DVD what format. Online publication about high technologies. Different DVD formats
In recent years, CD-RW drives have become familiar to all users. Almost any new PC is sold with CD-RW (or CD-RW + DVD-ROM combo) bundled. Moreover, many completely abandoned the use of 3.5-inch floppy disks. Manufacturers of modern laptops no longer equip their products floppy drives, magnetic information storage devices went to the past ...
At the same time, CD-RW drives have long reached its technological perfection. The maximum recording speed was decided not to increase to 72x (except in rare models with several lasers) and put the final point at 52x speeds. Peak rewriting speed is 32x and, apparently, will not increase. The volume of CDs, by virtue of its technological features, cannot exceed 750-800 MB. And if a couple of years ago, their capacity was the main advantage of CDs, now they are their main drawback. That is why DVD format discs are becoming increasingly popular on our expanses.
What is a DVD?
DVD - disk recording format. Unlike the CD, it has a greater density of data placement, the possibility of two-layer recording and more perfect protection of licensed disks from pirated copies. At the moment, the name DVD is nothing more than a "sonorous" set of letters. However, in 1995, the DVD abbreviation was decrypted as Digital Video Disk (Digital Videoisk). The fact is that the DVD was initially developed to change the outdated VHS format, and it was mainly intended for a comfortable watching of movies. After some time, it was decided to optimize DVD discs not only for multimedia use, but also for computers, as a carrier of information. Therefore, they decided to change the name of the format without changing the abbreviation. Thus, DVD from Digital Video Disk turned into a Digital Versatile Disk (digital universal disk). But the name did not "worry" and the DVD abbreviation has become just a set of letters.
DVD Format History
The first official information on DVD development appeared in the spring of 1995. It made public 10 major companies (Pioneer, Matsushita, Mitsubishi, Philips, Sony, Hitachi, JVC, Time Warner, Thomson and Toshiba) who participated in the format development. To avoid war of standards, these companies united in the so-called DVD Consortium. The main tasks were: the promotion of the format in the market, the agreed development of new specifications and licensing of enterprises recording information on DVD. Two years later, in 1997, a DVD forum was created. His tasks were the same as the DVD consortium. At the moment there are about 200 official DVD members. All of them are interested in the development of the format and participate in the development of new, more advanced formats like Blue-ray, EVD or HD DVD.
DVD outside and inside
Externally, DVDs are almost impossible to distinguish from conventional CDs. They have the same dimensions and externally similar to each other. However, read the DVD disk on the usual CD drive will not succeed. To do this, you will need a drive with the support of a DVD format, which, by the way, the usual CDs read without problems.
All information on the DVD is stored in the MicroDF file system (Micro Universal Disk Format). She was officially approved in 2000. Microudb supports high-capacity media and large sizes. File names are written in Unicode format, which ensures DVD compatibility with all operating systems For PCs, as well as with a variety of home appliances.
The essential difference between the DVD from the CD is the possibility of two-layer records of the disks. On one single-sided disk (there are two-way, with an information surface on each side) can be kept twice more information. Both layers have a reflective surface, only one of them has high transparency (up to 40%). When recording / reading, the beam simply changes focus, which allows you not to fall on both layers at the same time.

The higher capacity of DVDs is obliged not only by the possibility of two-layer recording of disks, but also greater density of information recording. A higher record density was achieved by reducing the distance between the information paths on the helix. This distance in the CD discs is 1.6 microns. DVD disks - 0.74 microns. The volume of DVDs, depending on their specific type, can be from 4.7 to 17 GB. Below is a list of all types of DVDs:
- DVD-5 - one-sided single-layer disk with a capacity of 4.7 GB;
- DVD-9 - one-sided two-layer disk with a capacity of 8.5 GB;
- DVD-10 - double-sided single-layer disk with a capacity of 9.4 GB;
- DVD-14 - double-sided disc: on one side - one layer, on the other - two; Capacity - 13.24 GB;
- DVD-18 - two-way two-layer disk with a capacity of 17 GB.
The most common discs - DVD-5 and DVD-10. The rest have fewer popularity due to greater cost and less prevalence of relevant production lines. Today on store shelves is not difficult to find any type of discs.
DVD protection
To protect DVDs from external damage and scratches of the surface, an additional transparent plastic layer was provided. It is applied over the information reflective surface and does not prevent the reading of the disc.
In different countries, the premieres of the same films take place at different times. And since the films of films are not interested in the appearance of the film where there has not yet been his premiere, it was decided to introduce the so-called zoning.
The whole world was divided into 8 zones. If you installed a disk drive from a "foreign" zone, it simply does not recognize it. Below is a list of DVD zones:
- Canada and USA;
- Japan, Europe, South Africa, Middle East;
- Southeast Asia, East Asia;
- Australia, New Zealand, Pacific Islands, Caribbean Islands, South and Central America;
- The territory of the former USSR, the Indian Peninsula, the main part of Africa;
- China;
- Reserved zone;
- Exterritorial zone: airplanes, liners, steamers ...;
In the fifth zone, as you can see, they placed Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and many more countries, ironically - with a high level of piracy.
Information on the DVD disk is encrypted under a certain region. Drives are also encrypted under the region in which they were delivered. When reading the disc, the drive is checked by the coincidence of the regions on the drive and disk and, depending on the result, continues or continues to read the drive further. There are also multizone drives and players that are not tied to a specific region. Now, however, they are rare, but still find them real. The so-called "mounted" devices (configured to read disks only one zone) can be changed to multizone in the event that it can change the zone (as a rule, it is allowed to change to 5 times). Set the zero zone, and your drive will become a multizone. Sometimes there are new firmware for drives that turn off the zonal dependence. But to flash such devices is much more dangerous than, for example, motherboards.
The DVD disks also use CSS protection technology (Content SCRAMBLING SYSTEM) - digital copy protection. To the disc cannot be copied to the PC, all information is encoded on it. And for the decryption you will need a key of two parts. One of them is on the disk, the second is programmed in the drive. When recording information on the PC, you will simply be brought to view the film, although the data is copied without problems. You can bypass such protection using a special software.
And finally, the last way of protection is analog recording protection. The principle of operation APS (Analogue Protection System) lies in the fact that when playing the film, interference is specifically created. And if you write a movie to another player, the image will be very distorted. So much that watch the movie will no longer work.
Features DVD Video.

As you know, the DVD technology thought in order to improve the quality of the movie viewing. DVD-Video disks are found in each store. And many new films go only on DVD. What do they differ from the usual VIDEO-CDs except the larger disk capacity? Externally DVDs with films are characterized by packing a rectangular shape, made in the form of a book. On each side of the package, a high-quality image of high resolution and text with information about the film is applied. Inside the box can be one or two disks. Sometimes on the second disk contains videos with fragments about film filming, interview with the director, film history / film company, etc.
Movies on DVD video possess the following features:
- On each disk with the film there is its own unique menu, in which the preview settings are made;
- On the disk there may be several sound tracks with translations into different languages;
- Each audible track can be recorded in high-quality formats with Dolby Surround support for multichannel acoustic systems;
- Subtitles in several languages;
- Formally film length is limited to 135 minutes of video high Quality. But in fact, it all depends on the type of disk, its capacity and the settings of the compression algorithm. The greater the volume of the disk - the longer the film will fit on it;
- The disk menu allows you to disconnect / enable subtitles, select the playback language and switch to the selected movie episode.
As part of this material, we do not think about the specifications of the DVD Audio standard, since this conversation requires a serious separate article.
With conventional CD-Dwarcs, everything is simple: they are either CD-R (Compact Disc Recordable), i.e. Operating discs, or CD-RW (Compact Disc Rewritable) - repeat disks. But with DVDs it is more difficult - there are many types of DVDs, and in such a variety it is easy to get confused.
Let's start with the decryption of the DVD abbreviation. Previously, the DVD abbreviation was decrypted as Digital Video Disc, since the first DVDs were intended only for recording video. Then, when the DVD was a possible recording of other data types, DVD "renamed" in the Digital Versatile Disc - a digital universal disk.
In essence, DVD is the development of CD technology, but about everything in order. The beginning of the DVD history can be considered 1994, when Sony, Philips and Toshiba began to create a new data carrier. In general, the initiator of all this was Hollywood - ordinary video tapes did not provide any means of protection against unauthorized copying. Yes, and at that time, an alternative medium (CD) did not provide proper quality of video playback - on a regular 700 MB to a normal disc was not allowed a movie of normal quality. It was required at least two disks.
In 1996, Sony, Philips and Toshiba presented the first specifications of the new data media - DVD-ROM (basic format, was used for data storage) and DVD-Video (add-on DVD-ROM format, designed to store video). Mostly DVD then used to store the video, therefore, the name Digital Video Disc is called.
In 1998, a new format was presented - DVD-Audio. Since the DVD format has already been used not only for storing the video, so as not to enter a new abbreviation and not confuse users, the word "video" should be replaced with the word "Versatile". In the same year, the DVD disk capacity was increased to 4.7 GB (it was originally 4.5 GB). Despite the fact that the DVD-Audio format appeared in 1998, the first DVD players (it was for DVD-AUDIO format) appeared in 2000 and was very expensive. In Europe, such players first appeared in 2001.
Now the new format is the popularity - Blu-Ray. Inexpensive combined drives appeared, and laptops are increasingly equipped with drives that can read Blu-ray. But Blu-ray format itself was announced back in 2002. Seven years have passed, and the format has not yet received special popularity.
The most interesting thing is that DVD is almost the perfect data carrier without special flaws. Judge for yourself. On DVD you can write from 4.7 to 18 GB (on a two-layer and double-sided disc) of information. You just count how many ordinary CDs need to write at least 4.7 GB.
What about the flash drive? The flash drive on 8 GB is not surprised now. But the flash drive is just the disadvantages. First, the 8 GB flash drive is much more expensive than DVD-RW on 9 GB. Secondly, due to the desire to save a great probability to buy a poor-quality flash drive, which will work less than the most common DVD-RW.
In addition, DVD supports various video formats (4: 3, 16: 9), multichannel sound and up to 9 different angles of view for cameras. In a word, if you need to record just data, you can do the usual flash drive, but if you need a media for video, then it is better than DVD while nothing is invented (Blu-ray is not accepted due to high cost).
DVD-Video and DVD-AUDIO support Dolby Digital, Dolby Digital Pro and Dolby Surround (multi-channel 5 + 1), which further adapts them to high-quality sound playback (both when watching movies and listening to audio componations). And if you add the possibility of interactive management to all this (scene sequence management, change of review cameras, subtitle call, bookmark support), then in general DVD has no competitors yet. CD and flash drive in this regard - not a competitor, and VHS-cassettes and is suppressed. In addition, VHS-cassettes are unreliable and just huge compared to DVDs.
Earlier, the disadvantages of DVD were high cost of both DVD players and writing drives. Now prices are so funny that the cost of equipment for recording and playing a DVD is not accepted. DVD blanks are also cheap, though, only those that are unilateral and single-layer, but in any case, the storage of 4.7 GB on the DVD will cost you cheaper than storing the same volume on the CD.
In addition to the high cost, before DVD had some compatibility issues. The fact is that, since 1996, various companies "petood" so much different formats that some drives could work with one formats, and with others - no (or, for example, did not support the recording of certain DVD formats). Today there is no such, and the most ordinary DVD drive can work with all available formats.
Now let's talk about DVD formats. When choosing DVD Dipers, pay attention to their marking.
Marking DVD-Doodle
- In addition to labels, the following labels that define the DVD standard may be on DVDs:
- DVD-ROM is a basic format, used for mass production of discs. Discs of this format can be bought already recorded, since the technology of their records is somewhat different from the recording of ordinary DVD duals at home.
- DVD-Video - "Add-in" above the DVD-ROM format, specifying the procedure for hosting files to DVD-ROM. In addition to the video, you can write pictures on such a disc (for example, the frames of the most interesting movie scenes), subtitles in different languages \u200b\u200band dialog boxes for the organization of the menu.
- DVD-AUDIO - Used to record high-quality sound. After all, the sound can be recorded on the usual AudioCD, and encode the MRC format, and write to the usual CD-R. The DVD-Audio sound is significantly superior to AudioCD and better than the DVD-Video (due to the fact that all the place is allocated only for sound, and you have to store more video, subtitles and other data to the DVD-Video). DVD-Audio format is recognized as the best audio format.
- DVD-R - "DWORD" of a single record. You can write everything to such a disc, music, video, pictures, data, but only once. Using DVD-R, you can create a DVD-Video or DVD-AUDIO format disk, but without protection against illegal copying. To create a disk with such protection, you need a disc for producers - DVD-authoring. Such discs are much more expensive than ordinary DVD-Rs, and not all drives can record DVD-Authoring discs. Therefore, before buying an expensive DVD-Authoring blank, make sure your drive supports records of this type.
- DVD-RW is a rewritable DVD. As in the case of CD-RW, you can record information to the disk, then wipe it, then write again, etc.
- DVD-RAM is another type of rewritable disk. His difference from the DVD-RW is greater reliability: if conventional DVD-RW can be overwritten about 100 times (cheap Chinese do not accept - well, if you managed to overwrite such a disc 10 times), then the DVD-RAM can be overwriting 1000 times. In addition, DVD-RAM allows you to record the disk on the tracks, which does not require the creation of the image of the future disk on the hard drive. It may turn out that you will not have 9 GB of free space on the disk. Minimum disk spacenecessary to record DVD-RAM disk any capacity - only 200 MB. But this type of disk has disadvantages: high cost, slowness (the recording speed is very small) and only computers can read it, but not all household players can read it.
- DVD + R / DVD + RW - new DVD format. The "+" sign in the marking means that the new format is better than the previous one. The advantage is at a higher velocity of recording such disks. Previously, not all drives could record discs with a plus. Now there is no such problem, and all modern actuators can record discs of both new and old formats. What disk choose? Now there is no special difference. If there is a desire to save, buy DVD-R / RW - they are slightly cheaper (just do not buy the cheapest - and do not say that I did not warn you!).
DVD-5 and DVD-10 discs are the most common and sought-after. DVD-9 and DVD-18 discs are on sale less often. This is due to the greater value and the fact that some players ( we are talking it is about domestic players, and not about dVD drives) Can not work with two-layer discs. All modern DVD drives can read and record two-layer discs, just need to turn the disk to perform read / write on the other side.
Some DVD manufacturers declare that their discs can store information for 50-100 years. Personally, I do not believe such applications - the DVD format appeared in 1996, and there was still little time to make such applications. Moreover, taking into account the pace of development computer technologyAfter 50 years there will be no drive that can read DVD. Recall the floppy disks: the last time the FDD drive was installed in my four-year computer. The first floppy disk was produced in the distance in 1971. It was the 8-inch IBM diskette. And the floppots 3.5 ", to which we are accustomed to at one time (or at least, caught them more), appeared in 1981 due to the efforts of Sony. Disks lasted on average 25 years. Of course, they still have on sale, you can buy Even the drives for reading a floppy disk, but by them almost no one uses. After all, the same flash drives and more compact, and allow you to record more information.
As for DVDs, I would recommend the following: Store DVDs need to be kept in a cool place protected from direct sunlight. It is advisable to store discs in separate boxes, and not each other - then scratches on the surface of the disk can form. Once every two years (or once a year, if you often use these discs) it is advisable to overwrite information from them to new DVDs, so you will reinsure to loss of data.
Perhaps now it is impossible to meet a person who would never hold a CD in his hands. IN lately These information media seriously passed their positions due to the active introduction of more technological storage devices based on solid-state memory. Nevertheless, it is unlikely to completely refuse disks yet.
The DVD container is quite sufficient to store most programs and multimedia files. Manufacturers indicate that the user is available 4.7 GB. In fact, for the maximum information container is 4.38 GB, which is explained by the difference in the calculation method. Today we will talk about digital technology Versatile Disc and will deal with the nuances of calculating the volume of such information carriers.
Problem with definitions
The term DVD is not surprising, does not have an unambiguous decoding. This technology was developed in order to replace the usual CDs CD, the capacity of which is increasingly not enough. Initially, the abbreviation DVD meant a digital video disk (DIGITAL VIDEO DISC). However, it later became clear that not only films can be recorded on it, but other files.

This was the reason for some of the fact that some began to invest a different meaning to the term, realizing the DVD Digital Universal (Versatile) disk. In general, both decryptions are true.
Increasing accessible volume
Earlier it was already indicated that the DVDs came to replace the CD, the capacity of which was not enough. In order to read the digital data recorded on the surface, it is necessary to use a thin laser beam. In the device drives, a special block consisting of a radiating element and focusing system is implemented. The main difference between the beam of light used to read and write information is that it is coherent, that is, is very narrow-controlled. This makes it possible to virtually eliminate the impact of phenomena of diffraction and interference of the light wave. When developing a CD standard, the miniature semiconductor emitters available at that time were not able to create a fairly narrow beam, so the width of the track on the metal base of the disk was about 1.6 microns. Subsequently, more advanced light-emitting diodes were developed, the beam of which was so thin that the width of the track was reduced twice. Thus, it became several times to exceed the same parameter CD. In addition to the width of the track, it was possible to change the distance between them, as well as the size of the pit.
"Pie" from disks
The DVD disk capacity is determined not only by the above size and configuration of the laser beam. These were created that, in fact, several discs in one product were combined at once while maintaining standard dimensions.

Such multilayer compacts can be compared with sandwich. In production, it is used not alone, but at once two tracks, but located in such a way that the reading beam of the laser fluently passes through the translucent upper surface. Their volume reached 8.54 GB. The maximum capacity of the DVD disk, the diameter of which is not 12, and 8 cm is 5.32 GB. A constructive drive can possess two emitters, each of which focuses on its depth (surface). There are models with one beam, the focus of which controls the electronics. Information container DVD could be even more when the so-called bilateral solutions were used. Externally, this is an ordinary compact, but record / reading is possible on both sides, for which in most drives it was necessary to turn the carrier. The capacity of a DVD disk of such a modification is from 9.4 GB (double-sided single-layer), until 17.08 (four layers, recording from two sides). Nevertheless, such "pies" were not widespread due to the higher cost of production and the need to treat them too gently, since the slightest scratch could lead to the impossibility of reading data from the deep layers.
Saving information
The RAM-disc is based on the technology of heating the surface with a laser beam. Their feature is the ability to formatting into familiar and selective deletion of files. Constructively such discs are located in special cartridges, which increases their reliability. Theoretically, if you remove a DVD-RAM from the case, you can work with it on the drive designated as MULTI. These are quite reliable solutions.

The information container DVD of this type is from 1.46 GB (single-layer one-sided, 8 cm) to 9.4 GB (double-sided). The term RAM means that overwriting is physically possible. Abbreviation can be translated as "memory with arbitrary access". In fact, this type of disk is intended for reserve copy Data to the appearance of alternative carriers was an excellent solution. Especially if you consider the stated data storage duration (about 30 years) and the number of overwriting cycles (more than 100 thousand). The disadvantage is relatively high cost and small distribution.
Video office
The following solutions are DVD-Video. Such discs are designed to record multimedia stream. Indicatically as "DVD-1 ... 18". The first four are modifications with a reduced diameter (8 cm against standard 12). The classics considered DVD-5, from which 4.7 GB (single-layer one-sided) can be considered.

Accordingly, the maximum DVD container in this category is 17.08 GB (DVD-18, two sides, four layers). Since the simplest focusing blocks are used in mass video players, which allows you to reduce the cost of production, not all models are capable of reading the discs of a large volume. Exception - single-layer double-sided, to work with which only turn the disk in the drive. Their disadvantage is the absence of a place for a label, so the name is indicated on the transparent part, next to the central hole.
Single recording
The appearance of drives capable of recording digital data on discs at home made a real coup in the backup and creating the most real films. DVD +R is initially sold without recording. The owner of a special drive can save any information that has been transformed into a digital form on such a disk.

The color of the mirror-blue, with a chip in the purple spectrum. The DVD container of this type is from 4.7 GB (one layer on one side) to 17.08 GB. The volume depends, as usual, on the number of layers and parties. But after all, due to the correct most common, the simplest compactons on 4.7 GB were obtained. Earlier, the recording could be done only with the help of a computer drive, now many video players have this opportunity that can save on wheels from TV. The problem of compatibility "-" and "+" r long ago remained in the past and is not considered in the article.
Multiple recording
The disadvantage of the previous type of discs is obvious - they cannot be re-recorded, deleting data. To solve this issue, fundamentally different discs called DVD + -RW were proposed. They can be used almost as a regular drive. The term RW is RWRITABLE, i.e. overwritten. The Capacity of the DVD of this class is exactly the same as the "simple" R. However, the two-layer is extremely rarely distributed due to the need to acquire a special drive capable of working with such discs.

In addition, rewritable solutions and so require a careful circulation, and the complication of their design means that with such discs actually have to blow out the dust. A random scratch on the surface may not allow the information from the lower layers. Thus, the "classic" is a single-layer one-sided disk. The surface color varies from gray to almost black. The number of overwriting cycles is officially about several thousand, however, in practice, such a disc can be recorded not more than 50-100 times. And then with the time the reliability of storage is reduced. Thus, DVD-RW are suitable for short-term storage of data and their transfer. The entry can be carried out by the block, as usual. At the same time, using the Windows Mechanism is also possible to work as a regular drive (read / recording arbitrary files). True, due to the fact that the standard of rewritable discs does not allow to develop high speeds, it is usually possible to be content with a fourfold, equal to 5.5 MB.
Feature recording
The standard DVD container can be a bit exceeded. This is achieved by using the LEAD-OUT zone. The Overburn function must be supported by the device itself. It can be activated in popular nero programAfter passing in "Options - Expert Properties." We do not recommend using this feature without as you can encounter the inability to read such a disc on a drive that cannot work with Overburn.
How volume is calculated
Many computer owners have long noticed that the CD is impossible to record that which is indicated by the manufacturer. In fact, no deception is not here. Just the manufacturers of discs from marketing considerations believe that in 1 KB 1000 bytes, although in reality 1024 (we will be erected into a tenth degree). With an increase in volume, this number grows in progression. Consequently, a standard DVD is placed no more "honest" 4.38 GB.
Directory DVD.
DVD
DVD is a family optical disks, the same size with CDs (CD), but significantly larger storage capacity achieved by increasing the record density.
The appearance of DVD. DVD-forum
At the heart of appearance DVD DiscoZ lay the idea to develop such a carrier of information that could be equally successfully used in sound and video equipment, in computer equipment, gaming consoles. It would ensure the rapprochement of different electronics regions.
DVD originally meant a digital video disk (DIGITAL VIDEO DISC). Later in connection with the decision on the expansion of the DVD functions, the abbreviation began to read otherwise - a digital universal disk (Digital Versatile Disk).
The development of DVD format was officially announced in September 1995 by a group of 10 companies: Hitachi, JVC, Matsushita, Mitsubishi, Philips, Pioneer, Sony, Thomson, Time Warner and Toshiba. In May 1997, a DVD-forum was created on the basis of this consortium - an organization currently consistent with more than 200 members.
The main tasks of this organization are the development and promotion of DVD format, developing coordinated specifications, as well as licensing activities of enterprises in the field of DVD technology. The forum employs special working groups on various aspects of DVD technology. International standards adopted on a number of specifications.
The most important advantages of DVD technology
Today, DVD is already widespread, tested by time and at the same time dynamically developing technology with enormous potential.
- record and reproduction of high-quality video and real-time audio, effective work with computer multimedia information, as well as ensuring effective arbitrary access to data, stored in the form of a plurality of small files;
- the volume of the disk is up to 4.7 GB (about 2 hours of MPEG-2) to the side to record into one layer and 8.5 GB to the side for a two-layer record;
- the ability to record information in two layers to each of the parties;
- unified UDF file system;
- the ability to record and multiple Revitaliss DVDs;
- backup compatibility with existing CDs - Geometric DVD sizes and CDs are identical, all DVD equipment can read CD-AUDIO and CD-ROM wheels (Multyread specification).
The first DVD formats
DVD technology originally relied on 3 main formats, the presence of which is determined by specific requirements for various areas of DVD applications:
- DVD-ROM is used to record data, including multimedia used in computer technologies;
- DVD-Video is used when writing video for their further viewing on video engineering or using a DVD-ROM drive attached to a computer. The format provides protection against illegal copying information;
- DVD-Audio is used when writing high-quality multi-channel sound. In addition, the DVD forum recommended additional support for video, graphics and other information.
Developed DVD formats
Only for reading
- DVD-ROM.
- DVD-Video.
- DVD-Audio.
- DVD-RAM
- DVD + RW (not supported by a DVD forum)
- DVD-RW.
- DVD-R (G)
- DVD-R (A)
- DVD-Vr.
Compatibility
The developers could not achieve a single approach when developing the format of the recorded disks. Competition predetermined the lack of support by one device of several recording formats. Therefore, discs recorded in one of the formats are usually not read on the actuators of other recorded formats. An attempt to overcome the disunity of recording formats has been made by Panasonic, which in April 2001 presented a device operating with DVD-RAM and DVD-R (G) formats.
Some devices may not understand the DVD disk format, which has been proposed after their release. Naturally, household electronics can be focused on a completely specific segment of the consumer market (DVD-Audio, DVD-Video, both formats), and it does not have to provide reading computer discs, which is defined by the DVD forum. At the same time, computer drives are equally well operating with video, audio, multimedia and other computer discs.
UDF file system
A great achievement of compatibility in DVD technology has become the unified Microudf file system adopted in 2000. The Microudf file system is an adapted version of the UDF file system in the DVD, which, in turn, is based on the International Standard ISO-13346. This file system gradually goes to replace the outdated ISO9660 created at one time to use in CDs. For the transition period (until you come out of circulation computer devices And the disks working in the ISO9660 format) will be used by the UDF Bridge file system, which is some combination of Microudf and ISO9660. Only Microudf can be used to record AUDIO / VIDEO DVDs.
The features of the microudf file system are as follows:
- independence from the software and hardware platform used (in this sense UDF is the optimal choice in archival systems);
- large container. The entire disk can be represented as a single volume;
- optimal transmission rate. The speed of reading and writing data in UDF format may be higher than the performance of many "native" file systems when large files indulge (for example, in multimedia systems)
- maximum possible file sizes;
- using Unicode font format, which ensures efficient international support;
- support for advanced file attributes, which is used in some "native" operating systems;
- support for long file names with the extension of the restrictions of the operating system. Maximum length of the file name 255 characters;
- interchangeability of DVD discs in consumer electronics and computer systems.
DVD prospects
The presence of different standards and specifications does not mean that DVD technology is in place. The efforts of various companies today are aimed at introducing the technology of the Blue Laser - with a smaller wavelength. This will increase the recording density on the disks with the improvement and other characteristics arising from here.
Calimetrics Inc invited ML technology (Multilevel), which allows three times to increase the capacity of standard DVD / CD. At the same time, there is no need to perform any refinement in the mechanism and optics of existing drives. To implement a new technology, it is enough to use a set of chips developed by this company. The essence of the technology is to be able to use as an information characteristic, the depth of peits (up to 8 levels) when working with disks. Note that similar technology, but for CD discs, is developing a TDK company in collaboration with other firms.
DVD formats read only
DVD-ROM. (Digital Versatile Disc Read Only Memory)
DVD-ROM discs are designed for use in computer technician. Information is entered on the disk only time - in its production.
The progress of DVD devices largely repeats the path passed by CD, and is directed by the main obsession to improve the speed characteristics and the introduction of the recording function. The first generation DVD-ROM devices used the CLV mode and read from the disk at a speed of 1.38 MB / s (in the traditional designation for DVDs it is 1x). The second-generation devices could read the DVD from twice the speed - 2x (2.8 MB / s). Modern DVD-ROM - third-generation devices - use the rotation control mode (CAV) with a maximum read speed of 4x-6x (5.5 - 8.3 MB / s) and more. Modern DVD-ROM drives (drives) support reading virtually all formats, including CD discs.
DVD-Video.
DVD-Video format is designed to store and play video. Like a DVD-ROM, this specification determines the ability to read information only - playback of records using video player (video discoders). The specification is based on the DVD-ROM format, but provides for a special way to place data that prevents the disk copying option. Video films in the encoded form are placed on the disk in the process of its production. Playing a DVD-Video is possible only on household video player (video discs) or on DVD drives connected to a computer. When using computer equipment, information decoding is carried out either hardware or software. Modern specification provides an entry to a disc of high-quality video (up to 2 hours in MPEG-2 compression format), as well as multichannel sound accompaniment In 8 languages, the selection of on-screen format, the titers in 32 languages, interactive control via the on-screen menu, up to 9 corner viewing directions, protection against illegal copying, distinction of viewing video products by region, the management of children's access to video materials.
DVD-Audio.
New generation of musical format after CD. The format specification defines high-quality multichannel sound, support for a wide range of sound quality (quantization 16, 20, 24 bits at a frequency from 44.1 to 192 kHz), playback of DVD players CD discs, support for more information (including video, text, menus, screensavers, convenient navigation system), communication with information support Web sites, expanding opportunities when new technologies appear.
There are two versions of DVD-AUDIO format: just a DVD-Audio - only for sound content and DVD-Audiov - for sound with additional information.
Special disk protection measures from pirated copying are developed.
DVD formats for multiple recording
Multiple recording
All known specification of rewritable DVD discs use multiple recording technology based on the physical principle of the phase state change (crystalline / amorphous) information layer under the influence of a laser with a wavelength of 650 (635) Nm (Phase-Change Recording). Reading information is carried out by determining optical characteristics The information layer in the various phase states when reflecting the laser rays (the same as when recording).
Material for multiple
As a working, the AVIST material created by TDK in 1995 is used. The characteristics of this material almost perfectly satisfy the requirements of the DVD Rewaging Technology:
- high reflective ability - up to 25-35%, which is quite enough to compatibility DVDs during playback;
- the ease of replacing the phase state both at high and at low recording rates, which is especially important when working with various applications. Applications operating with overwritten CDs (for example CD-E) carry out a recording at a rate of less than 3 m / s. Working with DVD-RAM data requires a working layer of a higher recording speed - from 3 to 6 m / s. When working with video information subjected to compression, the recording speed must exceed 6 m / s;
- the excellent ratio of signal-noise and phase change characteristics allowed TDK to achieve ultra-low dimensions of the marker (less than 0.66 mm);
- Avist maintains at least 1000 cycles of rewriting even at speeds less than 3 m / s. At higher speeds, the number of cycles of rewriting increases.
DVD-RAM (Digital Versatile Disc Random Access Memory)
Overwritten format developed by Panasonic, Hitachi, Toshiba.
The format is approved by the DVD forum in July 1997. Equipment and disks of this format were tested for 3 months in more than 20 computer manufacturing companies around the world. Over 160 forum participants voted for the adoption of the specification. Today it is the most common DVD format in the computer industry.
DVD-RAM drives read dVD-R discsOm. In turn, DVD-RAM discs can be read only by the DVD-ROM drives of the so-called third generation, manufactured from mid-1999.
The first generation of DVD-RAM discs contained 2.6 GB to the side. Modern - second-generation discs are 4.7 GB on the side or 9.4 GB for bilateral modification.
Two types of one-sided DVD-RAM disks are available - in the cartridge and without a cartridge. Cartridge discs are mainly designed for household video equipment, where it is necessary to eliminate the effect of external factors with intensive manual use. Cartridges in turn can be two species - open and solid.
The most important advantages of DVD-RAM disks are the ability to overwrite up to 100,000 times and the presence of a recording error correction mechanism.
The largest number of overwriting cycles among all DVDs, error correction mechanism and arbitrary disk access both during recording and when reading predetermined the maximum efficiency of this format in secondary storage devices. The overwhelming majority of mass storage devices are robotic DVD libraries - uses this technology.
DVD-RAM wheels can be used to record and play streaming video on hardware supporting DVD-VR specification (see below).
DVD + RW. (Digital Versatile Disc Rewritable)
The DVD + RW format is progressing only by its developers - Hewlett-Packard, Mitsubishi Chemical, Philips, Ricoh, Sony and Yamaha (not supported by the DVD forum).
On DVD + RW drives, you can write both streaming video or sound and computer data. DVD + RW discs can be overwritten about 1000 times.
The DVD + RW database has created a streaming video recording format - DVD + RW Video Format. Devices and discs operating in this format are positioned in the market as fully compatible with equipment operating in DVD-Video formats. This means that DVD + RW discs containing video materials can be played on a previously released DVD household apparatus.
Philips announced the start of the release of its DVD video recorder in September 2001 DVD + RW discs recorded on this device are also read by conventional DVD-Video players. This decision was proposed as a response step on the DVD adopted DVD specification of the DVD-VR (see below).
DVD-RW. (Digital Versatile Disc Rerecordable)
There are other names of this format: DVD-R / W and less often DVD-ER.
DVD-RW - multiple format developed by Pioneer. DVD-RW discs contain 4.7 GB to one side, are available in one-sided and double-sided modifications and can be used to store video, audio and other data.
DVD-RW discs can be overwritten up to 1000 times. Unlike DVD + RW and DVD-RAM formats, DVD-RW discs can be read on the first generation DVD-ROM drives.
TDK declares that the durability of the DVD-RW discs produced by it is about 100 years.
DVD formats for one-time recording
DVD-R. (Digital Versatile Disc Recordable)
DVD-R is a format of a single record developed by Pioneer. Devices based on this format were the first to be recorded on DVDs. The technology of recording is similar to those used in CD-R and is based on an irreversible change under the influence of the laser of the spectral characteristics of the information layer, covered with a special organic composition.
DVD-R discs can be recorded both computer data, multimedia programs and video / audio information. Depending on the type of recorded information, discs can be read on other compatible with the recorded device types, including DVD-Video video players and most DVD-ROM drives. Unilateral DVD-R discs accommodate 4.7 or 3.95 GB to the side. Double-sided discs are available only to a total capacity of 9.4 GB (4.7 GB to the side). Currently, the format does not support recording technology in two layers.
DVD-R disk durability is estimated for more than 100 years.
To protect against illegal copying, two specifications have been developed: DVD-R (A) and DVD-R (G). Two these versions of one specification use a different laser wavelength during information recording. Thus, discs can only be recorded on their appropriate equipment specifications. Playback of discs can be performed equally successfully on any equipment that supports DVD-R format.
DVD-R (A) (DVD-R for Authoring) is used in professional applications. In particular, the support of a special format (Cutting Master Format) allows you to apply these discs to record the source replica of information (pre-mastering) instead of normal use for these purposes DLT tapes.
DVD-R (G) (DVD-R for General) is designed for wider use. Disks of this format are protected from the possibility of beaten copying information from other disks. The format is supported in mass storage devices (for example, in robotic DVD libraries offered by Pioneer itself).
The DVD-VR specification is based on DVD-RAM and supported by the DVD forum. DVD-VR format allows you to record in real time up to 2 hours of high-quality video in MPEG-2 format per one-sided DVD-RAM disk with a capacity of 4.7 GB and provides features such as editing already recorded video materials, recording different types static images. Electronics based on this format is released, for example, Panasonic, Toshiba, Samsung, Hitachi.
Reference tables
Table 1. Capacity DVD discs
| Format | Specification | Number of parties | Number of layers | Capacity, GB * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DVD-Video and DVD-ROM | DVD-5. | 1 | 1 | 4.7, or more than 2 hours video |
| DVD-9. | 1 | 2 | 8.5, or more than 4 hours video | |
| DVD-10. | 2 | 1 | 9.4, or more than 4.5 hours video | |
| DVD-14. | 2 | 1+2 | 13.2, or more than 6.5 hours video | |
| DVD-18. | 2 | 2 | 17.1, or more than 8 hours video | |
| DVD-RAM (DVD-VR) | DVD-RAM 1.0 | 1 | 1 | 2.6 |
| 2 | 1 | 5.2 | ||
| DVD-RAM 2.0 | 1 | 1 | 4.7 | |
| 2 | 1 | 9.4 | ||
| DVD-R. | DVD-R 1.0 | 1 | 1 | 3.9 |
| DVD-R 2.0 | 1 | 1 | 4.7 | |
| 2 | 1 | 9.4 | ||
| DVD-RW. | DVD-RW 2.0 | 1 | 1 | 4.7 |
| 2 | 1 | 9.4 |
* 1GB - 1 billion byte
Table 2. Basic DVD parameters of the latter modifications
| Parameter | Disc type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DVD-ROM. | DVD-RAM | DVD-RW. | DVD + RW. | DVD-R. | |
| Capacity one side | 4.7 GB | 4.7 GB | 4.7 GB | 4.7 GB | 4.7 GB |
| Laser wavelength | 650 | 650 | 650 | 650 | 650 (g) 635 (A) |
| Reflective ability | 18-30% (two-layer) | 15-25% (2,6) | 18-30% | ||
| Recording method | Printing with matrix in production | Phase change | Phase change | Phase change | Change color dye |
| Record form | Not applicable | Wobbled Land & Groove | Wobbled Groove. | Wobbled Groove. | WOBBLE PRE-GROOVE |
| Interdrodial distance | 0.74 microns | 0.615 microns | 0.74 microns | 0.74 microns | |
| Minimum launch length | 0,40 | 0,28 | 0,40 | ||
| Number of zones | Not applicable | 35 | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| The method of controlling the rotation * | CAV. | Zclv CAV within zone |
CLV. | CLV (for video) or CAV (for data) | CLV. |
| Data recording speed | up to 8.31 MB / s (reading) | 2.77 MB / s | 11-26 Mbit / s, | 2.77 MB / s | |
| File system | Micro UDF and / or ISO9660 | UDF / UDF Bridge | UDF / UDF Bridge | UDF / UDF Bridge | Type1 UDF Bridge Type2 UDF |
| The cost of one-sided disk (drive) | $20-30($500) | $10-15 ($1000) | |||
* CLV - (Constant Linear Velocity) Permanent linear speed
CAV - (Constant Angular Velocity) Permanent Angle Speed
ZCLV - (Zone Constant Linear Velocity) Zone Permanent Linear Speed
| DVD formats Disc | Types of DVD drives | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DVD-RAM | DVD-RW. | DVD-R (G) | DVD-R (A) | DVD + RW. | DVD-Video. | DVD-Audio. | DVD-Player (Univer.) | |||||||||
| C. | Z. | C. | Z. | C. | Z. | C. | Z. | C. | Z. | C. | Z. | C. | Z. | C. | Z. | |
| DVD-ROM. | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| DVD-R (G) | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | ? | + | − | + | − | + | − |
| DVD-R (A) | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | + | − |
| DVD-RAM | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − |
| DVD-RW. | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − |
| DVD + RW. | − | − | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | − |
| DVD-Video. | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| DVD-Audio. | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | + | − |
| DVD-Audiov. | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
Note - In some cases, "+" means that reading or record does not contradict the forum DVD specifications, however, such devices can be not available on the market.
"-" means that the specification does not define a mandatory read or recording requirement, but the market may have devices providing this opportunity
This article discusses the basic concepts and principles used when creating DVD Video disks. All material is taken from a variety of sources located on the network. Where possible, I saved links to sources of information. If I suddenly forgot someone, do not be offended, please let me know about it.
DVD format
Physically, the DVD format is similar to CD with the difference that a laser beam with a smaller wavelength is used to work with DVD discs. Due to this, a large record density is achieved. Also, there are DVD discs with an additional layer for storing data, which increases the volume of stored data on one side twice. A single-layer DVD disk provides the ability to record up to 4.7 GB to one side, and a two-layer - up to 8.5 GB.
There are several varieties of DVD media. Initially, DVD Forum defined three types: DVD-R, DVD-RW and DVD-RAM. DVD-RAM is a physically rewritable format, but it is not compatible with the standard DVDOo format.
Logic organization DVD Video
Unlike the CD, which consists of tracks, the list of which is stored in TOC (Table of Contents), DVD has file System UDF.
DVD Video is logically divided into the following parts:
- FIRST-Play Section. Played first immediately after the disk is inserted into the device
- VMGI (Video Manager Information). Video Manager Information
- VMGM (Video Manager Menus). Menu Video Manager
- VTS (Video Title Sets). Sets of video applications
Each set of video applications (VTS) is logically divided into
- VTSi (Video Title Set Information). Information of video applications containing managers.
- VOB (Video Objects). Menu
- VOB (Video Objects). Data
- Backup VTSI
Each VOB (basic disk file unit) includes video, audio, subtitles and navigation data. When VOB is played, the player not only sequentially loses video, but also follows navigation commands to display the menu, accept commands from the user, etc. Each VOB includes individual cells (CELLS) associated with software chains (Program Chains - PGC), which provide the required interactivity using a simple programming language designed for DVD video. PGC are used to regulate video playback, audio and subtitles in VOB "ah, menu display, and entering and executing user commands. There are three types of PGC: sequential playback (SEQUENTIAL PLAY), arbitrary playback (Random Play) and mixed playback . Separate cells can be used by more than one PGC, which can determine various sequences of losing video, for example, to ensure seamless branching (Seamless Branching). PGC is subject to a set of commands for elementary programming, including mathematical and logical operators, conditional transitions, countdown time and t . d. There are 16 ordinary registers for more complex programming, and 16 system registers.
DVD-Video file organization
VOB "S and other data are located in the Video_TS directory. The table below shows a disk example with one set of video applications.
Audio, video and subtitles can contain no more than 9 VOB files relating to this video application, each of which does not exceed 1 GB. Thus, on DVD-5 there will be no more than 5 VOB files related to the video application, all 9 may be required for DVD-9. VTS files *. * Can be repeated for each set of video applications (VTS) and will be called VTS_02 *. *, VTS_03 *. * Etc. On each VTS will have one .FO I.BUP files, plus one or more .vob files.
Requirements for flow
One of mandatory requirements DVD Video standard to video stream - it must be encoded in MPEG-1 or MPEG-2. Thus, MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 codec is required for encoding the video recording. MPEG-2 use more preferably because it is more advanced and modern, however, if you need to get a video stream with a bit rate below 1 Mbps (about 10 hours of video on a standard single-layer DVD carrier), then in this case it is better Take advantage of MPEG-1 codec.
A digital video stream in the countries of the former CIS must comply with one of the requirements listed below due to the fact that standard DVD players can simply refuse to play a video object if the video stream format does not meet the specified requirements.
In the process of coding MPEG, redundant video data is eliminated in a series of nearby frames. Two adjacent frames usually contain many identical image elements. The information in them differs on a small part of all the information contained in the frame. A video compression is made, in which not all data of each video frame is used, and the dynamics of frame changes, as in most consecutive frames of one video-plot, the background almost does not change, and well-notable changes occur in the foreground. For example, a smooth movement of a small object occurs on the background of the unchanged rear plan. In this case full information The image is saved only for reference images. For other frames, only difference information is digitized: the position of the object, the direction and the magnitude of its offset, on the new elements of the background, opening behind the object as it moves. Moreover, this difference information is calculated not only compared to previous images, but also with subsequent (since it is in them as the object moves a previously hidden part of the background). The reference frames in the MPEG video stream must be inserted every 15 or 18 frames, due to the fact that it is the support or, as they are also called them, I-frames are used by video viewers when rewinding a video forward or backward.
To match the DVD Video format, the multiplexed stream bit rate should not be above 9.8 Mbps and at least 300 kbps. This parameter must be taken into account when receiving the final MPEG stream.
Basic concepts and definitions
DVD video. To play a DVD with video, a DVD-drive and MPEG-2 decoder (i.e., either a household DVD player with a hardware decoder, or a computer DVD drive and a software player with a decoder installed). DVD films are compressed using the MPEG-2 algorithm for video and various (often multi-channel) sound formats. A compressed video bit rate varies from 2000 to 9800 kbps, often a variable (VBR - English. Variable Bitrate). Standard video frame size PAL frame is 720 × 576 points, NTSC standard - 720 × 480 points. The audio data in the DVD film can be in PCM, DTS, MPEG or Dolby Digital (AC-3) format. In countries using the NTSC standard, all DVD movies must contain a sound track in PCM or AC-3 format, and all NTSC players must support these formats. Thus, any standard disk Can be played on any standard hardware. In countries using the PAL standard (most of Europe, Russia including), at first they wanted to introduce PCM and MPEG-2 formats as a sound standard for DVDs, but under the influence of public pressure and going against the wishes of Philips, DVD-Forum turned on Dolby AC-3 in the list of optional sound formats on disks and required formats in the players.
PAL (Phase-Alternating Line). Analog color television system was developed by the engineer of the German company Telefunken Walter Bruh and represented as a television broadcast standard in 1967.
NTSC (National Television Standards Committee). National Committee on Television Standards. Analog color television system developed in the United States. On December 18, 1953, a color television broadcast was started in the world with the use of this particular system. NTSC adopted as standard system Color television is also in Canada, Japan and a number of American continent countries.
MOVING PICTURE EXPERTS GROUP). Expert group on moving image. A group of specialists in submission of ISO, which is gathered to develop digital video and audio compression standards.
MPEG-1. Group standards for digital compression audio and video adopted by MPEG. MPEG-1 video is used, for example, in the VIDEO CD format. Video quality on video CD (VCD) is approximately close to the quality of VHS video cassettes
MPEG-2. A group of digital video coding standards and audio signals approved by ISO - International Organization for Standardization / IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). MPEG-2 standard is mainly used to encode video and audio when broadcasting, including satellite broadcasting and cable TV. MPEG-2 with some modifications is also actively used as a standard for DVD compression.
Quantity (frequency) frames per second. The number of fixed images that replacing each other when showing 1 second of the video and creating the effect of movement of objects on the screen. Than more frequency Frames per second, especially smooth and natural will seem to move. The minimum indicator in which the movement will be perceived homogeneous - about 10 frames per second (this value is individually for each person). In traditional film cinema, the frequency is used 24 frames per second. PAL and Sécam television systems use 25 frames per second (English 25 FPS or 25 Hertz), and the NTSC system uses 29.97 frames per second. Computer digitized video materials good quality, as a rule, use the frequency of 30 frames per second. The upper threshold frequency of the flashes, perceived by the human brain, is on average 39-42 Hertz and individual for each person. Some modern professional cameras can shoot with a frequency of up to 120 frames per second. Special chambers for ultrafast shooting are removed with a frequency of up to 1000 frames per second and above, which is necessary, for example, for a detailed study of the flight path of the bullet or explosion structure.
Interlaced scan. The scan of the video material may be progressive (line) or interlaced. With progressive scan, all horizontal lines (lines) of the image are displayed simultaneously. But with interlaced sweeps, alternately even and odd lines are displayed (also called frames of the frame). An interlaced divorce is often called in English Interlece (Eng. Interlace) or Interlaying. The interlaced edge was invented to display the images on the kinescopes and is used now to transmit video by "narrow" channels, which does not allow to transmit the image throughout. PAL, Sécam and NTSC systems are all systems with interlaced lintel. New digital television standards, such as HDTV, provide progressive debug. Although there are technologies that allow you to imitate progressive spread when the material is displayed with interlace. The interlaced rave is usually denoted by the "i" symbol after specifying a vertical resolution, for example 720 × 576i × 50 for PAL video. To suppress unpleasant effects that occur when viewing an interlaced video on the line screen, special mathematical methodsreferred to as deinterlacing.
Progressive sweep. Unlike interlaced scan, where only half of the image is formed for each frame (either even, or odd lines), an exemplated image is formed with a progressive scan, i.e. All lines. Currently, interlaced scan is used only in cheap electrical TVs.
Deinterlacing The process of creating one frame from two half-fold formats for further output to the screen with a progressive spread, such as a computer monitor. Used in computer video processing systems, flat-panel TVs, etc.
Resolution. By analogy with the resolution of computer monitors, any video signal also has permission (eng. Resolution), horizontal and vertical, measured in pixels. The usual analog television resolution is 720 × 576 pixels for PAL and Sécam standards, with a frequency of 50 hertz (one field, 2 × 25); and 648 × 486 pixels for NTSC, with a frequency of 60 hertz (one field, 2 × 29.97). In the expression 648 × 480, the first number indicates the number of points in horizontal line (Horizontal resolution), and the second number of the lines themselves (vertical resolution). New standard High-speed (eng. High-definition) HDTV digital television involves permission to 1920 × 1080 at a flareness frequency of 60 hertz with progressive spread. That is, 1920 pixels per line, 1080 lines.
The number of colors and color resolution of the video signal. Described by color models. For the PAL standard, the YUV color model is used, for Sécam YDBDR model, for the NTSC model YiQ, the computer technology is mainly used in the main RGB (and αRGB), less often HSV, and in CMYK printed technology. The number of colors that can display the monitor or projector depends on the quality of the monitor or the projector. The human eye can perceive, by different counts, from 5 to 10 million shades of colors. The number of colors in the video material is determined by the number of bits assigned to the color coding of each pixel (BITS PER PIXEL, BPP). 1 bit allows you to encode 2 colors (usually black and white), 2 bits - 4 colors, 3 bits - 8 colors, ..., 8 bits - 256 colors, 16 bits - 65,536 colors, 24 bits - 16,777,126 colors. The computer technology has a standard and 32 bits per pixel (αRGB), but this optional α-byte (8 bits) is used to encode a pixel transparency coefficient (α), and not for color transmission (RGB). When processing a pixel video adapter, the RGB value will be changed depending on the value of the α-byte and the color of the subject to the pixel (which will be "visible" through the "transparent" pixel), and then the α-byte will be discarded, and only the RGB color signal will go to the monitor .
Bitrate. The width (otherwise they say the speed) of the video stream or bit rate (Bit Rate) is the number of the processed bits of video information in a second time (denotes "bit / s" - bits per second, or more often "Mbit / s" - megabit per second; in English Designation "Bit / S" and "Mbit / S", respectively). The higher the width of the video stream, the fact better quality video. For example, for VideoCD format, the width of the video stream is only about 1 Mbps, and for DVD is about 5 Mbps. Of course, subjectively, the difference in quality can not be assessed as fivefold, but objectively it is. And HDTV digital television format uses the width of a video stream of about 10 Mbps. Using the speed of the video stream, it is also very convenient to evaluate the quality of the video when it is transmitted via the Internet. There are two types of streaming width control in video codec - permanent bit rate (eng. Constant Bit Rate, CBR) and variable bitrate (eng. Variable Bit Rate, VBR). The concept of VBR, now very popular, is designed to preserve the quality of video as much as possible, while reducing the total volume of the transmitted video stream. At the same time on fast scenes of movement, the width of the video stream increases, and on slow scenes, where the picture changes slowly, the flow width drops. It is very convenient for buffered video broadcasts and transfer the saved video on computer networks. But for run-down real-time systems and for direct ether (for example, for teleconferences) this is not suitable - in these cases it is necessary to use a constant speed of the video stream.
The aspect ratio of the screen. The ratio of width and height of the frame (ASPECT RATIO) - the most important parameter In any video material. Since 1910, the movies had the aspect ratio of the screen 4: 3 (4 units wide to 3 units in height; sometimes recorded as 1,33: 1 or just 1.33). It was believed that the viewer is more convenient to watch the movie on the screen of such a form. When television appeared, it adopted this ratio and almost all analog television systems (and, therefore, televisions) had the aspect ratio of the screen 4: 3. Computer monitors also inherited television standard of the parties. Although in the 1950s this is the idea of \u200b\u200b4: 3 in the root changed. The fact is that a person's field of view has a ratio by no means 4: 3. After all, a person has 2 eyes located on one horizontal line - consequently, a person's field of view is approaching a 2: 1 ratio. To bring the frame shape to the natural field of vision of a person (and, consequently, to strengthen the perception of the film), a standard 16: 9 (1.78) was introduced, almost corresponding to the so-called "golden section". Digital television Basically, also focuses on the ratio of 16: 9. By the end of the 20th century, after a number of additional studies in this area, even more radical ratios of the frame side began to appear: 1.85, 2.20 and up to 2.35 (almost 21: 9). All this is definitely designed to immerse the viewer into the atmosphere of the video material being viewed.
PCM. Pulse-code modulation (IRM or PCM - PULSE Code Modulation) is used to digitize analog signals before they are transmitted. Almost all kinds of analog data (video, voice, music, telemetry data, virtual worlds) allow the use of ICM modulation. To get at the input of the communication channel (transmitting end), the ICM-modulated signal from the analog, the amplitude of the analog signal is measured at equal intervals. The number of digitized values \u200b\u200bper second (or digitization speed) is multiple with a maximum frequency (Hz) in an analog signal spectrum. The instantaneous measured value of the analog signal is rounded to the nearest level from several predetermined values. This process is called quantization, and the number of levels is always taken into a multiple degree degree, for example, 8, 16, 32 or 64. The level number can be provided accordingly 3, 4, 5 or 6 bits. Thus, at the output of the modulator, a set of bits (0 or 1) is obtained. At the receiving end of the communication channel, the demodulator converts a sequence of bits to pulses with the same quantization level that the modulator used. Next, these pulses are used to restore an analog signal.
 Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference
Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare?
Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare? Social polls work on the Internet
Social polls work on the Internet Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments
Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens
Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens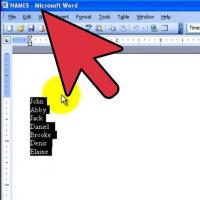 How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips
How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips How to see classmates who retired from friends?
How to see classmates who retired from friends?