with it will still be described in this book.
So, in this chapter, you got acquainted with the basics of optical disc technologies and now, armed with knowledge, can proceed with the development of the most nero programs. In its capacity and efficiency, she does not know equal, but also the requirements that it makes it more serious enough. However, we are ready for this - a variety of settings provided by the program to effectively perform operations with CD / DVD will not be an obstacle. Especially since the newest version Nero 8 Premium Reloaded is equipped with a so-called intelligent panel for managing work with numerous Nero 8 package programs. It greatly facilitates the execution of numerous operations with discs, allowing literally a couple of clicks of the mouse button to create professional-quality discs. We will proceed to studying it in the next chapter.
Destination
CD-drive drives CD-ROM, CD-R and CD-RW refer to optical information storage devices, reading which and record (only for CD-R and CD-RW drives) are produced by a laser beam.
Drive on CD-ROM. Designed for storing and reading information. Abbreviation CD-ROM (CompactDiskread-OnlyMemory) means a "CD only for reading". The information on the disk is represented as a sequence of deepening and protrusions located on a spiral path leaving the area near the axis of the disk. The deepening and protrusions are applied in an industrial way by stamping disc harvesting. The protrusion means the value of the binary digit "1", the deepening is "0". The CD-ROM hosts 780 MB of information. The read speed of the first CD-ROM information was 150 kb / s. The read speed of subsequent storage models began to be designated and calculated as xn, where N is the multiplier to multiply the initial speed to get the desired. Thus, recording on the x52 drive means read speed 52 times greater than the read speed of the first CD-ROM.
Design
The basis of the device is a rigid aluminum or steel frame. As in the drives of other types, the frame is the part of the structure to which all other nodes are attached, both mechanical and electronic. These include, in particular, the facial panel, the rawpanel, the volume controller and the disk removal button that gives the device functionally finished and attractive appearance. The receiving devices for media can be of different types, and are designed either to install CDs in special containers (Caddy), or represent retractable trays, so the front panels and fakes, as well as the methods of their fastening can be different.
Despite the fact that in drives with the ability of recording (CD-R) and multiple overwriting (co-in \\ l / 5, other laser emitters are installed, their design; in principle, the same as in conventional CD drives -Rom.
The main elements of the drive mechanism design. The sending tray is designed to install the disk. After the tray moves inside the drive, a special retainer (in the photo it is white) lifts the disk over the tray, and the spindle engine located under the clip spins the disk to the specified speed. The most responsible part of the CD-ROM drives is the optical head, which includes an aluminometellium (Gaalas) laser diode emitter (wavelength of 780 nm, radiation power of about 0.6 MW), photo sensor, optical system of automatic beam focusing and the mechanism of accurate tracking track . The optical head moves along two guides; The laser beam falls on the surface of the disk through the slot in the tray. A node consisting of an optical head and guides is sometimes called sleds (SLED).
In CD-ROM drives, CD-R and CD-RW are used laser emitters with different characteristics (they include power and working wavelength). But externally, they practically do not differ from each other.
Salazks should track the position of the spiral information path on the surface of the disk. Unlike discovers of flexible disks, in which the magnetic recording / playbacks can with sufficient accuracy "direct" on the tracks using a conventional stepper motor, in the overwhelming majority of CD drives for this, linear electric motors with a movable coil, similar to those used To move heads in drives on hard drives. The fact is that the positions of the concentric tracks on floppy disks are strictly fixed, which is consistent with the principle of operation of the stepper motor: its rotors can occupy only a few discrete positions. In addition, the tracks themselves are wide enough, which eliminates the need for accurate adjustment of the position of the heads. The radius of the spiral of a narrow information track CD changes continuously, so the head position must be constantly adjusted. This is done by changing the control current in the movable coil of the linear motor. However, in some CD drives, stepping electric motors with an extremely small rotor rotation step are used. Electronic nodes that ensure the movement of the sled in the desired direction are mounted on the main circuit board of the drive. Due to the movement of the salazzo, only coarse guidance of the optical head on the track is carried out. The exact tracking of it and the correction of rapid deviations in one or another side (arising from the non-idealness of the carriers) is carried out by the optical device of the head itself. The mass of the salad is too large so that they are able to react to such deviations.
CD Electronic Nodes
The electronic drive filling is usually located at the bottom of the drive and is closed by aluminum screen.eline. These are the main tasks - control of the mechanical drive, sound data processing to output the signal to the headphone socket and the implementation of the computer interface. Currently, the overwhelming majority of drives use ATAPI IDE or SCSI interfaces.
Flow diagram of a typical CD-ROM drive. It can be divided into two parts - the controller subsystem and the drive control subsystem. The controller subsystem interacts with the interface of the peripheral devices of the system, namely with the drive controller. Most of the most complex electronic drives of the drive relate to this subsystem.
The drive management subsystem develops commands for its mechanical part (providing and receiving and removing a CD, adjusting the frequency of its rotation, moving the sled, etc.), and also performs data decoding (from
EFM to normal binary format) and error correction. Analog signals from the output of the photo sensor are converted first to EFM signals, and then into the binary data stream and CRC code (Cross-Interleaved-Solomoncode codes are overlapping codes of Reda Solomon). All laser beam focus operations, tracking track, sled drive control (using feedback), the spindle motor and the reception mechanism and the disk removal mechanism are carried out by the drive circuit and the servo processor.
CD-ROM is the easiest view of the CD drive, designed only to read CDs.
CD-RW - the same as the previous one, but is able to record only on CD-R / RW discs.
To solve a wide range of informatization tasks, the following optical information storage devices are used:
CD - ROM. ( Compact. DISK. Read.- ONLY. Memory.) - memorable devices only for reading information from them;
CD - Worm. ( Write Once Read. Many.) - memorable devices for reading and single information recording;
CD - R. ( CD- Recordable) - storage devices for reading and multiple information record;
MO - magneto-optical drives that can repeat.
Operating principle All optical information storage devices are based on laser technology. The laser beam is used both to record a carrier of information and for reading previously recorded data, and is, in fact, the case is a kind of carrier of information.
1. DrivesCD- ROM
CD - ROM - CD (CD ), designed to store in digital form a previously recorded information and reading it using a special device calledCD - ROM - DRIVER - CD-ROM drive drive.
To the number of tasks to solve the deviceCD - ROM. , can be attributed: installation and software update; Search for information in databases; launch and work with game and educational programs; watching movies; Listening musicalCD.
History of creationCD - ROM. begins with 1980 when firmsSony and Philips. They combined their efforts to create technology recording and manufacturing CDs using lasers. Starting since 1994, drivesCD - ROM. It becomes an integral part of the standard PC configuration. Information carrier byCD - Discist is a relief substrate, which causes a thin layer of reflective material of the material, as a rule, aluminum. The record of information on the CD is the process of forming a relief on the substrate by "burning" miniature bar-pites with a laser beam. The reading of information is made through the registration of the laser beam reflected from the relief of the substrate. The reflecting section of the disk surface gives a zero signal, and the signal from the stroke is "one".
Data storage byCD -disci, like on magnetic disks, Organized in binary form.
Compared with hard drivesCD Much more reliable in transportation. The amount of data disposed onCD , reaches 700 - 800 MB, and subject to the rules of operationCD Practically does not wear out.
Fig. 3.7.. Geometric CD characteristics (but)and his cross-section (b)
Manufacturing processCD -Disc includes several stages. At the first stage, an information file is created for subsequent recording onto the carrier. At the second stage, with the help of the laser beam, information is recorded onto the carrier, which uses a fiberglass disc coated with photoresistive material. The information is recorded as a sequence of spirals located on the spiral (strokes), as shown in Fig. 3.7. Depth of each stroke-pit ( pit.) equal to 0.12 μm, width (in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the pattern) - 0.8 - 3.0 μm. They are located along a spiral track, the distance between the adjacent twists is 1.6 microns, which corresponds to the density of 16,000 turns / inch (625 turns / mm). The length of the strokes along the record track ranges from 0.83 to 3.1 μm.
At the next stage, a photoresistive layer and a disk metallization is performed. The disk made by such a technology is called a master disk. To replicate the CDs from the master disc, the galvanoplasty method is removed by several work copies. Working copies are coated with a more durable metal layer (for example, nickel) than a master disk, and can be used as replication matricesCD -Discs up to 10 thousand pcs. From each matrix. The replication is carried out by the method of hot stamping, after which the information side of the base of the disk, made of polycarbonate, is subjected to vacuum metallization with a layer of aluminum and the disc is coated with a layer of varnish. The disks made by the hot stamping method, in accordance with the passport data, provide up to 10,000 cycles of error-free data. ThicknessCD -Disc is 1.2 mm, diameter - 120 mm.
CD-ROM drive Contains the following main functional nodes:
boot device;
optical-mechanical block;
drive control systems and automatic regulation;
universal decoder and interface block.
In fig. 3.8 Dana Design optical-mechanical drive block CD - ROM. which works as follows. Electromechanical drive leads to rotation disc placed in the boot device. The optical-mechanical block provides the movement of the optical-mechanical reading head along the disk radius and reading information
.
 .
.
Fig. 3.8. Design of the optical-mechanical drive blockCD - ROM.
The semiconductor laser generates a low-power infrared beam (typical wavelength of 780 nm, radiation power of 0.2 - 5.0 MW), which falls on the separation prism, reflected from the mirror and focuses the lens on the disk surface. The servomotor on commands coming from the built-in microprocessor moves a movable carriage with a reflective mirror to the desired track on the CD. The beam reflected from the disk focuses the lens located under the disk, reflected from the mirror and falls on the separation prism, which directs the beam to the second focusing lens. Next, the beam falls on the photo sensor, which converts light energy into electrical impulses. The signals from the photo sensor come to the universal decoder.
Automatic tracking systems for disk surface and data record tracks ensure high accuracy of reading information. The signal from the photo sensor as a sequence of pulses enters the automatic control system amplifier, where tracking error signals are highlighted. These signals come to the automatic control system: focus, radial feed, laser radiation power, linear speed Drive disk.
Universal decoder is a processor for processing signals read fromCD . It consists of two decoders, an operational storage device and a decoder controller. The use of dual decoding makes it possible to restore lost information by volume up to 500 bytes. The operational storage device performs the function buffer memoryAnd the controller manages error correction modes.
Interface block it consists of a digital data converter into analog signals, low-pass filter and interface interfaces. When playing audio information, the DAC converts encoded information into an analog signal that enters the amplifier with an active filter low frequencies And further on sound cardwhich is associated with headphones or acoustic speakers.
Below are given performance characteristicswhich need to be considered when choosingCD - ROM. With regard to specific tasks.
Data transfer rate ( Data. Transfer. Rate. - Dtr.) - the maximum speed with which data is sent from the media of the information into the computer's RAM. This is the most important drive characteristic.CD - ROM. which is almost always mentioned along with the name of the model. Directly with the data rate of the data is associated with the speed of rotation of the disk. First drivesCD - ROM. Transmitted data at a speed of 150 KB / C, as well as audio accounting discs. The transfer rate of the following generations of devices is usually multiple of this number (150 KB / s). Such drives received the name of drives with two-, three-, four-time speeds, etc. For example, 60-speed driveCD - ROM. Provides reading information at a speed of 9000 KB / s.
High drive data transfer rateCD - ROM. It is necessary primarily to synchronize the image and sound. In case of insufficient transmission speed, there may be skipped video frames and sound distortion.
However, further, over 72 times, increase the speed of the drivesCD - ROM. It is inappropriate, because with further increase in the speed of rotationCD The required level of reading quality is not provided. And, in addition, a more promising technology has appeared -DVD.
Ready quality characterized error coefficient ( EROR Rate.) and represents the probability of obtaining a distorted information bit when reading it. This parameter reflects the device's ability.CD - ROM. Adjust read / write errors. Passport values \u200b\u200bof this coefficient - 10 -10 -10 -12. When data from a contaminated or scratched section of the disk is read, groups of erroneous bits are recorded. If the error fails to be eliminated by the helpful code (used when read / write), the data reading speed decreases and repeatedly repelly occurs.
Average access time ( Access Time. - AT.) - This is the time (in milliseconds) that the drive is required to find the necessary data on the carrier. Obviously, when working in the inner parts of the disk, the access time will be less than when reading information from external sections. Therefore, the passport of the drive is given the average access time, defined as the average value when performing several data readings from different parts of the disk. As the drives improveCD - ROM. The average access time is reduced, but nonetheless this parameter differs significantly from the hard drives similar to drives (100-200 ms forCD - ROM. and 7 - 9 ms for hard disks). This is due to the fundamental differences of the structures: in hard disk drives, several magnetic heads are used and the range of their mechanical movement is less than the range of moving the optical drive headCD - ROM.
Volume of buffer memory - this is the volume of operational storage deviceCD - ROM. used to increase the speed of access to the data recorded on the carrier. Buffer memory (cache memory) is installed on the memory microcircuit board for storing read data. Due to buffer memory, data placed in various areas of the disk can be transmitted to a computer at a constant speed. Volume of buffer memory of individual drive modelsCD - ROM - 512 KB.
Middle Drawing - average time in hours, characterizing the trouble-free driveCD - ROM. . Average work on the failure of various drive modelsCD - ROM. 50-125 thousand h, or 6 - 14.5 years of round-the-clock work, which significantly exceeds the term of moral aging of the drive.
During the development of drives on optical disks, a number of basic information recording formats on CD.
FormatCD- DA ( Digital. Audio.) - Digital audio CD with a sound time of 74 min.
FormatISO. 9660 - The most common standard of logical data organization.
FormatHigh Sierra. ( HSG.) proposed in 1995 and provides reading data recorded on a disk in formatISO. 9660, using all types of drives, which led to wide replication of programs onCD and contributed to the creation of CDs oriented on various operating systems.
FormatPhoto.- CD designed in 1990-1992. and is designed to record onCD , storage and reproduction of static video information in the form of high-quality photo images. Disk formatPhoto - CD. Holds from 100 to 800 photographs of the corresponding permissions - 2048x3072 and 256x384, and also saves sound information.
Any CD - ROM drive Containing text and graphic data, audio or video information refers to the category of multimedia. MultimediaCD There are in various formats for various operating systems:DOS, Windows, OS / 2, UNIX, Macintosh.
FormatCD- I. ( INTRACTIVE.) designed for a wide range of users as a multimedia disk standard containing different textual, graphic, audio and video information. Disk formatCD - I. Allows you to store video with sound accompaniment (stereo) and playback duration up to 20 minutes.
FormatCD- DV ( Digital. Video.) provides recording and storage of high-quality video with stereo sound for 74 minutes. When stored, compression is ensured by the methodMPEG -1. ( Motion. Picture Expert. Group.).
Reading disk is possible using a hardware or software decoder of the standardMPEG.
Format 3D O.designed for gaming consoles.
CD - ROM can work as a standard interface to connect to the connectorIDE (E - IDE ) and with high-speed interfaceSCSI.
Most popular drivesCD - ROM. In Russia - products with trademarksPanasonic, Craetive, Samsung, Pioneer, Hitachi, Teac, LG.
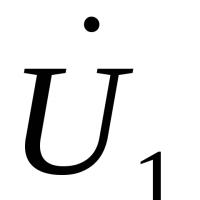 Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it
Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it Effective job search course search
Effective job search course search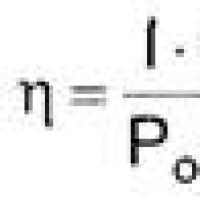 The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode
The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF
How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF Why the fired program window is long unfolded?
Why the fired program window is long unfolded? DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT
DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT What to do if the mouse cursor disappears
What to do if the mouse cursor disappears