UMTS and LTE frequencies in Russia: new generation standards. Allowed and prohibited ranges in radio frequency distribution in the range of 800 MHz
As a result, brief search was formed a list of VHF frequencies, where to me with his walkie-talkie (from the word "in general") and where I can, but in the case of BP, you can and you need. It is clear that in the forbidden bands, almost everything is working closed (encoded), and much and not at all in the radiotelephony mode, so there is nothing to do there - neither on the reception or (especially) to the transfer. In the list, I left only those stripes in which I can theoretically carry with my wagon (for its available ranges forbidden to look for themselves). Which of them specifically sits, I will not write - just do not climb there, and the point. This is the Ministry of Internal Affairs and FAPSI. Discreteness in the frequency bands I also do not specify, for there is no need:
Prohibited frequency ranges:
139.174 - 139.242 MHz
148.000 - 149.000 MHz
149.000 - 149,900 MHz
157.875 MHz
162,7625 - 163,200 MHz
168,500 - 171,150 MHz
169.455 MHz
169.462 MHz
171.150 - 173.000 MHz
173.000 - 174.000 MHz
406.000 - 406.100 MHz
In addition, the band "Cosmos - Earth" ( 136.000 - 137.000 MHz) And the strip "Earth - Cosmos" ( 406,000 – 406.100 MHz, it is exclusively for satellite emergency radio beacons - indexes of disaster points).
Next - Sea Range Channels:
– 156.325
MHz (actually the seabed channel is not, but it falls into it; what happens there - I am xs);
– 156.300
MHz - Service Channel 06 for managing courts. It can be used to communicate between ships and aircraft during search and rescue work, so it is not for figs with its PTT button;
– 156.525
MHz - Special Channel 70 - It is prohibited to work in a radiotelephone mode (used to transmit a digital dialectful call, the Sea analogue of SMS-messages DSC);
– 156.800
MHz - 16th channel, international disaster, security and challenge in marine mobile service for radiotelephony. It is for the search and rescue of the piloted spacecraft. Limited from both sides by two forbidden protective strips (channel 75 - protective strip 156.762 – 156.7875
MHz and Channel 76 - Protective Strip 156.8125 – 156.8375
MHz).
In addition, it should be remembered that part of the seabed channels is not intended for simplex communication, but for duplex ( 1–7, 18–28, 39, 60–66, 78–88 ), and in general: work on the transfer in the maritime range from the shore to whom it has been banned. You will go out in the sea - at least on what (inflatable or chalkboard for surfing) - then you can. True, you can still run away - they will catch, spread, blow away and then be afraid.
Just in case, here are still forbidden frequencies (inaccessible my wages, but still let them lie down, suddenly who need it):
243.000
MHTS
300.200
MHTS
254.000
; 254.685; 380.000; 393.100
MHz is the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation
273.000 – 300.000; 300.000 – 390.000
MHz - Fapese bands, governmental communications, security and defense of the Russian Federation. They include more different, narrow undergrounds with different discrete inclination; There is nothing to do in general.
145.500 MHz is a general gaining frequency for radio amateurs. However, it is possible to work on transmission there only if there is an official RL-call sign and from a registered radio.
It is clear that the list is not complete (Yes, he cannot be complete). In addition, I do not pass for his current accuracy - for, as one literary character said, "Time is flowing, and we are with it." You need to check.
Separate list of emergency frequencies in ranges 2 m and 70 cm for survivalors and anticipants of BP:
145.450 MHz (this is the Ministry of Emergency Situations, Yeah)
145.945 MHz (??? xs)
433.450 MHz (16th channel LPD)
What is 4G (LTE)? According to Wikipedia LTE (literally from English-Termevolution - long-term development, often referred to as 4G LTE) - standard of wireless high-speed data transfer for mobile phones and other terminals working with data (modems, for example). It increases throughput and speed due to the use of another radio interface along with the improvement of the network kernel. The standard was developed by 3GPP (a consortium developing specifications for mobile telephony). Wireless interface LTE is incompatible with 2G and 3G, so it should work on separate frequency. In Russia, three frequency ranges are allocated for LTE - 800, 1800 and 2600 MHz.
LTE FDD and LTE TDD
The LTE standard is two species, the differences between which are quite substantial. FDD - FrequencyDivisionDuplex (frequency variation of the incoming and outgoing channel) TDD - TIMEDIVISIONDUPLEX (temporary separation of the incoming and outgoing channel). Roughly speaking, FDD is a parallel LTE, and the TDD is a serial LTE. For example, with a 20 MHz width of 20 MHz in the FDD LTE, part of the range (15 MHz) is given to download (download), and part (5 MHz) for unloading (UPLOAD). Thus, the channels do not intersect in frequencies, which allows you to work simultaneously and stable for downloading and unloading data. In TDD LTE, the same channel in 20 MHz is completely given and both for download and for unloading, and the data is transmitted to that and the other side alternately, and the priority is still loading. In general, FDD LTE is preferable, because It works faster and more stable.
Frequency Ranges LTE, Band
LTE networks (FDD and TDD) work at different frequencies in different countries. In many countries, several frequency ranges are operated immediately. It is worth noting that not all equipment can work on different "bands", i.e. frequency bands. FDD ranges are numbered from 1 to 31, TDD-ranges from 33 to 44. There are additionally several standards that have not yet been assigned numbers. Specifications on frequency bands are called bands (Band). In Russia and Europe, Band 7, Band 20, Band 3 and Band 38 are mainly used.
In Russia, four frequency bands are used for the 4th generation networks:
As an example, I will give the frequency distribution among the main Russian telecom operators in the LTE2600 range (Band7):
As we see from this scheme, the biline got only 10 MHz. Rostelecom also got only 10 MHz. MTS - 35 MHz in the Moscow region and 10 MHz across the country. And MegaFon and Yota (this is the same holding) got a 65 MHz for two in the Moscow region and 40 MHz throughout Russia! Through Yota, only a megaphone in 4G standard is virtually working in Moscow, in other regions - megaphone and MTS. In the TDD range throughout Russia, in addition to Moscow, television will be operated (space TV, etc.).
Full distribution of operators frequency cellular communication In Russia, see.
4G LTE network in Russia
| Operator | Frequency range (MHz) DW / UP | Channel width (MHz) | Type of duplex | Strip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yota. | 2500-2530 / 2620-2650 | 2x30 | FDD. | band 7. |
| Megaphone | 2530-2540 / 2650-2660 | 2x10 | FDD. | band 7. |
| Megaphone | 2575-2595 | 20 | TDD. | band 38. |
| MTS | 2540-2550 / 2660-2670 | 2x10 | FDD. | band 7. |
| MTS | 2595-2615 | 20 | TDD. | band 38. |
| Beeline | 2550-2560 / 2670-2680 | 2x10 | FDD. | band 7. |
| Tele 2 | 2560-2570 / 2680-2690 | 2x10 | FDD. | band 7. |
| MTS | 1710-1785 / 1805-1880 | 2x75 | FDD. | band 3. |
| Tele 2 | 832-839.5 / 791-798.5 | 2x7.5. | FDD. | band 20. |
| MTS | 839.5-847 / 798.5-806 | 2x7.5. | FDD. | band 20. |
| Megaphone | 847-854.5 / 806-813.5 | 2x7.5. | FDD. | band 20. |
| Beeline | 854.5-862 / 813.5-821 | 2x7.5. | FDD. | band 20. |
The distribution of frequencies among operators by regions of Russia can be found.
For those who are hard to remember the band bands or at hand there is no suitable directory, I recommend the small android application of PFRequence, the screenshot of which is shown below.
Categories LTE.
Subscriber devices are classified by category. The most common categories of the 4th category CAT4 are the most common today. This means that the maximum achieving speed mobile Internet The reception (DOWNLINK or DL) can be 150 Mbps, to transfer (Uplink or UL) - 50 Mbps. It is important to note that this is the maximum achievable speed in ideal conditions - the main of which - you are not far from the tower, besides you, there are no more subscribers anymore, optical transport and others are connected to the base station. The most common categories of subscriber devices are shown in the table.
The table requires some explanations. Here are mentioned "aggregation of carriers" and "additional technologies". I will try to clarify what it is.
Frequency aggregation
Under the word "aggregation" in this case it is understood as the association, i.e. Frequency aggregation is the frequency merging. What does this mean - I will try to explain below.
It is known that the transmission rate depends on the transmission channel width. As we have seen from the table in the previous section, the width of the channel for download, for example, MTS is equal to 10 MHz in the band7 range (except Moscow), the return is also 10 MHz. To increase the download speed, the operator redistributes the frequencies purchased in the ratio of 15 MHz to load and 5 MHz to return. Other providers come in the same way.
One day, someone from the developers came into the head a bright thought - and that if the signal is not transmitted on one carrier frequency, but on several simultaneously. Thus, the transmission / transmission channel is expanding and the speed will theoretically increase significantly. And if another carrier to transmit according to the MIMO 2x2 scheme, we get an additional speed gain. Such a reception scheme was called "Frequency Aggregation". The Internet uses the Internet 4G + or LTE-Advanced (LTE-A).
The table indicates that for cat.9, it is necessary that the transmitter and receiver can be able to transmit and receive a signal on three carrier frequencies (in three bands) simultaneously, the width of each channel should be at least 20 MHz. For CAT.12, it is necessary to additionally to antenna devices were connected according to the MIMO 4x4 scheme, i.e. In fact, you need 4 antennas at the receiving and transmitting side. Mysterious symbols 256Qam mean a specific type of signal modulation that allows you to more tightly pack information. Those who want to familiarize themselves with this topic in more detail can begin to get acquainted with the material in the article in Wikipedia and with the local links.
Categories receiving devices
Frequency aggregation scheme is actively developing by Russian providers, many agreements on the mutual use of frequency ranges are concluded, an antenna farming is reconstructed basic stations. However, there is one problem - on the receiving side, the subscriber must be able to receive a signal at several carrier frequencies at the same time. Not all smartphones, tablets and modems support frequency aggregation and, therefore, cannot work in 4G +.
Since 2016, the documentation for smartphones indicates frequency ranges (bands) and the LTE category in which they know how to work. For example, for the 2017 smartphone, Huawei P10 Plus, among other parameters, is indicated:
In addition, this smartphone has an embedded antenna IMO 4x4 and the corresponding modem that allows you to process signals at once on two carrier frequencies. If your smartphone supports frequency aggregation, then the Setup tab\u003e " mobile network»Will look like this:
If so, your smartphone supports LTE-A.
Thus, the manufacturers of smartphones began to catch up cellular operators. Unfortunately, it is impossible to say the same modem manufacturers. Until now, the most productive modem gives the maximum speeds of 150/50 Mbps, i.e. Belongs cat.4. While this circumstance is not too sad, because Such speeds, if they are achieved in practice, deserve admiration. However, the production of mobile routers seems to begins to catch up with smartphones. Cat.6 routers from Huawei Netgeer (not supported by Russian bands began to appear on the market. So the router Huawei E5787S-33A can be bought on Aliexpress about 10 times to 10 thousand RUB.
It must be said that the real speeds achieved in 4G + mode are far from the claimed, but they are significantly higher than in the simple mode 4G. The author conducted a number of experiments in Moscow, where it is not difficult to find LTE-A (MegaFon operator), with a CAT.12 smartphone, the results of which are shown in the screenshots. The first screenshot - speed for LTE-A (frequency aggregation is enabled), the second screenshot for LTE (frequency aggregation is turned off). I note that for some reason, when performing a screenshot, the 4G + icon disappears plusics. Why - I do not know, when testing, plus was - see screen.
Six measurements were performed for each mode. Speed \u200b\u200bwhen the frequency aggregation turned on is noticeably higher, although not at times. Measurements were carried out near the tower, during the day.
Those who want to experiment with LTE-A
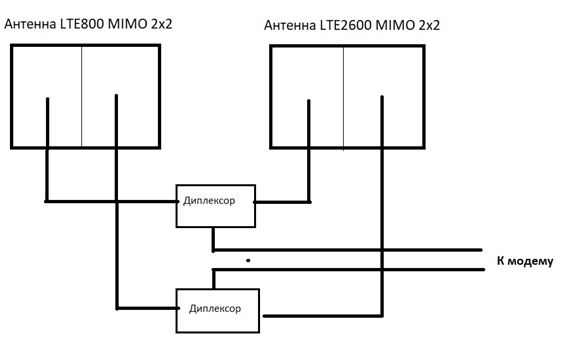
If LTE-A appeared in your area, which you were convinced, measuring the frequencies of the operator you choose (the provider distributes the Internet at two frequencies, for example, LTE800 and LTE2600, i.e. uses a combination of B7 + B20) and your hands will be squealing It is, you can try to use a circuit of two MIMO antennas with diplexers.
After starting the application, go to its settings and check the box at "Deterpix the GMS / UMTS / LTE frequency" item.

Then the main screen should displays the information you are interested in frequency range.

In our case, the smartphone connected to the TELE2 network according to 4G standard at a frequency of 1800 MHz (Band 3).
Quick reply: 800 megahertz u modern processors - this is normal. Moreover, it is a very cool chip, not a device failure. Consumption of electricity in such a "low" mode is minimal. And as soon as all the blatant power is needed in 2-4 Gigahertz - the processor will be issued instantly, or even adds to the nominal frequency another 300-500 MHz. Self adds, by the way.
But why is the processor frequency sometimes decreases to "indecent" 800 megahertz?
What is a CPU, is it a processor?
One of the key devices of any computer (and the smartphone, television, TV and even Wi-Fi Router) - Central processor. This is a microcircuit with a matched box, and in the thickness - in a couple of matches. CPU laptops are less. In phones, the processor area is generally comparable to a copper coin. CPU, by the way, is a standard abbreviation for processor designation, "Central Processor Unit". Russian analogue - CPU, "Central Processor".
Processor task: Calculations. Everything that happens on the PC screen, and everything that is hidden somewhere in the depths of the Iron Box - these are numerical transformations, and no more. Even the letter on the monitor is not just a letter; This is a symbol presented:
- Numeric code
- Color and font with defined digital designation
- Points on the screen that have their own numeric coordinates
Above only an incomplete example of calculations only about one letter with which the CPU works.
What is the frequency of the processor and how to understand this characteristic?
The clock frequency (speaking is simple) - the number of simple digital operations that the processor is capable of performing per second. 2.5 gigahertz \u003d 2 and a half billion of operations by adding, subtraction or multiplication simple numbers. Frequency is one of the many characteristics of the CPU, but far from the only one. The higher the frequency - in principle, more than processor. But - it is "in principle."

The truck engine is at times more powerful and larger than 3-4-cylinder motorcycle motor. But faster and more dynamic is the passenger car. So with the processor frequency
Turn to the example. The more powerful engine of the car - the faster this car? This is not so. Let's say the KAMAZ motor is at times more powerful than the engine of the car. And which of these two cars is faster? True, the smallness with ease will leave behind the multi-torque Makhin despite all the hundreds of Kamaz "horses". So and with frequency - the more powerful, the fact that the computer is faster. But only other things being equal.

Typical processor frequencies are not "growing" for years 10-15. As the Pentium 4 with their 3-3.4 GHz appeared at one time, so these frequencies remained a certain standard for productive systems. A further growth of this characteristic leads only to exorbitant increase in heat dissipation and energy consumption - this is the law. And who needs a computer, refractory electricity like a vacuum cleaner? And with a heat dissipation of a small iron? A laptop that can work without a socket no more than half an hour is also a strange device.
Because processor creators (first of all, from Intel and AMD) work on the enhancement of other CPU characteristics. The number of the smallest "organs" of the processor - transistors increases, simultaneously decreases their size; The delays between individual CPU blocks are categorically reduced - this is progress in computer performance. Banal increase in clock frequency has long exhausted itself. Why is that? Plants need water and sun - but they are good only to certain limits. If you pour the flower with water, then it will die. If you put a rose in the desert - she burns. So the processor frequency is good only to a reasonable limit, and then harmful.
My computer is operating at 800 megahertz - what to do?
Rejoice for progress computer equipment And for the fact that you have a decent modern PC. After all, processors of our time (approximately from 2007-2008) - so powerful devices that most often they simply have nothing to load. Excessive power is needed only at the moments of high computer loading. As a truck does not need hundreds of horsepower, when he transports only the driver without cargo - this is also an extra gigahertz, electricity is eaten (and the battery reserve of the laptop is safely spent).
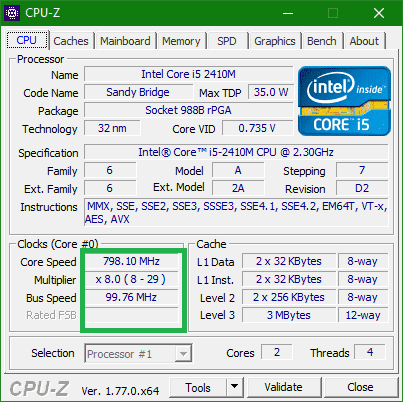
800 megahertz processor (in the screenshot and at all 798.1) is modern technology lowering power consumption.
Processor designers decided to "reset" excess frequencies when they do not need a computer. Did you move away from the keyboard with the mouse? After a minute, the operating system "will understand" that you can turn off redundant resources, and another 50-100 nanoseconds (exactly nano!) It will reduce the frequency of the processor. It took the power (for example, when opening a browser, pages, or even a regular "notebook") - and through the same 50-100 ns frequency jumped from indecently weak 800 MHz to the classic 2-3 gigahertz. Almost instantly.
Electricity saves, fans are spinning quieter, laptops work longer - here are some advantages of an instant lowering clock frequency. Disadvantages of low frequency reduction technology? They are not at all!
Why exactly 800 MHz?
This minimum frequency is convenient and creators of processors, and manufacturers motherboards Together with other computer equipment. The standard 800 megahertz as a low frequency of the computer is like 220 socket volts and 50 of the same sockets.
Moreover, operating systems "More convenient" to work with fairly fast processors. Minimum windows requirements 7 (and modern "dozens") make up the same 800 megahertz. If the CPU "Thread" frequency is up to the lower, OS is able to mistakenly "think" that resources are not enough for its comfortable work - and stop working.
Modern clock frequencies: "Nominal" practically does not happen!
Finally, about the "nominal frequency" of the processor. This characteristic is declared by the manufacturer for each processor model. Let's say modern Intel Core i5 6500 (Skylake Generation) has:
- 4 nuclei;
- 6 megabytes of the third level cache coach;
- built-in video card (graphic kernel) generation HD 530;
- the transistors of the size of 14 nanometers (the less - the better and modern)
- "Basic" clock frequency 3.2 gigahertz (\u003d 3200 MHz);
- heat dissipation - 65 watts (the less - more economical and "colder");
- bunch of magnificent technologies like Intel Speedstep..
It is this technology "floating" frequency called Speed \u200b\u200bSTEP is responsible for lowering the frequency up to 800 megahertz. But even more interesting, that the same technology automatically "accelerates" the processor from the nominal 3.2 up to 3.6 gigahertz, when the computer needs more power.

Processing frequency monitoring: Basic - 3.33 MHz, however this moment intel technology Speedstep increased the frequency to 3.46 MHz. During idle frequency drops to 800 MHz.
Typical SPEED STEP Work Scenarios:
- the processor is not really loaded (it works text editor, audio player and pair of messengers) - the frequency drops to 800 MHz;
- a few tabs are open in the browser, the processor requires more power to 1-2 nuclei of 4 - there is a work on the nominal 3 gigaherts;
- CPU is loaded at full power - you can raise the frequency to 3.6 gigahertz (if 1 kernel is loaded) or at least up to 3.3 GHz (if all 4 kernels are loaded). Yes, energy consumption will increase - but in permissible limits. And the main thing is the complex resource-intensive task will be completed faster (and immediately it will be possible to lower the frequency to the "energy-saving" 800 megagoz).
Let us note again: frequency switching occurs automatically, the user's response is not required. Growth or drop in frequency is an almost instant process: faster than blinking eyes. Moreover, with each fresh generation of processors, the moment of switching frequency decreases - in the near future to lower the delay time from 50-100 nanoseconds up to 25-30 ns.
RESULTS
Frequencies decrease not only in processors, but also in video cards, and in other components computer Systems. Frequent for the sake of electricity savings and decline in heat dissipation. This is a normal procedure that does not just have to cause anxiety - this is a reason to be proud of the scientific and technical progress of mankind and evolution central processors in particular.
Development of standards GSM 900, GSM E900, GSM 1800 He contributed to the improvement of communication channels, but did not solve the problem of Internet access at the level, as a modern person requires.
These standards relate to the second generation (2G) in which EDGE, GPRS protocols were used to transmit data, which made it possible to reach a speed of up to 473.6 kbps - catastrophically low for a modern user.
To date cellular standards One of the most important requirements is determined by the data transfer rate and the purity of the signal. Obviously, it affects the development of the mobile operator market. So at one time in Russia, 3G networks appeared, which won the mass attention of users. And now it is for this reason that the number of people who choose 4g increase.
The feature of the standard UMTS.
The main feature that distinguishes the UMTS standard from GSM is that using WCDMA, HSPA +, HSDPA protocols allows users to gain access to a better mobile Internet. At speeds from 2 to 21 Mbps, you can not only transmit a larger amount of data, but even make video calls.
UMTS covers more than 120 largest Russian cities. This is a standard in which the popular now mobile operators (MTS, Beeline, MegaFon and Skylink) provide a 3G Internet service.
It is no secret that high frequencies are more efficient for data exchange. However, Russia has its own nuances that make it impossible to use in some regions, for example, UMTS frequency of 2100 MHz.
The reason is simple: frequency UMTS 2100.which is actively used for the 3G Internet, the obstacles get sached. This means that the high-quality signal is disturbed not only distances to base stations, but also increased vegetation. In addition, some regions for this frequency are practically closed due to the operation of air defense systems. Thus, several military bases were placed in the southwestern part of the Moscow region, and, accordingly, an unbelled taboo was introduced on the use of this frequency.
In such a situation for the 3G Internet applies UMTS 900.. Waves in this frequency range have a higher penetrating ability. At the same time, at such a frequency, the data transfer rate rarely reaches 10 Mbps. However, if we consider that a few years ago in many cities I could not even think about the Internet coverage, it is not so bad.
At the moment, with a popular UMTS900 show excellent results Huawei E352 and more stable version E352B, as well as E372, E353, E3131, B970B, B260A, E367, E392, E3276.
LTE: What bands will work the standard of the future?
The logical development of UMTS developed in 2008-2010. LTE is a new standard whose goal is to increase the speed of signal processing and bandwidth, and in the technical plan - simplify network architecture and thereby reduce the time when data transfer. In Russia, the LTE network officially launched in 2012.
It is LTE technology that determines the development of a new generation mobile Internet in our country - 4G. This means access to online broadcasts, quick transmission of large-volume files and another advantage of modern Internet.

At the moment, 4G Internet is supported by LTE 800, LTE 1800, LTE 2600 standards, with LTE Cat.4, Cat.5, Cat.6 protocols are used. This allows in theory to obtain the data transfer rate up to 100 Mbps at return and up to 50 Mbps at the reception.
High frequencies LTE. They become an ideal solution for regions where the population density is high enough and where such a data transfer rate is very important. These include, for example, large industrial cities. However, if all operators become only in the range LTE 2600. - the problem with the coating of the radio signal will instantly arise.
Now seizures of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Krasnodar, Novosibirsk, Sochi, Ufa and Samara can take advantage of the 4G technology. In Russia, Yota became one of the first operators who developed the fourth generation of mobile standards. Now such major operators as megaphone and MTS have joined them.
The optimal today is the development LTE 1800.: This frequency is more economical and allows you to enter the market to new companies that offer services. mobile communications. Even cheaper to build networks at a frequency of 800 MHz. Thus, you can predict what exactly LTE 800. and LTE 1800. will be the most popular among operators and, accordingly, we have with you.
Frequencies LTE various mobile operators
- MegaFon: Frequency LTE 742.5-750 MHz / 783.5-791 MHz, 847-854.5 MHz / 806-813,5 MHz, 2530-2540 MHz / 2650-2660 MHz, 2570-2595 MHz (license to Moscow and Moscow region );
- MTS: Frequency LTE 720-727,5 MHz / 761-768,5 MHz, 839.5-847 MHz / 798.5-806 MHz, 1710-1785 MHz / 1805-1880 MHz, 2540-2550 MHz / 2660-2670 MHz, 2595 -2620 MHz (license for Moscow and the Moscow region);
- Beeline: Frequency LTE 735-742.5 MHz / 776-783.5 MHz, 854.5-862 MHz / 813.5-821 MHz, 2550-2560 MHz / 2670-2680 MHz.
Rostelecom: LTE 2560-2570 / 2680-2690 MHz frequency.
Yota: frequencies LTE 2500-2530 / 2630-2650 MHz.
Tele2: Frequencies 791-798.5 / 832 - 839.5 MHz.

Alarm signal at different frequencies
When you fall into the zone of unsure reception of the signal or for a large distance, you are moving away from the base station of your operator, without an additional antenna can not do.

Directional antennas UMTS 900. The signal has an elementary bundle and allow you to significantly increase the level of communication. In this case, not only the Internet connection becomes more stable, but also the quality of voice transmission during telephone conversation. Without an UMTS 2100 antenna, it is not necessary if you want to use the Internet during a trip: due to permanent switching from tower to the tower, the data transfer rate disastrously drops.
Directional antennas LTE. 800 and antennas LTE 1800. – optimal option To gain 4G signal at the corresponding frequencies. These standards have a higher penetrating ability and signal range.
However, the data transfer rate is higher in LTE 2600, thanks to which 80% of users in Moscow have already switched to this standard. And purchase antennas LTE 2600. It is a prerequisite for those who chose 4G LTE 2600 (Megaphone, MTS, Beeline, Rostelecom, Yota) to get the maximum speed of the Internet. AmplifierLTE Signal It will be guaranteed to obtain a stable data transfer at high frequencies.

Solutions from GSM repeater.ru
| LTE 800. | |||
The economic situation and the impossibility of full use of the range of 800 MHz forces the operators to actively develop 4G in the frequency band of 1800 MHz. Moreover, most experts believe that by 2020 to 50% of the total coverage will be provided precisely by LTE 1800. The economic efficiency of this range compared with 2600 MHz is much higher compared to 2600 MHz, and the cost is minimal. About how operators are engaged in "smart refontaming" GSM in LTE in practice, what advantages and disadvantages are, we found out at MTS technical specialists in the Urals.
Currently, in Russia, 4G networks work in 83 regions of 85. And in the overwhelming majority of LTE territories operates in the range of 2600 MHz. And only in 15 regions there are test or commercial networks 4G 1800 MHz (Moscow, St. Petersburg, Leningrad and Tula region, Krasnodar region, Bashkiria, Tatarstan). In the Urals, examples of commercial use of this standard are in the Sverdlovsk and Kurgan regions, KHMAO, YNAO (operator "Motive"), as well as in the Chelyabinsk region (MTS). And if in the case of the "motive" the causes of the use of the GSM spectrum - the company has no license to use frequencies of any 800 MHz, nor 2600 MHz, then the activity of MTS may seem strange. Although strangeness in this case is explained.
Distribution of LTE networks in the world in ranges (analysis of 400 LTE networks, OVUM and GSMA data):
These are the reasons for such activity in the MTS itself. First, the economy. LTE 1800 is much cheaper and more efficient.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe base station operating on the "voice" frequencies of 1800 MHz is four times larger than that of the equipment at 2500-2700 MHz, and the use of this equipment for the development of data networks will allow networks in the shortest possible time, because the same The territory can be covered with fewer base stations. In this case, the LTE-1800 signal enters the closed rooms than the signal of base stations operating in higher ranges. The increased range of radiocrytia allows to provide a high-speed network of 4G distant settlements, car tracks, as well as zones with frequency restrictions, - says Konstantin Kubantsev, Technical Director of the Chelyabinsk branch of MTS.
The aggregation of the spectrum of 1800 and 2600 MHz in each of the two bands of a strip of 10 MHz in each of the two bands allows you to increase peak data rates from 75 Mbps to 150 Mbps, and in the case of an aggregation of three carriers at once - up to 225 Mbps. In April 2015, MTS tests in Bashkortostan at 1800 + 2600 + 800 MHz frequencies with a total bandwidth to 35 MHz demonstrated peak speeds up to 260 Mbps.
According to manufacturers of telecom equipment and companies providing a radio network optimization service based on the geolocation of subscribers, up to 80% of traffic is generated in rooms. This fact definitely gives the advantage of the range of 1800 to 2600 MHz. Losses to penetrate the room for 1800 MHz are significantly lower than for the range of 2600. Traffic will bring better than the range whose penetration is better. The difference between WCDMA2100 and DCS1800 is quite noticeable, but due to an average of more sensitive 3G terminals, the difference is leveled.
The LTE-1800 standard supports up to 90% of LTE devices of leading manufacturers, including Apple, Samsung, HTC, Huawei, LG, Nokia, Sony, ZTE, and others. With its development in Russia, the owners of gadgets can also use 4G-Internet, which do not support other LTE ranges, such as iPhone 5, iPad mini.
If you continue comparison, according to Konstantin Kubanseva, LTE-2600 exacerbates the already tense situation with the search additional objectswhich is required to install equipment. "In cities, there are extremely few buildings to which we can go and get permission to install equipment from the owners. We are constantly faced with failures. There may be no one year to come to negotiations."
As a result, the company decided that the LTE-2600 would be used in the largest cities in the zones of the highest load on Internet traffic. True, in this case, you need to solve issues related to the provision sustainable signal indoors, including using indoor coating.
In other cases, LTE-1800 will be used. Under it will not have to change the existing infrastructure, to invest serious investment in the construction of new base stations and spend a lot of time.
Distribution of income from Russian mobile operators by traffic types:

As a result, the main volume of base stations in the regions after a few years will have to two-band networks - 1800/2600 MHz or LTE800 / 2600 MHz, depending on the presence of frequency resources in each specific region.
The second reason for the growth of interest from MTS is a restriction on the use of a range of 800 MHz. Despite the fact that the operator received the appropriate frequency assignments and is already paying for rent, their implementation is hampered by the operation of missile defense systems, as well as the work of military and civil airfields. Existing rules do not allow using frequencies within a radius of 40 km from airports. With this problem, operators face all over Russia to the same extent.
Questions of full use of the range of 800 MHz are quite acute. We are actively discussing problems with the Ministry of Communications. Just yesterday, within the framework of our communication, Dmitry Alchazov was transferred to the Deputy Minister, who oversees these questions in the government, our offers. He promised to help. Well, while we are trying to work in the conditions that we have now, "says Konstantin Kuban.
On the question of why the first region in the Urals, where the operator began to massively launch LTE-1800, became the Chelyabinsk region, the company responded that a year ago, a complete modernization of the network was completed in the Southern Urals. During this time, Motorola, who worked without a small 10 years, was replaced by Ericsson the most modern generation with widespread support for LTE-1800. There is no old amplifier, switch or switches on the network. At the same time, the capacity of the backbone network was expanded.
All this allowed us to use a 3G / LTE multi-standard network. Moreover, the LTE will be given priority for data transfer. Thus, we will unload our 3G networks, "says Konstantin Kuban.
Under LTE-1800 in the Chelyabinsk region in MTS, the lane was allocated in 5 MHz from those available 15. According to the operator's technical specialists, this band is enough for an existing number of 4G subscribers. In this case, the quality of the 2G network and its capacity will not suffer. In the company in the company I will analyze the possibility of increasing the frequency band up to 10 MHz in each specific location.
As for Shering 4G with Beeline, then in MTS stressed that an agreement relate exclusively to LTE800 / 2600 MHz networks. Access to LTE1800 will have only the company's own subscribers.
Currently, the dual-band network is already working in twenty settlements Chelyabinsk region, in particular, in Zlatoust, Miass, as well as in small cities, such as Ozersk, Troitsk, Satka, Emanzhelinsk, and in the field of summer recreation, residents and guests of the region - on Lake Usildy and others. Also in 2015, the LTE-1800 network will be launched in Chelyabinsk and Magnitogorsk in order to improve the coating of 4G inside buildings.
In the near future, MTS is going to introduce the Single Ran platform (Single Radio Access Network) with the possibility of organizing the coating of all gSM standards, 3G and LTE with one base station.





 Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference
Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare?
Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare? Social polls work on the Internet
Social polls work on the Internet Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments
Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens
Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips
How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips How to see classmates who retired from friends?
How to see classmates who retired from friends?