What is a Dolby Digital decoder on a TV. Dolby Digital Plus VS Dolby Digital: Telling About Technologies Dolby Decoders
49 990 rubles.
AV Receiver ONKYO TX-L50 Black
With DTS decoder. With Dolby Truehd decoder. Dolby Digital Decoder - Dolby Digital Plus. Weight: 4.00 kg. Dimensions 435x70x325 mm.
buy in online store Audovo.credit is possible | possible self-help
video reviewphoto
21 988 rub.

Receiver Yamaha RX-V385 Black
With the number of HDMI inputs 4. DTS decoder. With the power of the front channels 260 W. Standard - 5.1. Dolby Truehd decoder. With a signal-to-noise ratio of 110 dB. Automatic surround sound calibration. Dolby Digital Decoder - Dolby Digital. Weight: 9.30 kg.
buy in online store Player.ru.credit is possible | possible self-help
video reviewphoto
34 000 rubles.

Pioneer VSX-S520 SIL
The minimum reproducible frequency is 10 Hz. With HDMI in front of the front panel. The number of HDMI inputs is 4. The power of the front channels is 80 W. Acoustics connectors - Spring latches. With Dolby Truehd decoder. Dolby Digital Decoder - Dolby Digital. Maximum reproducible frequency 40,000 Hz. Signal ratio / noise 80 dB. Standard - 5.1. With DTS decoder. With an input for iPod. Height: 325 mm. Depth: 435 mm. Weight: 4.00 kg.
buy in online store Pokupaemtut.video reviewphoto
21 990 rubles.

AV receiver Yamaha RX-V385 Black
Dolby Truehd decoder. With the power of the front channels 260 W. Decoder DTS. Automatic surround sound calibration. Dolby Digital Decoder - Dolby Digital. With a signal-to-noise ratio of 110 dB. Standard - 5.1. With the number of HDMI inputs 4. Weight: 9.30 kg.
in online store Audovo.credit is possible | possible self-help
video reviewphoto
17 990 rubles.

AV Receiver Pioneer VSX-323 (Black)
With HDMI in front of the front panel. With support for 1080p (HDMI) signal. Dolby Pro Logic Decoder - Dolby Pro Logic II. Acoustics connectors - screw. With Dolby Truehd decoder. Standard - 5.1. Schemery - semiconductor. With thin administration. With an input for iPod. Dolby Digital Decoder - Dolby Digital Plus. With DTS decoder. With headphone output on the front panel. The number of HDMI inputs - 4. With gilded connectors. With the control of the remote control of other components.
in online store KTV.video reviewphoto
38 812 rub.

AV Receiver Pioneer VSX-S520-B
With the power of the front channels of 80 W. Dolby Truehd decoder. With a maximum reproducible frequency of 40,000 Hz. With the number of HDMI inputs 4. The connectors for acoustics - spring latches. Login for iPod. HDMI in front of the front panel. Dolby Digital Decoder - Dolby Digital. Decoder DTS. With a minimum reproducible 10 Hz frequency. Standard - 5.1. With a signal-to-noise ratio of 80 dB. Height: 325 mm. Depth: 435 mm. Weight: 4.00 kg.
A more modern format of multichannel surround sound, called Dolby Digital, was created in 1992. In the Dolby Digital format, also known as AC-3, there were deficiencies inherent in Dolby Surround. This made it possible to raise the perception of sound in the home theater to a new level.
As can be seen from his name, Dolby Digital is a digital format, that is, it implies a recording of sound information in the form of a sequence of zeros and units. Therefore, Dolby Digital is applicable only when using funds that provide or transmit digital information, such as DVD, laser drives or digital satellite television systems. Dolby Digital phonogram cannot be recorded on a regular VHS magnetic tape (however, in the order of the experiment, it was recorded on S-VHS). Nevertheless, Dolby Digital was chosen as a surround sound format for North American DVD issues, as well as as a standard for high definition television. Dolby Digital can be transmitted and using a digital satellite television system, although in this case, in this case, you will need a special digital Dolby Digital Digital Receiver to receive the audio signal.
In addition to digital Fashion Information encoding, Dolby Digital is distinguished by the fact that in this format there are six discrete (separate) audio channels. Their discreteness makes it possible to eliminate the possibility of unwanted leakage of sound from one channel to another. It should be reminded that more old system Dolby Surround was matrix: it used to fold information from front and rear channels into two channels - right and left - and subsequent separation of them when playing sound. Since in the Dolby Digital system, the signals of different channels are not mixed, it can provide them with almost perfect separation. As a result, Dolby Digital has unprecedented opportunities to accurately locate the sound anywhere in your living room.
In addition, the Dolby Digital is not monophonic, but the "split" environment channel. This means that the left and right speakers can play completely independent signals. Dolby Digital best transmits the idea of \u200b\u200bthe film creators.
When using Dolby Digital, all five channels transmit a complete frequency spectrum of sound signals perceived by human hearing - from the lowest (20 Hz) to the highest (20 kHz). Another advantage of Dolby Digital is the presence of an absolutely independent channel of transmitting additional low-frequency information that allows you to provide the best transmission of sounds that occur during explosions and blows.
Because five discrete broadband channels are used plus a separate NCE channel, Dolby Digital is defined as 5.1-channel format. At the same time 1 after the point (.1) denotes the NCE channel having a limited frequency band.
How does the Dolby Digital system work
Dolby Digital generates a single data stream, in which the signals of every catanal are located one by one, like six railway line wagons. The speed of the digital stream of all six channels is 384 "000 bits per second (384 kbps). To compare, we note that the two channels of the digital sound on the CD form the data stream at a speed of 1" 411 "200 bits / s. In other words, In Dolby Digital, each channel is encoded using ten times less than the number of bits than when recording to a regular CD. As a result of the loss of such a significant amount of information, the Dolby Digital sound quality is worse than that of the CD.
Disadvantages of Dolby Digital format
The disadvantages of the format include a high degree of compression of information (11: 1).
Dolby Digital EX.
Dolby Digital Ex - format with an additional central rear channel obtained on the principle of matrix coding; denotes how 6.1.
Dolby Digital.
Film with digital and analog sound
Dolby Digital. (AC-3, ATSC A / 52) (Did Digital) - spatial sound system developed by Dolby Laboratories, Inc. ("Dolby Labs"), led by dolby, a pioneer of the audio and video industry.
Format standardized Advanced Television Systems Committee, he was assigned the code A / 52, Dolby Digital (DD) is a trademark.
Modern Dolby Digital systems provide six digital sound channels. The left, central and right front channels allow you to accurately determine the position of the sound source on the screen. Separate "separated" left and right rear side channels enhance the feeling of presence, creating volume. And the additional low-frequency channel adds the heat action on the screen.
In the film industry, the Dolby Digital soundtrack is encoded optically directly on the film between perforation holes. Placing a digital audio track on the same medium as the film allows it to coexist together with an analog path without attracting additional data carriers, and also provides absolute synchronicity of the image and sound. In the cinemas of the IMAX system, the sound is written on a separate hard disk and synchronized with a film window using the SMPTE temporary code.
The digital stream at the output of the encoder is a sequence of audioframes (Pack AC-3 FRAME). The information contained in it can be conditionally divided into two parts: the main (main information) and additional (Side Information).
The audio code of the encoder includes six audio blocks. Each audio block contains information about 512 references for each of the encoded signals (Audio 1, Audio 2, ..., Audio N). Due to 50% of the temporary overlap in the audio block for each of the signals, 256 samples of the previous block and 256 new references are included. In six audio blocks of the audio forming, the total number of processed references for each of the input signals will be 512 × 6 \u003d 3072. Note that if the number of encoded sound signals is 5 (3/2 format), then the total number of references is contained in one audio , will be (512 × 5) × 6 \u003d 15360, but taking into account 50% of the temporary overlap here only 15360 ÷ 2 \u003d 7680 new references.
After segmenting the sampling time, the sound signal of each channel is converted to a new set of digital data by means of a modified discrete cosine transformation (SDCP). Segmentation of sound signals with a 50% overlap of samples and their conversion from the time to the frequency domain is performed at the Frequency Domain Transform. Before the orthogonal conversion of sampling of sound signals is weighed by the window function. The latter is presented in the standard A / 52 table.
The conversion of the sample of the audio signal from the time domain can be performed by one long (512-point) or two short (256-point) transformations. In the first case, 256 will be obtained, and in the second, respectively, 128 + 128 MDC coefficients. With a short sample, the MDCP coefficients of both segments containing 128 values \u200b\u200bare combined into one common block by alternating them. In this general unit there will also be 256 MDCP coefficients.
Long transformation is most preferable for signals slowly varying by amplitude over time. It has a better resolution permission. A short conversion provides better time resolution and is used for signals whose amplitudes are rapidly changing over time, for example in the area of \u200b\u200bsound attack. The Block Switch Flags flag (BLKSW Flags) indicates which transformation (long or short) is applied when calculating the MDCP coefficients. The BLOCK Switch Flags parameter is turned on in the output stream of digital data as additional information and is used by a decoder when performing a reverse orthogonal conversion.
At low speeds of digital data transmission in the Dolby AC-3 encoder, use is provided special procedure Combining channel signals (Coupling), allowing you to do with a smaller number of bits when they are encoded.
In the Dolby AC-3 system, each MDCP coefficient is presented in a floating point format with two values: exponential (or order) and mantissa: xD [k] \u003d a [k] × 2 -b [k], where a [k] and b [k] - Mantissa and the order of the K-th conversion coefficient. The order is equal to the number of zeros in front of the first unit of the binary representation of the MDCP coefficient. It is essentially its large-scale coefficient (or normalizing multiplier). For example, if the MDCP XD [k] \u003d 0.158 and its binary representation is recorded as 0.001010000110, then the order (large-scale coefficient) B [k] \u003d 2, and the mantissa is 0.1010000110 in binary or a [k] \u003d 0, 6308 in decimal calculus systems. The MDC coefficient sign is taken into account when coding a mantissa. Before encoding mantisms are normalized (Normalize Mantissas). Exhibitors and Mantissa MDCP coefficients are encoded separately in the ECODE EXPONENT Blocks and Quantisse, Encode Mantissas.
In the bit distribution unit (BIT Allocation), the disguise effect is taken into account. The procedure for selecting bits is a hearing model that allows you to estimate the maximum allowable (threshold) noise level, which is still masked by a useful signal in the coding band, and in accordance with the data of these calculations, it is highlighted with the corresponding number of discharges when coding Mantiss Code of these calculations. All specified calculations are performed in the block, called the psychoacoustic model usually. Each normalized mantissa is quantized with the number of quantization steps corresponding to the number of bits defined in the BIT Allocation module.
The procedure for encoding the MDCP coefficient in the Dolby AC-3 encoder is a number varying from 0 to 24. Therefore, the code word should have at least m \u003d 5 of the discharges (2 5 \u003d 32). The maximum order in the encoder is limited to the value 24.
It is known that if the spectrum of the sound signal is analyzed using a filter bank, each of which has a sufficiently narrow frequency band, then the difference in the signal energy levels between adjacent filters rarely exceeds 12 dB. This circumstance is taken into account when encoding orders. When encoding orders in the Dolby AC-3 encoder, a differential pulse-code modulation is used when the order is not encoded, and the difference between the values \u200b\u200bof the order of adjacent MDCP coefficients. The first value of the order for the signal of each channel in the very first low-frequency analysis band is encoded. This is always a four-bit code word, which corresponds to a range of changes from 0 to 15. The order next up the frequency of the analysis band is defined as the difference between the current and previous values \u200b\u200bof the orders of the corresponding CDCP coefficients. In the Dolby AC-3 encoder, the resolution of the differential pulse-code modulation (discreteness of the change of orders) is limited to -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 when coding. The maximum change in the orders of neighboring MDCP coefficients is ± 2, which corresponds to ± 12 dB.
The differential value of the procedures of the CDCP coefficients are combined into groups. For the grouping procedure, three possible strategies designated in the standard as D15, D25 and D45 are used. In strategy D15 each couple, and in the D45 strategy already each four Differential values \u200b\u200bof orders are represented by one value of the number M in the digital data stream.
Differential values \u200b\u200bof the orders obtained directly from the initial MDCP coefficients in practice do not always give the maximum difference in neighboring coefficients not exceeding the range ± 2, which requires the corresponding tables of the Dolby AC-3 standard. Therefore, before coding requires additional processing of array of orders. With its help, some values \u200b\u200bof orders decrease, but at the same time they change the corresponding values \u200b\u200bof the Mantissa so that zeros appear in their binary representation. After performing this operation, the maximum differential order will no longer exceed the desired value equal to ± 2.
The selection of the strategy (D15, D25 or D45) coding of the CDCP coefficients is a compromise between good frequency resolution, time resolution and the number of bits required for the encoding of the exhibitor. Strategies D15 and D25 can be used to encode signals having an uneven spectrum when the Zcsponent value varies rather quickly from one analysis band to another. If the spectrum of the signal is sufficiently smooth (flat), then the D45 coding strategies are used.
After selecting the code encoding strategy, the Dolby AC-3 encoder combines code words corresponding to the differential values \u200b\u200bof the Exhibitor in groups. For all modes of operation of the encoder sets of numbers M for three adjacent (k, k + 1, k + 2) MDCP coefficients M [K], M, M are grouped and encoded as one seven-lit word according to the rule:
The mantiss change range of MDCP coefficients lies in the range from -1 to + 1. The MDCP coefficient is taken into account when coding the mantissa. The process of Mantiss Quantization MDCP coefficients in Dolby AC-3 has the following features:
- the number of possible quantization steps corresponds to the following row of numbers: 0, 3, 5, 7, 11, 15, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 512, 16384, 65536; Uniform quantization of mantiss;
- with the number of quantization steps, equal to 3, 5, 7, 11 and 15, the so-called symmetric quantization is used, in all other cases - asymmetric;
- with the number of quantization steps, equal to 3, 5 and 11, the codewords of the mantiss are combined into groups. With three quantization steps, three code words corresponding to the three mantiss values \u200b\u200bare encoded by one five-bed code word. At five feet of quantization, the three codewords of mantiss are grouped and encoded by one seven-bit codes. With 11 quantization steps, two codewords of mantiss are grouped and encoded by one seminy code word; In other cases, there is no grouping procedures.
With symmetrical quantization, instead of the quantized mantiss values, their indexes specified by the corresponding table are included in the digital thread. For example, if the number of quantization steps is 3, and the Mantissa value lies in the range from -1 to -1/3, then the value of -2/3 will be transmitted to the decoder, and it will correspond to the MC \u003d 0 index. If the Mantissa value lies In the range from -1/3 to +1/3, the decoder is transmitted to zero, and the MC \u003d 1. Index is encoded, and finally, if the Mantissa value is in the range from +1/3 to +1, the value is transmitted to the decoder. equal to +2/3, and the corresponding table index Mc \u003d 2. Similarly, in the form of tables, the values \u200b\u200bof the mantiss values \u200b\u200bare set and the corresponding indices for the number of quantization steps of equal, respectively, 5, 7, 11 and 15. Such a quantization method allows to reduce the number required bits. For all other quantization steps (32, 64, ..., 65536), indices are encoded, but Mantissa themselves MDCP coefficients.
The next step is coding and packaging into a digital stream of table indexes of quantized mantiss values. With symmetric quantization to reduce the bits required to encode indexes, additionally is additionally used. For example, with the number of quantization steps 7, the Mantissa index varies from 0 to 6. To coding this number of numbers, 3 bits are required. At 11 quantization steps, the Mantissa table lies in the range from 0 to 10, and at 15 quantization steps it is already in the range from 0 to 14. In this case, the number of bits required for the encoding of each of them is respectively 4 or 5. Grouping of table indexes allows Reduce the number of bits required for their encoding at 3, 5 and 11 quantization steps. With 3 and 5 quantization steps, three tables of Mantissa, and at 11 quantization steps, two tables of Mantissa are encoded by one code word according to the following rules:
Group_code \u003d 9mc [a] + 3mc [b] + Mc [C]; Group_code \u003d 25mc [a] + 5mc [b] + Mc [C]; Group_code \u003d 11mc [a] + mc [b],
where group_code, group_code and group_code are codewords of groups of table indexes of mantiss, respectively at 3, 5, 11 quantization steps; MC [A], MC [B], MC [C] - Mantiss's table indexes of MDCP coefficients with numbers A, B and C. So, with three steps of quantization of the mantiss (n \u003d 3), the code word of the group consisting of three indices will contain 5 bits, therefore, 5 ÷ 3 \u003d 1.67 bits will be spent on the coding of each mantissa in this case. At n \u003d 5, the codeword of the Mantiss Group will be presented by a seven-bit number, and the coding of each mantissa will require 7 ÷ 3 \u003d 2.33 bits. And finally, with n \u003d 11, 7 ÷ 2 \u003d 3.5 bits will be required to coding each mantissa, and at n \u003d 15 - 4 bits, etc.
The encoder defines the length of the code word code of each mantissa or the table index corresponding to it, after which the Mantissa is unpackled by a special procedure.
When working in the sound combining mode, the encoder combines high-frequency parts of the source signals in a specific frequency band in one common signal and generates additionally the so-called coordinates of the combination. The latter will be used by the decoder to restore the energy ratios of the high-frequency parts of the spectrum of each source signal subjected to the combination procedure. After decoding, the combined parts in each of the recovered signals will have the same spectral composition and differ only in the level.
The encoder generates a common signal by simply adding the MDCP coefficients of the combined signals. At the same time, the CDMA coefficients from the 37th to 252th are grouped into 18 subbands (the so-called union bands) of 12 coefficients in each such subband. The lower and upper frequency boundaries of the combination bands are set by the user. The coordinates of the union are calculated for each unification of the subband signal. They are the ratio of maximum CDCP coefficients of each integrated signal and the total signal in the union subband. Further, coordinates are converted to the format of floating semicolons and are included in the output data flow as additional information. The total (combined) signal is encoded in the same way as the signal of independent channels.
Dolby AC-3 System Decoder
Dolby AC-3 decoder receives the procedures of the MDCP coefficients in coded and packed form. To unpack them and decode, you need to have additional information on the number of transmitted exponentials in the signal of each channel and the strategy of their coding (D15, D25, D45) used in the encoder. The decoding process of orders is carried out in the Decode Exponent decoding unit. After decoding the orders, the unpacking procedure, decafing and denormization of Mantiss MDCP coefficients (Dequantize, Denormalize Mantissas) is performed. For its execution, the parameters of the psychoacoustic model are used, the parameters that define the distribution of bits in the encoder, as well as the restoration of the values \u200b\u200bof the CDCP coefficients. The dignification operation of the Mantissa is made through the shifts of the category of the mantissa code word to the right. In this case, the number of shifts is determined by the order of the corresponding CDCP coefficient. If the encoder has been used in the encoder to combine a series of channels, then, obviously, the decoder must perform the reverse operation (de-coupling) using the transmitted decoder in the data field for more information Connection coordinate values. In the inverse orthogonal IDCP (Inverse Transform) block (Inverse Transform), an inverse conversion is carried out reconstructed in the signal decoder into a temporary area.
| SI | Bsi. | Audio Block 0 | Audio Block 1. | Audio Block 2. | Audio Block 3. | Audio Block 4. | Audio Block 5. | AUX DATA. | CRC. |
|---|
Scheme 1. Data Dolby AC-3 Data Audio Structure.
| Block Switch Flags. | DITHER FLAGS. | Dynamic Range Control | Coupling Strategy. | Coupling Coordinates. | EXPONENT STRATEGY | Exponent. | Bit Allocation Parametrs. | Mantissas. |
|---|
Scheme 2. Structure of Dolby AC-3 audio block data.
The structure of the audio data in the Dolby AC-3 standard is shown in the chart 1. The audioframe header (Header) field contains SI synchronization information (Syncronizator Information) and BSI data configuration information (bit stream information).
The Si data field includes a synchronous (0000 1011 0111 0111, or OB77H), noise-resistant encoding bits (CRC code), sampling frequency and audio-size size. The audioframe of the Dolby AC-3 system includes two 16-bit words of the CRC code, the first of them should be at the beginning of each frame after the word synchronization, and the second - at its end. The BSI data field contains information about the configuration of the digital data stream, for example, such as the type of service, the mode of operation of the encoder (that is, the number of encoded signals or the type of sound format), the absolute acoustic signal level of each channel, information about language, about time and other.
The structure of the audio block data is shown in circuit 2.One includes the following bits fields: Block Switch Flags - the parameter of the orthogonal conversion length; DITHER FLAGS - a sign of the presence of additional noise; Dynamic Range Control - Dynamic Range Control Data Transmitted Signals; Coupling Strategy - information about combining signals (what channel signals are combined and starting at what frequency); Coupling Coordinats - coordinates of combining for the signal of each channel; EXPONENT STRATEGY is the selected strategy for encoding orders; Exponents - code words CDCP coefficients; Bit Allocation Paramets - Psychoacoustic model parameters; Mantissas - Mantiss codes of MDCP coefficients.
Technologies Dolby Digital.
Dolby Digital EX.
Ex is a prefix used to designate Dolby Digital Sound Sound Channels: Two frontal, central, low-frequency, rear volumetric sound and two side volumetric sound.
Dolby Digital Surround-EX
Dolby Digital Surround-EX adds the soundtrack the third canal volume sound. The idea belongs to the sound engineers of the studio Skywalker Sound. Technology is developed in conjunction with Dolby Laboratories and Lucasfilm Thx.
Dolby Digital Live.
Dolby Digital Live (DDL) is a multichannel (5.1) audio coding technology in real-time AC3 format proposed by Dolby Technologies. Designed to transmit multichannel sound from games and other applications to the receiver over the S / PDIF interface (optical or coaxial).
Its use allows you to get rid of restrictions, because of which only ready-made on digital interfaces can be transmitted (i.e., the multichannel tracks are called in the AC3 or DTS format), which are usually sound accompanying films), and in games the possibilities of digital output were limited to ordinary stereo sound. (For full-fledged 5.1 in games in such cases, a three-wire analog connection is required if it is, of course, possibly.)
The principled and unrelated disadvantage of DDL technology is a certain loss of sound quality from compressing it in AC3 format (comparable to the transition from CD-Audio to mp3 with a high bit rate) that, however, is completely uncritical for the main intended use.
Currently, this technology is found primarily in motherboardsEquipped with REALTEK Alc882D, Alc888DD and ALC888H codecs, as well as with some C-Media Codecs. Such cards can be found on the phrases "AC3 ENCODE" or the actual "Dolby Digital Live" in product descriptions.
Also, this technology begins to be embedded in laptops, where in the conditions of a place deficiency for "unnecessary" analog connectors, the greatest advantages are one connector.
From individual audio cards with support for this technology, Terratec Aureon 7.1 is worth noting, and in popular sound cards of the Creative family X-FI Support DDL is missing, but (according to unofficial information) in the future it is not excluded its introduction by the back of the new version of the drivers.
For 2010, the following models with support for this technology can be distinguished from the Creative X-Fi family: Creative X-Fi Titanium 7.1, Creative X-Fi Titanium Fatal1ty Pro 7.1, Creative X-Fi Titanium Fatal1ty CHAMPION 7.1
Dolby Digital Plus.
MIPS Technologies and Dolby Laboratories presented a new audio building technology for devices that support video playback and high-definition audio, such as HD DVD and Blu-Ray players. The audio technology was named Dolby Digital Plus and will be able to be used in MIPS32 microprocessor cores.
Also Dolby Digital Plus will improve the quality of sound content recording on HD DVD and Blu-Ray Disk Media, thanks to supporting even more channels than it was possible with Dolby Digital. Companies will provide SOC-solutions to developers (System-On-Chip) of the type of integrated Dolby Digital Plus codec based on MIPS kernel.
Features:
- Multichannel sound with independent channels
- Supported to 7.1 channels * and the ability to have multiple audio programs in one thread
- Dolby Digital output output for compatibility with old devices
- Maximum stream speed up to 6 Mbps
- Bitrate from 3 Mbps on HD DVD and up to 1.7 MBPs on Blu-ray Disc
- HDMI is supported
- In one stream may contain material in different languages.
- New features when encoding for audio professionals
- Preservation high Quality On more efficient data transfer rates (200 kbps for 5.1 channels)
"Dolby Digital Plus supports more than 8 audio channels. HD DVD and Blu-Ray Disc standards now limit this number up to 8.
Dolby Truehd.
Dolby Truehd is one of the first two formats of uncompressed sound (compressed without loss), available only for optical HD players. Despite the fact that the Dolby TrueHD codec is optional, this format is widely supported by players and Blu-ray discs (much more than DD +, which is often absent on Blu-Ray disks). Dolby TrueHD uses Meridian Lossless Packing (MLP) compression algorithm. Dolby TrueHD digital stream can accommodate up to 14 separate audio channels, but in practice it works from 6 (5.1) or 8 (7.1) channels. The Dolby TrueHD standard supports a bit of 24 bits and sampling frequency up to 192 kHz (for maximum uncompressed 63 Mbps), but for Blu-ray currently available 8 channels from 24 bits and 96 kHz (or alternatively, 6 channels with 24 bits and 192 kHz) for the maximum compressed flux of 18 Mbps. Search for available Dolby TrueHD films on Blu-ray disks showed that today it is possible to obtain only half: 6 channels with a sampling frequency of 96 kHz and a depth of 24 bits (which corresponds to an uncompatted thread 13.5 Mbps and compressed 9 Mbps With, for example, on disks with the concerts of the Dave Matthews and Tim Reynolds group, which received excellent points for quality on the Cinema Squid website).
The Dolby TrueHD track feature for Blu-ray films is as follows:
- Audio codec - Dolby Truehd.
- Channels (sound circuit) are almost always 5.1, it is very rare 6.1 and 7.1.
- The audio clarity data is often missing, but usually the values \u200b\u200bare as follows: 16 bits at a frequency of 48 kHz or 24 bits at a frequency of 48 kHz; For some concert discs, these values \u200b\u200bare 24 bits at a frequency of 96 kHz.
- The flow value is usually absent, but is usually 4,608 kbps (4.5 Mbps, which corresponds to six channels at a frequency of 48 kHz and 16 bits). The highest meaning that we saw on Blu-ray commercial concert disks was 9.0 Mbps, which corresponds to six channels at a frequency of 96 kHz and 24 bits. The maximum value for Blu-ray is 18 Mbps.
Dolby technologies on optical media
| HD DVD. | Blu-ray Disc | DVD-Video. | DVD-Audio. | Lazidisk | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codec | Hardware support | Number of channels (max.) | Max. Flood velocity | Hardware support | Number of channels (max.) | Max. Flood velocity | Hardware support | Number of channels (max.) | Max. Flood velocity | Hardware support | Number of channels (max.) | Max. Flood velocity | Hardware support | Number of channels (max.) | Max. Flood velocity |
| Dolby Digital. | Before | 5.1 | 504 kbps | Before | 5.1 | 640 kbps | Before | 5.1 | 448 kbps | In addition to video compatibility with conventional DVD players | 5.1 | 448 kbps | Additionally | 5.1 | 384 Kbit / s |
| Dolby Digital Plus. | 7.1 | 3 Mbps | Additionally | 7.1 | 1.7 Mbps | Not used | |||||||||
| Dolby Truehd. | 8 | 18 Mbps | 8 | 18 Mbps | |||||||||||
- The sound of Dolby Digital first appeared in cinemas in 1992 in the film "Batman returns".
- The impetus for the development of Dolby Digital Surround-EX served the need for a sound picture of the span of a spacecraft over the auditorium in the film "Star Wars. Episode I. Hidden threat. "
see also
- Dolby Atmos.
- Immsound
- Digital sound
Literature
- Digital Audio Compression Standart (AC-3) /Doc.a/52, 1995-12-20
- I. A. Aldrina, E. I. Vologodin, A. P. Efimov, etc. Electroacistics and sound broadcasting: a textbook for universities / edited by Yu. A Kovagin. - M.: Hot Line-Telecom, Radio and Communication, 2007.- 872 p.: Il.
Links
| Compression audio (comparison formats) | |
|---|---|
| Codecs | |
| Speech / voice | |
| Without loss | |
| Standards and formats |
|
| Mediconteners | |
|---|---|
| Video / audio | |
| Audio | |
| Graphic formats (compression) | |
| Raster | |
| Vector | |
| Complex | |
| Broadcast video formats | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A television | |||||||||||
| Analog |
|
||||||||||
| Digital |
| ||||||||||
Dolby Digital is an inserted decoding device that creates six-channel sound support of satellite digital broadcast programs or multimedia video content recorded on a digital video tape, a digital audio tape or from a video server.
What is a Dolby Digital decoder on a TV
Dolby Digital decoder is represented as a system of perfectly clean sound. Channels (left - central and right - frontal) allow you to establish the location of the sound source. Separately distributed channels carries the viewer covering and pouring with sounds with sounds.

Why do you need Dolby Digital decoder in tv
The Dolby Digital processor has become a continuation of the Dolby multichannel sound encoding system previously implemented. In the absence of noise reduction signal, Dolby works on the principle of noise reduction, and in the case of its presence, it allows a powerful productive audio signal to interrupt the noise of lower level. That is why this technology applies a psychoacoustic hearing model.
Attention! In the event that the signal fills the separate part of the spectrum, noise reductions Dolby reduces the noise level in certain parts of the spectrum in which there is no productive signal, making it insignificant. This is because the sound signal hides only the nearest frequency noise.

Dolby Digital Prefix Clamps Many other reserves:
- increases device resources, guarantees high accuracy sound in 5.1 format;
- creates the correct stereoscopic sound 5.1 with the use of various stereo handphones;
- increases the sound distance when using speakers for musical sound reproduction;
- creates a spatial perception when using stereo handlers.
- enhances low sound frequency;
- strengthens high frequency and improves the quality of sounding music by correcting the effects of high-frequency pulses;
- adds significant mono sound reproduction;
- controls the sound level by maintaining a stable volume level.
How to use Dolby Digital decoder
In order to configure the system device, the TV must support standard settings.

At the same time, video recording must also correspond to DD + format. As a rule, it is used in all BluRay and on separate commercial channels.
To transfer the Dolby Digital Plus video content from the video player to the TV, and then on the equipment of the multimedia complex will be required standard hDMI cable 1.3.
Q. What is DTS?
A. The most accurate technologies of the surround sound. DTS Digital Surround is a decoding coding system, representing six (5.1) 20-digit sounds of quality wizard. In the process of coding, the DTS algorithm records 6 channels of 20-bit digital audio information on the space, which was previously occupied by only 2 channels of the 16-bit linear PCM (format of a conventional CD). In the process of reproducing the DTS decoder, the initial 6 20-bit channels restores. Each of these 6 channels for sound quality exceeds a 16-bit linear PCM format of ordinary CDs.
Q. How does DTS format relate to Dolby Digital (AC-3)?
A. DTS master quality format for laser drives (LD), CDs (CDs) and DVD uses a compression ratio four times smaller than Dolby Digital and as a result surpasses its sound quality.
Q. What equipment is needed to play DTS?
A. 5.1 Channel electronics with DTS decoder and 5.1 acoustics, i.e., a system with 6 separate electronic channels and speaker systems: front left and right, rear left and right, central channel and ".1" low-frequency channel for special effects. Electronics can consist of any 5.1 channel surround channel with a built-in DTS-decoding circuit or an external DTS decoder, plus 6 amplifier channels (or 5 channels and channels and active subwoofer). Since the advanced Motorola's advanced chip, which can be easily embedded in any multichannel apparatus, all new models (including integrated receivers) may contain both DTS and Dolby Digital.
A popular analogy is AM and FM radio broadcasts. You cannot accept AM signals on the FM receiver and vice versa. However, to expand the choice of choice, your radio can be equipped with both technologies, so you can choose any movement of the switch. And while AM \u200b\u200bbroadcasting low quality has always found practical use, success FM broadcasting is a clear sign of the existence of a high-quality sound.
Q. What is the RF demodulator?
A. In cases where the sound on the Laser Video Discs (LD) is recorded in Dolby Digital format, an additional RF demodulator device is required (embedded in the decoder or external) so that the decoder receives a digital signal ready for decoding. Such a problem arose due to the fact that the Dolby Digital format developers had to be "squeezed" into the LD soundtrack format, approved long before Dolby Digital. For DVD video disks this problem does not exist.
Q. SP / DIF Specification.
A. SP / DIF - (Sony and Philips Digital Interconnect Format) Digital format, approved by IEC958 1989-03, transmits in a sequential code sound information On the left and right channel from speed up to 48 kbps \\ s with the size of words up to 24 bits. SP-DIF Receivers (usually this DAC) are automatically configured on the transmission rate and bit. Electrically is a 0.5 volt signal transmitted by a coaxial 75 RCA Omo Cable, or the Toslink optical cable. The output of the usual CD player fits into the SP / DIF standard. Read more (links http://www.hut.fi/misc/electronics/docs/audio/spdif.html. or http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/srg/han/docs/sp-dif.txt)
Q. Is it true that people really hear all these differences?
A. At least they are confident about that.
Q. Why are the opinions of listeners about the quality of sound diverge?
A. There are at least three approaches to the assessment, which is "perfect sound" and most of the listeners refer themselves to one of the following three groups:
1.
"It should sound like real living music." These people know how the performer's live voice sounds, as one or another tool without an amplifier sounds, they remember how the orchestra sounds in the orchestra. Such people want absolutely accurate playback.
2.
"It should sound as the sound engineer thought it." The sound engineer listened to the exceptionally good sound equipment, which comes from microphones and mixed them as it considered it right. This is perhaps not as in reality, but exactly how he wanted to be better.
3.
"It should deliver the greatest pleasure." It does not matter, good or bad it sounds, it does not matter what sound engineer wanted, but if on some audio equipment listening to me brings pleasure, then it is the best.
Based on this, it is clear that no system will satisfy at once. Someone wants to hear a deep bass, another that men's voices sounded like a man's, the third, so that the violins sound like violins. Audio systems rarely do everything equally well. This is especially true of acoustics. It will be absolutely correct to choose columns on your personal taste. Of great importance is addictive to the sound of that equipment that you already have. Another reason why most people cannot determine the difference in sound: as long as you do not listen to the system that is able to restore the surround sound space on the stereo signal, you may never understand what is possible. Some records are very good quality When playing on good hardware, it is possible to completely clear the place of a tool. However, this can not be heard on not enough good equipment or record. Finally, some simply cannot hear the difference. Not because the deaf, and simply incredited ear or do not know what exactly to listen, it is possible to have some deviations in the hearing (for example, the age reduction of sensitivity to high frequencies or hearing damage from very hands-free music on rock concerts, etc. ).
Q. Is it true that the type of column cables affects the sound?
A. Timplel Terminals: Cables are wires with connectors attached to them. Wires are usually stranded, concluded in the screen braid and insulating material. Cables can make noise into the transmitted signal, act as a filter (and thus change the frequency characteristic of the system), bring clocks due to incorrect connections. It is definitely that different cables "sound" in different ways due to differences in ohmic resistance, intermetrical containers, different connectors. The effect of exotic curls of the conductors is not sufficiently studied. In general, these effects (not counting resistance) should not be noticeable, although many listeners note a significant difference in sounding on different cables. On each specific system, this effect is specific and the only way to achieve a better sound is a sample method. Connectors need to be attached to the column with great strength, because The input resistance of the speakers in itself is very low and the connector resistance of the connector in just 1 ohm will significantly affect the power given by the column.
Q. What are the column cables and what do they differ?
A. There is a wide range of column wires worth from $ 0.2 to $ 300 per foot. Used material - from copper to silver. Besedless copper on the sound is not different from copper simple, and if you hear the difference, then for some other reason. Resistance cable is a very significant characteristic. The higher the resistance, the greater the effect of the cable has on the sound. Copper Copper 1.7 micro / cm, serabra - 1.6 micro / cm, gold - 2.4. Gold is not oxidized, so contacts do not need to be cleaned periodically, silver is oxidized, but its oxide film is also well conducted. Copper is oxidized and its oxide is a isolator, so it is not suitable for connectors. The cable is shorter and thicker, the less its resistance, capacity, inductance, the less because of it distortion.
Q. What are the connectors for the speakers better?
A. The worst connectors are spring contacts. Clips under the screw are much better. Gold-plated "blades with a slot" or spidestees on audio standards are inexpensive with a very stable mehanic contact and minimal resistance. Gold-plated bananas are also very good for columns, and although more than spidestees, they provide a large area of \u200b\u200bcontact and convenience when reconfiguring the system. Gold-plated connectors are always better than connectors with any other surface for two reasons: firstly gold does not corrode even under the influence of active chemicals, and secondly, it is a very soft metal and, being strongly compressed between two plates, it fills slightly Available always scratches and cracks, increasing contact area.
Q. What can be said about inter-block connections, for example, between the tuner and the amplifier?
A. Inter-block connections transmit a significantly weaker signal than column cables. Here is the voltage range from -2B to + 2V with a current to several microampers (for comparison in column cables, the voltage from -70B to + 70V with a current to several amperes). Inter-block connections may be conventional RCA (nonbalans) and balance sheets. Most home audio equipment uses conventional RCA connections. Better gold-plated, like Vampire Wire. Unbalanced cables differ in shape, materials and price. Cheap have one central dwelling and on-screen braid. Average (at a price) have a central core of two conductors of the twisted twisted pair and tightened into the braid. Dear can be diverse and from different materials (for example, stranded silver wire with rubber aggregate). Balanced compounds in audio systems are used to get rid of low-frequency buzz and other interference caused by power sources. On the unbalanced lines, the low-frequency buzz is caused by the uncondition of the source and the receiver or the difference between the potentials of the Earth in the system components with different power sources. Balanced connections help to avoid interference. Transmit 2 signals in antiphase. The junction can be performed on active elements or on a transformer. The other methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Cables have an XLR connector, giving a good mechanical connection. Balance cables have three conductor: two for a signal and one for the screen. It should be used at lengths of more than 4 meters, when installing professional equipment on courts. For most systems, the most important aspect is the mechanical reliability between the connector and the wire. There are mono objective reasons, due to which cables can be distorted into the signal. These are all the same resistance and intermaro capacity, screening quality, twisted pair quality in the balance cable.
Q. Are there any difference between digital cables?
A. There are three types of digital cables from transport to a DAC or audio processor: coaxial, optical plastic (Toslink) and fiberglass (AT & T ST). Theoretically, they all have to "sound" is absolutely the same (bits in the bit). However, there are people who claim to hear the difference, and most of them prefer fiberglass.
Q. What should I listen to when buying acoustics?
A. The most important thing is to listen to her things that you know. The seller will per-withdraw you such entries that emphasize the good sides of the AU. Therefore, do not be lazy to grab a few of your CDs. Do not waste time, switching to two dozen things every 3 seconds. If the budget allows you to choose, ask the dealer to choose a couple of different speakers suitable to the size of the room and your tastes and listen each. When you stop in your choice, spend another half an hour on listening to make sure that it's not for nothing in vain money. Very good to listen to the record of human speech. Most people are cobled out when the human voice sounds haired. When listening to the musical instrument of the solo or in a small ensemble, make sure that the sound from it is such as it should be. Most people have heard the piano "live", so the recording of the piano is very indicative. Blues, jazz or light music with simple tools And women's vocals are also a good dough for acoustics. Try something simple and quiet to hear possible noises, and complex, with a variety of tools entering simultaneously, make sure that the system will work correctly on large loads. Sellers tend to offer to listen to things that always sound wonderful. Ask to put your favorite record in order to say to yourself: "But I still haven't heard of this tool."
Q. What to pay attention to when comparing acoustic systems?
A. When you compare the sound of two different pairs of columns, try to carefully set the exact same volume on both. This will not necessarily be on the same position of the volume control. The ear can distinguish between the difference even at 0.5 dB. The first and most importantly - the sound should be natural. If you are listening to vocals, close your eyes and imagine that the ilemale is with you in the same room. Sounds natural? The same applies to the tools. They should also sound like in reality. The very first to your impression should be: "What wonderful sound". If your reaction becomes: "How many details!", Most likely these speakers will soon become annoying you. If you immediately note a powerful bass to yourself, then the system is re-loaded low. The most common start-up error is the purchase of speakers with a very powerful bass, because their sound "is impressive." After a short time, you tire from "shocks on your head." And low and high frequencies are very important, but when listening to nothing should be allocated or dominated. Sit and listen. Check to hear each tool separately and all the work as a whole, composed of individual parts so that it does not feel that some kind of tool makes your attention to yourself. Check how the thing sounds on high volume and at low. Some speakers are good "play" if the sound is quiet and "chopping" on the high volume. Others, on the contrary, "hoarse" at a very low volume and work well if the sound is loud. Permissible, and sometimes it is desirable to estimate the naturalness to move with stereo on mono. Mono is a good test for both the room and the speakers. The sowing image must be stably in the center and do not move depending on the volume or on the signal frequency. If mono is not withstanding, then the stereo is unlikely to get good. Large sizes are capable of reproduced low frequencies on high volume, but this does not mean that small sizes cannot "play" bass. They just can't do it loud. Good speakers can "restore the scene", having some tools on the left, others in the center, third on the right. On bad speakers, it is much more complicated to determine the tools.
Q. Why do you need a subwoofer? How much do they need - one or two?
A. First, it is needed to add basses to systems where they are missing. And secondly, to translate low frequencies to a separate loudspeaker and thereby reduce the level of intermoduding distortions caused by nonlinear mixing of different frequency signals. Thirdly, the subwoofer will increase the total power of your speaker system. To improve the sound of a good system, the subwoofer should be built into it "softly" without bursts and failures in the CHX, expanding the existing lower range. Most subwoofers have a crossover, which is located between the amplifier and columns and separates the lower frequencies on the subwoofer, and higher on the column. This separation can improve the system, may not affect the sound, and may also damage. Most small speakers have an increase in low frequencies to compensate for the decline in the characteristics due to small sizes. Completely made subwoofer will improve the sound of small speakers. Even for large acoustic systems, the subwoofer can benefit when it is properly configured. However, the better the original system, the greater the likelihood that an additional subwoofer can damage. For the human ear, low frequencies are not determined towards, so someone can say that one subwoofer is enough. That's right, but not quite. Some believe that two subwoofers need to correctly reproduce the stereo picture, despite the fact that there are few information in low frequencies. Another reason - in addition to very low, the subwoofer reproduces the frequencies of up to 100 Hz, and this is the frequency with a distinguishable direction, unless, of course, the subwoofers are located at least in the meter of each other. Finally, despite the fact that the records of musical instruments rarely have frequencies below 50Hz, almost always there is a low-frequency acoustic noise, which can add a feeling of spatiality if the subwoofers place far from each other.
Q. How to connect subwoofer to stereo system?
A. Many subwoofers (active) have their own amplifier and crossover. These are connected immediately to the output of the preamp. Passive subwoofers can be connected in parallel to the main columns or separate bass amplifier with the crossover. Use the delivery manual from the delivery kit.
Q. What is the receiver?
A. This is a tuner, amplifier and preamp in one case. Typically, the receiver has inputs for a CD player, cassette deck, vinyl turntable and 1-2 more additional inputs. It has a switch of inputs, volume controls and timbre, as well as a pair of or more speakers.
Q. What is a tuner?
A. The tuner is a radio receiver to which the columns cannot be attached directly. Sometimes the receiver in a higher quality tuner than in the receiver. All tuners take FM range, and some are also am. The tuner signal is required to be strengthened.
Q. What is DAT format?
A. To date, this is the most common professional digital format of 2 two-haired magnetic tape. On the Dat Tape (Digital Audio Tape) placed 2 hours of recording with a resolution and dynamic range, as on CD. The recording can be carried out at a speed of 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz (for CD) and 48 kHz (DAT standard). Dat cassette looks like VHS cassette.
Q. What is Dolby B, C, S, HX Pro and DBX?
A. Dolby B, C, S and DBX are systems that increase the signal / noise ratio of magnetic records. All work approximately the same: reduce the dynamic range of the signal when recording and expanded when playing. Dolby B works mainly at high frequencies, increasing their amplitude when recording and reducing the amplitude during playback, while the high-frequency noise actually decreases. Recorded Dolby B Cassette can be listened to the usual tape recorder without Dolby B processing, but the sound will be too bright, which will have to compensate for the tone regulator. With Dolby, processing is achieved more (8-10 dB) than Dolby b Noise reduction due to the use of a larger frequency range and volume change level. Playing such a tape on a conventional tape recorder without Dolby with sounds sufficiently unpleasant for most people. Some believe that the ribbies recorded in Dolby are best sounded only on the deck on which they were recorded. Dolby S is operating at an even larger frequency range than Dolby C and reaches even greater noise reduction. The advantages of this system are: 1. Many believe that the use of Dolby S gives great proximity to the original rather than Dolby C, 2. Dolby S entries are not so terrible when playing on Decah Dolby B, 3. Cassette with Dolby S Recording is not so sensitive with changing Type deck. DBX is similar to Dolby B, C and S, but uses compression at all frequencies-luxury and high. But Use The Same Compression On All Frequencies, High and Low. However, DBX is more common in the professional market. DBX is incompatible with Dolby and playing such a cassette on a conventional tape recorder is not possible. All noise reduction systems have two drawbacks. One of them lies in the fact that the compressor will not be able to suppress a strong signal until "hear" his short fragment. It is this fragment and takes place to exit without compression. The same applies to weak Signalwhich spent some time remains uncommon. These delays are well audible when listening. The second lack is that if there are smear in the frequency response of the system, then they will only be reinforced with the compressor. For example, if there is a failure of 2DB in the magnetophone at a frequency of 1 kHz, then when playing a failure in the signal will be 4 dB. Therefore, many prefer the system at all without noise reduction. Dolby HX Pro has no relation to noise reduction, no compression and is designed to improve frequency response when working with cheap ribbons.
Q. Can CRO2 tape damage the deck calculated on a normal film.
A. Can not. Everything will work fine. Such tapes are no more abrasive than ordinary. Decks designed for CRO2 or Metal tapes have another offset and frequency correction in order to "squeeze" from the tape maximum and align the CH.
Q. What is the difference between VHS HiFi and Beta HiFi?
A. For sound in VHS HiFi, amplitude modulation is used; In Beta HiFi - frequency.
Q. How do the audio records on the HIFI video recorder, the usual tape recorder and DAT tape recorder relate?
A. VHS HiFi and Beta HiFi are analog records using modulation when recording video and audio signals on video tape. On VHS ribbon there are special audio tracks. The quality of HiFi record on VHS is better than in low-cost cassette decks, but worse than good cassette deches with noise cancellation systems, and worse than DAT records. Therefore, in cases where you need high-quality recording, Use the Deca with manual recording level setting.
Q. What is better: Music center or system from individual components?
A. Some musical centers sound well enough. Even several "audio" manufacturers produce such combined systems. Um. The centers have a number of advantages: they are cheaper, occupy less space, easier to manage and install, no wire web. If you are planning to buy a music center, then do it better in the Hi-Fi store, where the purchase can be "listening" and choose products of audioil companies, such as TEAC. The weakest place of a good music center is his loudspeakers. The best music centers are generally shipped without loudspeakers, leaving the buyer the opportunity to choose to taste. Why then so much conversations about systems from individual components? From a multicomponent system, you can get a significantly better sound. The component system is harder to establish, set up, it takes more space and is more expensive. At the same time, such a system has flexibility. You can replace power amplifier or CD player if they are not satisfied. You can engage in the selection of individual components. In the case of music. The center can not do anything if anything does not suit you. To most music. Centers can not be connected to either MD or the player with "vinyl" nor VCR or many other necessary equipment.
Q. What is Bi-Amping? BI-WIRING?
A. Most acoustic systems are connected to the amplifier of one pair of wires for each column. Inside the column, the signal (transformed pre-) is distributed to crossover loudspeakers. Some columns have the ability to connect a BI-Wiring cable, while 2 pairs of wires on the column are removed from one output of the amplifier; One pair connects to loudspeakers serving medium and high frequencies, and the second pair to low-frequency speakers. To Bai Wiregua (so pronounced) belongs in different ways. Some argue that no difference does not hear, others claim that hear a tangible difference. The most acceptable explanation may be the fact that the separation of cables is separating and caused by the noise (weak power average and high frequencies and represent the main load for the low frequency amplifier). The cables must be able to spread apart from each other at least several. Santimeters. In all cases, the effect seems to be weak. Biamping means that 1 stereo amplifier is connected to each column that allows BI-Wiring, one channel, which is connected to the RF connectors, and the second channel to the LC connector to this column. Accordingly, the second column is connected through its stereo amplifier. In another configuration: one stereo amplifier is loaded with the speakers of both columns, the second, respectively - LF speakers. The meaning of Bai amping (so pronounced) lies in the fact that for the "swing" of low frequency speakers is needed significantly higher power than high. Thus, you can connect to a powerful stationary amplifier to a powerful stationary amplifier, and for the upper items to choose an amplifier outstrike, but weaken.
Q. What do letters "add" on my CD drive?
A. No relation to the quality of recording does not have this letter code. It refers to the equipment and tools used by recording. The first letter A means that the original entry was in analog form (D-in digital). The second letter indicates what equipment was used when mixing and editing the record. The third letter indicates the equipment used at the final entry, for CD naturally always "D".
Q. What is a class A amplifier, class B, class AB. What is Class C and D?
A. All of these terms refer to the characteristics of the output stage of amplifiers. Briefly: Class A amplifiers sound better than everyone, cost more than everyone, and more others spend electricity; Class AV amplifiers compete with Class A in the quality of sound, dominate the market, consume less energy, cheaper, less and easier. Class D amplifiers are used only for special applications, for example. Bass guitar or subwoofer amplifier. They are even less than the AB class, more efficient, enhance the signal less than 10 kHz (less than the audible range). The class B and C audio amplifiers are not applicable. The class A includes amplifiers with output transistors to which a constant displacement is supplied, so the current is constantly flowing through them. The most important advantage of their HT is the most linear, i.e. Improved distortions are minimal. The main disadvantage is inefficiency, because Even in silence mode, the amplifier continues to heat the atmosphere. 50-cotton amplifier class A large and heavy. Among the HIGH-END amplifiers, only 10% work in class A. In class amplifiers, the output transistors have a zero offset, therefore, at a zero signal, the transistors are locked and current, but introduce very strong distortions due to the nonlinearity of the gain in the zero area. These distortions are very well audible and make such amplifiers unsuitable even for unassicuating listeners. Class amplifiers are like a class in with all its disadvantages and also do not have applications in Hi-Fi. In the AV class amplifiers, there are 2 transistors in the output cascade, as in the class B, but both with a small displacement that shall with both transistors on linear mode. Most amplifiers in the market - class AV. Class D amplifiers are used in the output cascade pulsed modulation, i.e. Transistors are either open or closed. Therefore, such amplifiers are the most economical, kp. Some reaches 80%, but distortions made by such amplifiers are slightly higher than that of the AV class. At the output of the class D amplifier, there is a passive LC filter to get rid of the switching frequency. This filter introduces a phase shift and nonlinearity, and also cuts high, which makes it beneficial only for subwoofers. Make a class D amplifier with a full frequency range, of course, it is possible, but it will have to significantly increase the frequency of switching transistors (\u003e\u003e 40 kHz), build a high-risk unlit filter, however, in the other devices of your system, the increased frequency of switching will be successfully guided in the form of interference .
Q. What is Super Audio CD?
A. This is a new standard (abbreviated SACD) progresses: Sony, Philips. Supported: Mobile Fidelity, DMP, Telarc. Of course, COLUMBIA and SONY music directories are also candidates for release in this format. It is planned for official introduction: in Japan in spring, in America - in autumn 1999. Two-layer CD. An external translucent layer (HD) contains a 2 or multi-channel high-resolution musical record, made using sony process DSD (Direct Stream Digital). The large container of this layer is achieved by reducing and sealing the pit. The inner layer (CD) is the usual CD CD with a resolution of 16 bits / 44.1 kHz. Absolute compatibility with current CD players. It is supposed to release new names of the discs simply with the mark of SACD, on which the buyer may not pay attention to. After some time, it creates a collection of SACD records and it is ready to modernize his player. From a technical point of view, complete CD compatibility is questionable. Is everything CD-Shniki be able to read the inner layer through the external? Further, the increase in the cost of production of disks is inevitably, although Sony does not reveal specific numbers. It turns out the owner of the CD player, satisfied with 16 / 44.1 sound, will be forced to pay more for new discs, which will sound worse on its device?
Q.Smask about dad drives.
A.The so-called DAD discs promoted by Classic Records use a DVD video standard that allows you to record on a 2-channel audio dvd 24 bits / 96 kHz. The coming DVD audio format makes this temporary measure unnecessary.
Q. What are the prospects for the appearance of a purely audio format for DVD?
BUT. The DVD audio standard is progressing: JVC, Matsushita, Pioneer, Toshiba. Supported: Warner Music Group. There is an official introduction: autumn 1999 (there are difficulties with copyright). Here is its basic properties:
1.
Quantization frequency, word length (number of bits in each sample), number of channels, etc. Parameters are determined by the recording producer. For example, the disc may contain a 2-channel mix 24/96 and at the same time a 6-channel version of the same music with 24/96 front channels and 16/48 rear channels. Quantization frequencies are possible 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz, 88.2 kHz, 96 kHz, 176.4 kHz and 192 kHz with any resolution from 16 to 24 bits. Records encoded at 176.4 and 192 kHz are limited to two channels. The transfer of a multichannel signal in this case would require exceeding the maximum DVD data rate of 9.6 million bits per second. The manufacturer of the recording selects the recording parameters depending on the characteristics of the music, the duration of the fragment, the quality of the recording equipment. Recording parameters are transparent to the user: it just presses the Play key, the player defines them independently.
2.
DVD audio players will be equipped converter making a 2-channel mixfrom multichannel records. The manufacturer of the record can set the sound of this mix, inserting codes into the data flow controlling the player converter. This feature is called SMART (System Managed Audio Resource Technique) Content. If the producer did not insert these codes, mixing occurs arbitrarily. As mentioned above, the producer may record its own 2-channel version in addition to multichannel, but it requires an additional disk space, and therefore leads to a decrease or time of sound, or quantization frequency, or permissions.
3.
Another option to use Smart Content: Producer can lay there player or Decoder Settingswho considers it necessary for optimal recording sound.
4. MLP (Meridian Loseless Packing)
Even the DVD audio disk is not able to accommodate 6 digital audio channels quantized by 96 kHz with a 24-bit resolution. Therefore, compression is necessary. In 1998, MLP became part of the DVD audio standard. All DVD audio players will contain a MLP decoder, but for recording the use of MLP is not mandatory. If the disk is short or only 2 channels are used, the recording producer may not apply MLP. MLP provides space savings on a disk about 40% compared to unproken volume (see table). It is important that MLP is really a compression process without loss: after packaging and unpacking, the data is absolutely (beaten) are identical initial data, and sound quality is the same. This gives him an obvious advantage over compression methods, leading to losses, in particular, Dolby Digital and DTS. Since DVD-ROM drives will also play DVD audio discs, each DVD-ROM drive will contain a MLP decoder. That is, the small British high-end company will receive the author's fee from each sold personal computer equipped with a DVD-ROM drive.
Q. Will digital outputs from DVD audio players
A. Availability of DVD audio players digital outputs High resolution causes a clear concern to sound recording companies. Therefore, digital outputs of DVD audio players will be built on the basis of conventional SPDIF interfaces, AES / EBU, which we have in CD players. Instead, a digital output will be a multipional connector, called FireWire or, according to its technical name, IEEE1394.
FireWire is a very broadband interface that can carry a digital video signal, a multichannel digital audio signal with high resolution, computer data and control codes. These codes allow all Hi-Fi components of the system or home theater "talk" with each other, so that each component "knows", which other components are connected to the system. Such a bidirectional connection makes it possible to ban DVD-audio digital outputs under certain circumstances. For example, if you want to play a DVD audio disk using an external DAC, control codes will be allowed. But if you try to write this data stream, firewire interface Tell a DVD audio to the player that digital output is connected to the recording device and disable the digital output.
It seems that DVD audio players will not have digital outputs until the FireWire standard is universally established. Instead, look for 6 RCA analog outputs. High-End "Affiliates will be forced to produce single-block DVD audio players with six DAC channels. However, for purists stereo, there are still several 2-channel DVD audio devices.
 Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference
Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare?
Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare? Social polls work on the Internet
Social polls work on the Internet Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments
Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens
Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens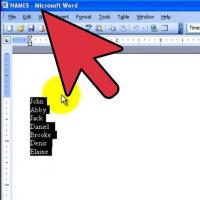 How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips
How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips How to see classmates who retired from friends?
How to see classmates who retired from friends?