Motherboard form factors. Advantages of hard drives in different form factors
Decisions on the base hard disks Form factor 2.5 "and 3.5"
Hard disks in two form factor 2.5 "and 3.5" are practical differences and scope of application.
|
Often, instead of specifying a particular hard disk form factor in inches (and double quotation is indicated precisely inch), Computer equipment suppliers use SFF and LFF abbreviations, reduce Small Form Factor phrases and Large Form Factor, respectively. It is easy to guess that any (and SATA, and SAS) hard disks of a smaller form factor 2.5" Received the designation SFF. HDD, and more 3.5" - LFF. HDD. It is no secret that in modern high-performance hard disks of form factors 3.5 "and 2.5" manufacturers use plates of the same size - from 2.5 "HDD. Therefore, often the capacity, and performance parameters 2.5" and 3.5 "models of rigid disks of one manufacturer look the same Moreover, some manufacturers announced the cessation of the production of high-performance rigid sizes 3.5 ", leaving the top models of HDD only in the form factor 2.5". The availability of high-performance hard disks forms 3.5 "is steadily reduced. Based on the realities of the modern market, manufacturers consider it economically inappropriate to use more than 2 plates inside one hard disk. For reference, in the hard disk of the form factor 2.5 "(15 mm height) it is possible to install up to 3 plates, and in 3.5" HDD to 5 plates. |
 2.5 "Disc |
 3.5 "Disc |
 |
What to do to those consumers who cannot or do not want (for all sorts of reasons) to use modern hard disks for form factor 2.5 "? Manufacturers offer an intermediate solution - the use of 2.5 "hard disks in the form factor 3.5". As a 3.5 "hard disk is offered the usual 2.5" Hard disk installed at the factory by the manufacturer in a special metal mounting case - a carriage. It should be noted that the extraction of this hard disk from the mounting case in some manufacturers is incompatible with the warranty. From the undoubted advantages of such a design, it should be noted that the engineers of the manufacturers accurately calculate the dimensions and rigidity of the design, the standard of connectors and mounting holes are guaranteed for 3.5 "hard disks, the cooling optimality of the hard disk installed inside is optimal. |
If the transition to a smaller form factor is inevitable, what will give consumers to the transition to 2.5 "Form factor of rigid disks?
What are the differences, the pros and cons of disk subsystems on the basis of rigid disks of various form factors and their applications? In two words - what's the difference?
Obviously, the smaller the dimensions of the hard disk, the more such hard drives should fit inside the server.
To date, the following number of hard drives are traditionally installed in the rack mounting servers:
| server height | quantity 3.5 "compartments | quantity 2.5 "compartments | ||||
| 1U | 4 compartments | 8 compartments | ||||
| 2U | 12 compartments | 24 compartments | ||||
| 3U | 16 compartments | 32 compartments | ||||
| 4U. | 24 compartments | 48 compartments | ||||
In general, (as can be seen from the table), it is possible to set 2 times more hard disks for the form factor 2.5, compared to servers of the same size, but with 3.5 "hard disks.
As already mentioned earlier, in the segment of corporate class hard drives, maximum capacity Discs of two different form factors - the same, based on this, the use of the disk subsystem with compartments 2.5 "allows you to double the maximum total storage capacity. And even when using hard drives of the low price range, in which, for today, maximum volume The hard disks of the form factor 3.5 "are about 2 times more than 2.5" disks, the maximum capacity of disk subsystems with compartments of different form factor will be approximately the same.
As an additional bonus of 2.5 "hard disks, it is obvious that due to smaller dimensions (2.5" disk less than 3.5 "disk to depth) disk subsystem in the server occupies a smaller volume, which allows manufacturers to slightly reduce the dimensions of the servers. It should also be noted that most modern SSD ( solid-state drives) Available in form factor 2.5 "and use in server 2.5" compartments guarantees compatibility when installing SSD drives, and, especially relevant, in the future - with possible server upgrading.
|
Hard disks of smaller sizes are actively used in systems with small dimensions, in high-density servers, modular and blade servers. For example, in one housing 2U height, 4 dual-processor servers and 24 hard disks of the form factor 2.5 "are located, that is, 6 hard disks of 2.5" form factor are connected to each server. To obtain the same amount of 3.5 "disks, the server housing must be 2 times higher - not 2U height, but 4U. Such a parameter, as the maximum volume of disk space, is certainly important, but not always. In the disk subsystems of the corporate class servers, the performance of the disk subsystem (the number of I / O operations per second, IOPS) is much more important than the overall capacity of the disk storage. The number of RAID groups (LUN) of the subsystem and their performance (IOPS) increase with increasing the number of connected hard drives, so it is obvious that more 2.5 "disks will give a serious advantage compared to a small array of 3.5" HDD. |
For comparison - two 2.5 "hard disk from 10.000rpm (revolutions per minute) of the corporate class on a good RAID controller will exceed one 3.5" disk with 15.000rpm. At the same time, the price of two 2.5 "10.000rpm disks with a volume of 300GB and one 3.5" 15.000rpm disc of 600GB volume will be approximately the same.
Such a parameter as a linear read / write speed on external tracks, theoretically, should be higher in rigid disks 3.5 "than in 2.5" (with the same spindle rotation speed and with the same recording density) simply due to the physically larger plate, but in the reality of the differences Minor, since in high-performance hard disks of different form factors there are often plates of the same size.
In general, the greater the rigid disk server, the greater the power consumption (power supplies must be more powerful), and more heat release (the server ventilation system and cooling costs) should be more powerful. However, compared with 3.5 "models of hard drives, modern 2.5" hard drives have 2 times less power consumption (in all modes) and, as a result, less heat dissipation and cooling costs. Thus, the server with 24 2.5 "hard drives consumes electricity and warms the surrounding space less than the server with 12 3.5" hard disks.
Reliability of hard drives is always paid great attention. Due to the reduction of dimensions (and additional engineering solutions) 2.5 "Hard disks have increased vibration resistance and mechanical impacts. This is confirmed by the manufacturers themselves, the latter's work on the recent models of 2.5" hard disks is 2 million hours compared to The best models of 3.5 "hard drives, in which MTBF is declared at 1.3-1.6 million hours.
And the last, despite the fact that it is not relevant in servers, but 2.5 "discs produce a slightly smaller noise during operation compared to 3.5" models.
As a result, you can briefly formulate the pros and cons, as well as the scope of use of hard drives of various form factors.
Advantages of hard drives in different form factors
- 3.5 "LFF - more volume of one disk, less than the price for gigabytes:
- with the same record density, the larger plate is placed more information
- the maximum capacity of one HDD is greater (in the segment of the hard disks of the low price range)
- cheaper cost in terms of a gigabyte volume of disk
- 2.5 "SFF is more capacity and performance per unit space occupied by a server or storage system in a rack:
- 2 times more storage capacity in a limited space - smaller dimensions and, as a result, a large container density per unit volume of space (gigabyte / cm. Cube) or per unit size in a rack (gigabyte / Unit)
- above the performance of the storage system in a limited space is smaller dimensions and, as a result, a large input-output density of the disk subsystem per unit volume of space (IOPS / cm. Cubes) or per unit size of the server in the rack (IOPS / Unit)
- 2 times less power consumption (in all modes) and, as a result, less heat dissipation and cooling costs , modular and blade servers
- in systems with high productivity of the disk subsystem due to a large number of fast hard drives -
- in systems with a large number of RAID groups -
- in systems with maximum reliability of all components -
- in low or limited power systems -
Now the finished computers can be bought in most home appliances stores. But this approach suits not everyone. Assembly from components to the order allows you to make a system unit that is suitable for the tasks of a particular person. In addition, such a computer will be unique.
Usually, when drawing up configuration system Block, the case is chosen, which is called, "for delivery". Yes, this approach is fair for office PC, where the goal is to save. Previously, when computers of modern ATH-format only appeared in Russia, most buildings were different only in the height and design of the front panel, people did not think over the choice at all. The most popular format was Tower (ordinary tower). Game and powerful configurations were collected in Full-Tower (the same tower, but one and a half times, or even two above) most often with the door on the front wall. Horizontal, so-called Desktop, on which monitors stood, gradually disappeared from the sale. Initially, all the housings were "just gray boxes", then silver and black colors entered the fashion.
If someone thinks that everything is also left - just has not been in a computer store for a long time. Now on the shop windows you can meet the hulls of all kinds of forms, colors and sizes. And when assembling, for example, a small computer, it is the case most often becomes defining. Not to get lost in this manifold, today's article will help.
MIDI-Tower and Mini-Tower sizes.
Despite the desire for miniaturization, vertical buildings such as MIDI-TOWER remain most popular. Approximate dimensions: width 15-20cm, height 43-45 cm. Such enclosures are able to accommodate a full-sized standard ATX-format motherboard, a standard size supply unit, several hard drives and drives. Application universal. Sizes are acceptable both for high-performance computers and for office PCs. Expansion slots most often 6. However, such a number of expansion cards do not need modern computers, especially office. MICROATX motherboards immediately have built-in sound and network cardsand processors - built-in video. Thanks to this, you can save on the dimensions - use mini-tower housing. It is lower than MIDI-Tower (about 33-35 cm high), however, and install in them it will get a bit: 1-2 optical drives, 1-2 hard disk and about 4 expansion slots.
The presence of a power supply in the Tower-format enclosures and its location.
Often the enclosures of this format are equipped with built-in power supplies. In the case of an office computer, the hardest work for which is the table editors and email, you can use simple housings with a built-in power supply, 300-450W. The multimedia PC, as well as the game average, can do the 500-600W block, pre-installed in the housing. Most often, such a decision saves, but for serious workstations, or powerful gamers of this computers will not be enough. Power supplies built into the housing, usually simple series with a minimum set of connectors, connect a powerful video card, or a large number of Hard disks will be difficult.

Micro-Tower and Slim-Desktop sizes.
And what if the case is even smaller? This is how Micro-Tower and Slim-Desktop appeared. The first is lower than mini-tower, and the compartment for 5.25 inch drives is just one. The second is already than standard towers. Reduce the width allows the location of the power supply vertically, sometimes even in front. The optical drive compartment is also located vertically or is generally absent. This allows you to have a housing both standing and lying, that is why there is a word Desktop in the title. In such buildings, computers usually collect with low power consumption, and, accordingly, heat generation, since the air movement in them is difficult.

Desktop sizzy.

Full-Tower, Ultra-Tower and Super-Tower sizes.
Non-standard solutions and modding.
And what if you want something non-standard? It is possible to purchase a favorite body that will fit into the design of the room or an office. For example, pink. If your favorite color is black, the variety of enclosures, of course, increases, but the manufacturers have not considered him the only one. The choice of materials is not limited to steel - various are used in the finish. Budget segment. In this range there are housings for office system units with BP 350-400W, you can also find the housings for HTPC with BP 200W with support for MITX-format motherboards. Number of ports, expansion slots and pre-installed fans minimally.
3500r - 6000r. Cases with a capacity of 450-500W, or Mitx-enclosures with 300W BP, you can collect already a multimedia computer for the house, but some interesting decisions, as in the previous group, do not have to wait.
6000r - 13000r. Here you can already find interesting options, closer to the upper boundary - even the body of type Full-Tower with a window on the side wall, adjusting the speed of rotation of the fans and 600 W power supplies in which you can easily collect, for example, a media server with a large number of hard drives. Modern video cards, even powerful, requirements for BP are not as high as before, which means the game computer of the initial, average, and even above the average level will feel good in the housings of this range. It is worth it, of course, pay attention to the number of cabinet fans, one on the front wall, and one on the rear - the required minimum. However, the missing number can always be purchased separately.
Cases without a built-in power supply.
900r - 2500r. First level. Office housings, the most simple black boxes. However, the hull of the upper price range (2000P-2500R) during the installation of a powerful BP does not interfere with both at home. At the same time, do not forget about compatibility with components, such as playing video cards.
2500r - 8000r. Average level. There is everything here, as described in the article. And ordinary towers, and cubic cases with interesting color solutions, and aluminum housings for HTPC, and Full-Tower for a system of any power.
8000r - 22000r. Upper level. Maximum thoughtful in terms of design, materials and cooling of the body. Suitable for the most demanding users. It is in such buildings that "top" systems are collected.
From 22000r. Premium level. There is no upper price limit. For those users who are not ready to put up with the fact that someone will have a similar housing. Often produced in small batches, from unusual materials. Possess a memorable design.
Introduction For the past few years, the market personal computers very much changed. A large number of users using computing equipment for traveling on the Internet or as a home entertainment center, it became approaching the PC, as an ordinary home appliance. As a result, the structure of demand for all computer parts has changed much. Many have suffered from this, including manufacturers of components.
In the light of the fact that the number of computer enthusiasts is gradually shrinking, manufacturers of motherboards began to face that the demand for their high-end products decreases. On the other hand, all the increasing integration of system logic sets began to lead to the fact that most motherboards from different manufacturers have become strongly like each other in their characteristics, without giving manufacturers of high-end boards to stand out in a number of them like. In this situation, those from manufacturers of motherboards that do not have large OEM orders began to feel somewhat insecure, because in the production of some cheap solutions "will not leave."
One of the ways out of the impending crisis for the manufacturers of motherboards has become the diversification of production and the proposal of completely different types of products. As we can observe, many of the former manufacturers of motherboards began to produce video cards. Some reached the server market. Part of the manufacturers began to offer laptops or PDA. Other manufacturers began to produce and actively promote the so-called Small Form Factor (SFF) PC. We will dwell on them in more detail.
SFF PC is small computers designed to use the house or in the office. Combines their key feature, the following from the name, namely a small size. At the same time, SFF computers have a number of other advantages in front of their fellows, such as a reduced level of noise. But it is rather a consequence, not the reason. In addition, according to its design SFF PC, manufacturers try to make people looking out in such a way that in the eyes of an inexperienced user looking at SFF PC, the line between the computer and any other household appliances.
SFF PC is supplied in the form of Barebone sets, that is, in the form of a kind of "skeletons" to create ready-made systems. This is not surprising. If the release of special motherboards and enclosures to establish on their capacities to manufacturers of boards, they cannot produce processors or hard drives. Therefore, the classic Barebone SFF PC includes a housing with a power supply, a motherboard with an integrated graphics core, or a video card. However, the completion of the supply of various Barebone kits can vary.
Today, our laboratory was the first such skeletal set of Small Form Factor PC from FIC. Naturally, we could not deny yourself the pleasure to test her. Especially since its small size and quite "adults" characteristics, he won the sympathy and your submissive servant.
Specifications and appearance
So, the SFF PC from FIC, Samba (SM) -1845 was received for testing to the laboratory.This skeletal kit, as the official specification says, is designed to build a home or office computer based on socket processor 478 Intel Celeron or Intel Pentium 4 with 400-megahertz System Bus. In the motherboard used in SAMBA-1845, the I845 logic set with support for PC133 SDRAM is used, and there is also an AGP 4x slot, which is possible to install AGP video cards SLIM-forms of factor.
In order for the reader to receive an idea of \u200b\u200bthe size of Small Form Factor PC, we give the photo samba-1845 next to the traditional mini-tower from Inwin:

I note that Samba (SM) -1845 allows both vertical and horizontal installation of the system unit.
More SAMBA-1845 specifications look like this:
Support Socket 478. intel processors Pentium 4 and Intel Celeron with a bus frequency of 400 MHz;
Intel 845 logic set with southern ICH2 bridge;
Two DIMM slots supporting up to 1 GB PC133 SDRAM;
AGP 4X slot and two PCI slots;
AC97 audio codec CS4299 with SPDIF support;
One 3.5 "Inner compartment for ATA-100 hard disk, one 3.5" External compartment for standard 1.44 MB of drive, one 5.25 "External compartment for external ATA-100 optical drive;
Integrated 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Controller Intel 82562;
150 W power supply from Delta;
Four USB 1.1 port (two on the front panel and two - on the rear);
Two IEEE1394 ports (one four-pin and one six-contact);
Two PCMCIA Type II slots;
Dimensions 310 (width) x 360 (depth) x 93 (height) mm.
In addition, the package of Samba (SM) -1845 includes 3.5 "1.44 MB of a drive, as well as a SLIM-video card manufactured by FIC, based on the GeForce2 MX 200 chip.
On the front panel SamBA-1845, the front parts of the discs for the drive and the CD-ROM are located (the front panel of the CD-ROM closes the door); Two PCMCIA Type II slots that can be used to connect additional devices to a computer traditionally oriented in laptops; Power On Button and Multiple connectors closed with valve. Having moved the valve, we discover two USB 1.1 ports, a six-contact and four-contact Firewire ports and a microphone input. These are the possibilities of samba-1845, addressed to the user face.

Deploying Samba (SM) -1845 to 180 degrees, we find a power connector, one consecutive and one parallel port, network RJ45 port, two more USB 1.1 ports, PS / 2 connectors for connecting mouse and keyboard, audio input and audio - Like, as well as optical SPDIF output. In addition, there can also be a video output with a video card that comes with Samba (SM) -1845. As you can see on the rear panel, Samba (SM) -1845 allows installation and two additional cards Extensions.

After removing the lid with Samba (SM) -1845, it is found that to convert this skeletal set to a full-fledged SFF PC, you must install the hard drive and the CD-ROM drive, as well as the processor and memory. In addition, Samba (SM) -1845 will allow the installation of two at the request of the user additional PCI Expansion cards, for example, modem and USB 2.0 controller, but this is not yet exhausted at this capabilities. Supports two PCMCIA Type II slots allows you to connect to Samba (SM) -1845 almost any external devices.
Motherboard
Unlike other Barebone manufacturers, FIC uses a special motherboard for its Samba (SM) -1845, and not a serial integrated fee that is sold and separately. However, it is quite explained. SAMBA (SM) -1845 has a number of unique features that we will talk about.
The Motherboard with the SFF PC itself is based on the i845 logic set and supports two DIMM slots for PC133 SDRAM. Unfortunately, this should be recognized by the main disadvantage of Samba (SM) -1845: The fee does not allow the installation of any more modern types of memory, as a result of which the performance of the system built on Samba (SM) -1845 will be significantly limited to the type of memory used. SAMBA designer solution (SM) -1845 looks even more strange if take into account the fact that the PC133 SDRAM and DDR SDRAM have now have almost the same cost in the market. Therefore, the only justification of the designers of this SFF PC can only be the fact that the I845 logic set with SDR SDRAM support is somewhat cheaper than their DDR fellow.
Also, the choice as a base for Samba (SM) -1845 chipset I845 led to the fact that although the board supports Socket 478 processors, the official support of the 533-megahertz tire does not have. So, if you follow the instructions, it is necessary to install in Samba (SM) -1845 either Celeron or Pentium 4 with a 400-megahertz tire. However, as shown in practice, Samba (SM) -1845 without any problems can work with more modern processors With 533 megahertz tire.
As a plus applied solution, it should be noted that the motherboard supports external video cards, and this makes it possible to perform in the future upgrade not only processors, but also the video subsystem.
External SAMBA Slots (SM) -1845 are performed on an additional riser card. Thus, the FIC engineers managed to achieve significantly reduce the height of their SFF system. The Riser card applied to Samba (SM) -1845 has two PCI slots and one AGP 4X slot.
The choice as the chipset of the I845 chip chip also led to the fact that the board uses a somewhat outdated southern bridge ICH2. However, it is possible to attribute to its major disadvantages to its lack of support for USB 2.0 protocol, which is not difficult to refund, if necessary, using external controllers, the benefit of free PCI slots at Samba (SM) -1845 is.
Otherwise, the board supports the entire set of integrated devices implemented both through the chipset, as part of which the AC'97 Sound should be noted (CS4299 codec) and USB and through external controllers, for example, two IEEE1394 ports.
PCMCIA controller should be mentioned separately, thanks to which Samba (SM) -1845 has a truly remarkable extension capability through PCMCIA Type II cards.
I also note that on the SAMBA board (SM) -1845 only one IDE channel is divorced. However, taking into account the fact that the Samba system itself (SM) -1845 is not intended for recruiting more than two devices, this fact does not look like a large drawback.
BIOS, which is controlled by Samba (SM) -1845, this is the usual Phoenix / Award v6.00pg with a minimum number of settings. Given the fact that the specified system is positioned on the home market and office computersThe simplicity of its configuration is its undoubted and substantial plus.
The video card, which is included in the SAMBA kit (SM) -1845 is the usual GeFroce2 MX200 with 32 MB of SDR memory production of FIC itself.

This video card allows you to get an initial-level video method, which, however, it is quite successfully improved by replacing this video card to more modern. By the way, not only Slim video cards can be placed in Samba (SM) -1845, as the instruction requires. Some small classical format video cards can also be installed in Samba (SM) -1845.
Power Supply
A few words I want to say about the power supply used in Samba (SM) -1845.
For its Barebone FIC used a small block from the Chinese company Delta Electronics. Despite the low power of 150 W, this unit is compatible with the ATX 2.03 specification and has an additional 12-volt cable for use with Pentium 4 motherboards. At the same time, given that only one hard drive and one can be installed in the SAMBA system (SM) -1845 optical driveAlso, it is not allowed to install video cards with high energy consumption (by virtue of the possibility of using only small video cards), 150 W power should be quite enough for systems built using very powerful processors, with frequencies up to 2.6 GHz.
Also, the unit has three additional power cables, as a result of which, after installation in the case of the drive, CD-ROM and Winchester free "tailings" does not remain.
The specified power supply has one small fan, which is intended, obviously, to cool the block itself. On the blowing of the air through the entire case (and this is clearly necessary, given the possibility of using the Pentium 4 family processors in Samba (SM) -1845) its power is clearly not enough.
Cooling system
In the light of the fact that SFF PC is by definition a small computer, the traditional cooling systems cannot be applied in it. Moreover, manufacturers are trying to make their SFFs and as low as possible, so the number of fans in such systems are trying to reduce. As mentioned above, the fan applied in the power supply is unable to cool the block itself. Therefore, the widespread solution for SFF PC is a cooler, at the same time a cooling processor and an air exchange in a housing with the environment.The solution selected by the FIC engineers for SAMBA cooling (SM) -1845 is characterized by simplicity on one side and originality - on the other. The processor is put on the AVC aluminum radiator, which is fastened directly to the body with four spring-loaded bolts, and smoothly over it is a large fan that ears the air outward through the holes cut into the housing lid.



Thus, not only effective cooling of the processor, but also other components of the system due to the fact that the fan blows the air not only through the processor radiator, but also through the entire system.
As for noise, the system contains only one large and one small fan that noise is not so strong. According to official data, which reports FIC, the SAMBA noise level (SM) -1845 does not exceed 30 dB. By the way, the large main fan, located above the processor - the low-speed and frequency of its rotation is about 2500 revolutions per minute.
Assembly
When describing the skeletal system from FIC, we will try to assemble a full-fledged computer based on it. The first thing that will be needed is to open the case. This requires a cross screwdriver - the SAMBA cover (SM) -1845 is screwed in three screws. After removing the lid of the user, the following picture opens:
After removing the plank, to which the fan is attached, the user gets easy access to all system nodes. True, for the mounting of the Winchester requires the removal of the basket over the power supply, but this operation is unlikely to relate to time consuming, since the basket itself is fastened with two screws, access to which is carried out without problems. The positive point is also the fact that the hard drive in the basket is not fastened hard, and through four rubber gaskets, also designed to reduce the noise level produced by Samba (SM) -1845.
The only question that may occur during the assembly process after installing the hard drive, the actuator CD-ROM, processor, radiator, memory, and, if necessary, the expansion cards are how to connect one 80-cable motherboard, hDD and optical drive, given what disk and CD-ROM connectors are at a sufficiently large distance from each other and are directed in different directions. Fortunately, the package of Samba (SM) -1845 includes a specially curved IDE loop, thanks to which iDE connection Devices are simple enough.
As a result, we get samba (SM) -1845 assembly:

After installing the fan in the place, the location of the components in the system looks somewhat close, however, it is also a Small Form Factor PC.
I note that in the assembly process it turned out that the labeling of the DIMM modules is incorrectly applied and after assembling the kit it refused to start. However, the reason for the problems was quickly clarified, the memory module is rearranged, and after that everything went like oil.
So, the system is assembled, it's time to move to tests.
Test results
Before moving directly to the results of the tests, I want to talk about the surprises that occurred when preparing for testing. As it turned out, despite all the statements of the specification, as well as the fact that the i845 logic set in Samba (SM) -1845 does not officially support the 533-megahertz tire, our system has successfully started with the Pentium 4 2.4B processor, designed to use this Tire frequencies. At the same time, the system really worked at the frequency of Quad Pumped Bus 533 MHz. In this regard, it was decided to test it with the Pentium 4 2.4B processor since the behavior of Samba (SM) -1845 with such a CPU is extremely interesting.As a result, the composition of the test system was as follows:
SFF PC Samba (SM) -1845;
Intel Pentium 4 2.4B processor (tire - 533 MHz);
Memory - 256 MB PC133 SDRAM;
Fujitsu MPG3409AH hard drive;
CD-ROM ASUS 32X.
During testing, the system has manifested itself extremely stable, no complaints about it from this point of view. The power of the 150-watt power supply also had enough to power the system described above even during its operation in the most stringent conditions.
As a result, the following indicators were obtained:
| Test | Result |
|---|---|
| SYSMARK 2002. | 211 |
| SYSMARK 2002, Internet Content Creation | 291 |
| SYSMARK 2002, Office Productivity | 153 |
| 3DMark2001 SE, DEFAULT | 1545 |
| Quake3 Arena (Four), Fastest, 640x480x16 | 169.8 |
| QUAKE3 ARENA (Four), High Quality, 800x600x32 | 50.6 |
| PCMark2002, CPU Score | 5797 |
| PCMark2002, Memory Score | 4090 |
Actually, the results of surprise do not cause. Low indicators in 3D graphic tests are explained by the weakness used in Samba (SM) -1845 video card - NVIDIA GeForce2 MX200 with 32 MB of SDR SDRAM. At the same time, the frequencies of this video card are 175 MHz on the chip and 167 MHz - in memory. In general, for 3D Samba games (SM) -1845 can be recognized only conditionally.
As for the results in the processor tests and in the SYSMARK 2002 office test, it should be noted that they are inferior to the results obtained on full-fledged systems with a similar CPU, only 10-15%. This lag is caused by the application in Samba (SM) -1845 low-performance PC133 SDRAM.
However, apparently, trying to eliminate this disadvantage, FIC will soon begin supplying the new version of its SFF PC, Samba (SM) -1845GL. This skeletal system will be based on the i845GL chipset and support DDR266 memory. True, due to the selection of the chipset, this time the system will have the ability to use external graphic AGP cards, and the Intel Extreme Graphics graphics core will be applied to the I845GL. However, in Samba (SM) -1845GL, the upgrade of the video subsystem will be possible by using external graphic maps PCI format, Fortunately in Samba (SM) -1845GL Number of PCI slots will be brought to three. Also, the new version of Samba (SM) -1845GL will support the USB 2.0 protocol, implemented by the possibilities of the southern ICH4 bridge.
Returning to the results of our testing, it is also necessary to note the effectiveness of the cooling system used in the SAMBA (SM) -1845. During operation and stress tests, the processor temperature was not raised above 67 degrees, and the temperature inside the case was always below 37 degrees.
conclusions
Small Form Factor PC Samba (SM) -1845 looks like a good basis for a home or office computer in cases where this computer is not planned to be used for 3D games. Otherwise, the characteristics of Samba (SM) -1845 are such that this platform will be quite enough to use in virtually any areas where high computational system performance is not required. In addition, Samba (SM) -1845 has a pleasant design and works with a very small level of noise.Unfortunately, with all the undoubted advantages of such a solution, it is necessary to note a significant disadvantage of FIC Samba (SM) -1845. This Barebone system is deprived of all support from FIC. The company does not offer any new BIOS firmware nor new drivers for Samba.
Pros:
Stylish design and small sizes;
Low noise;
Two additional PCI slots and support for AGP video cards;
Support PCMCIA Type II;
Support USB, IEEE1394, Ethernet and AC'97 sound;
Easy assembly.
Minuses:
Work with PC133 SDRAM;
Low-performance graphic subsystem;
Absence uSB support 2.0;
No online support on the FIC website.
The process of assembling a new stationary computer or an old upgrade is always accompanied by a non-small number of questions, the answers to which you need to get in a timely manner, that is, before buying expensive components. Therefore, at the PC configuration plan, the user, first of all, should determine which motherboard form factor will be applied in it. After all, it is he who sets a bunch of parameters for the future assembly, ranging from the size of the computer's system block housing, ending with the cooling system built into it. Based on this, in this topic, we consider which form factors of motherboards, their types, formats, sizes, purpose, etc.
What is a motherboard form factor
Motherboard form factor is a standard installed by the manufacturers, specifying its overall and connecting dimensions, that is, the size of the mounting to the housing, the number and location of the interface slots for connecting random access memory, video cards, different types of extension cards, entering and output ports and other necessary interface connectors.
As you can see, this parameter does not directly affect the appearance in general, the collected system unit and its hardware filling. If you choose not the correct motherboard form factor, then the consequences may be sad, leading to unplanned budget consumption. Here you need to take into account many factors: this is the size of the system block case, its inner space To install expansion cards, video cards, processor, power supply, disk system, Well, cooling systems.
If the configuration is designed for a powerful gaming computer, then the last of the listed items is required to pay special attention.
Overview of motherboard classifications Let's start with the most popular form factors in circles and ending the MP of the professional level intended for specific tasks.
Form factors of system boards for office and gaming PCs
ATX Form Factor
This format of MP is the most in demand for building stationary computers of any configuration, ranging from the office version, ending with a powerful gaming station. ATX format boards have standard dimensions of 30.5x24.2 cm, which allows manufacturers to easily empower them with all the necessary functionality and a full-fledged complete base with slots, ports, interface connectors, power supply and so on.
To important constructive features This sizes of MP should be attributed to the fact that they are compatible only with the buildings of the system units of the same ATX standard. On the one hand, it seemed to be a minus, but on the other, the assembly of computers with their use can save the user cash From the budget allocated to them.
First, the computer assembled on their base is less demanding on the cooling system, because the components of its hardware filling do not have to use in a small case, which means they have good ventilation without the use of expensive cooling systems.
Secondly, the segment of buildings compatible with the motherboards of the ATX form factor is greater than other sizes. Therefore, collecting a computer, the user does not have difficulty choosing the body of the future PC for the financial side of the issue or the choice of model.
MicroATX (MATX)
This sizes of motherboards is a trimmed version of the ATX standard. This concerns both sizes and a complete base. The dimensions of the MP of this standard are 24.4x24.4 cm. They are fully compatible with the enclosures of the previous format, but not vice versa. Often, MicroATX boards may be similar to configuration with their collections of the ATX standard. That is, they can be equipped with the same chipset, but with a smaller number of PCI slots designed to install various expansion cards.
In addition, not rare MP MICRATX sizes are equipped with a built-in graphic core, and there are no ATX configuration similar. It follows that the system boards of this form factor are not targeting the construction of gaming systems, and in most cases are oriented only to create office destination computers.
Flexatx
Flexatx form factor is the following evolution aside to reduce motherboards and cheapening computers collected on their base. MP this format They have a size of 22.9x19.1 cm and are intended only for office PCs. They, like their predecessors, are fully compatible with the buildings of the system units of ATX format and with their power system.
An important distinguishing feature of the MP of this standard, which allows them to achieve not a high selling cost, are their more scarce complete base. In some cases, they are not even equipped with expansion slots, and the user has to be content only uSB ports and IEEE-1394 / FireWire.
Below in the video, the main differences between the MP family of the ATX family and the highlights that should be paid attention to, collecting a new PC.
Motherboard formats for compact PC
DTX and MINI-DTX
DTX and MINI-DTX form factor, represented by AMD, are focused on building compact, quiet, energy-bearing and inexpensive computer multimedia systems HTPC. The dimensions of the MP of this sizes are 24.4x20.3 and 17x20.3 cm, respectively. They have full compatibility with the ATX standard on the size of the mount and on the power connectors.
The disadvantages of this standard include limited opportunities Extensions due to the presence of only 2 slots - 1x PCI and 1X PCIE and the use of only low-profile cards installed in these slots.
Mini-ITX
The format of MINI-ITX motherboards developed by Via Technologies is mechanically and electrically compatible with ATX Form Form. Their sizes are - 17x17 cm. Thanks to the use of embedded processors, SSD disks as file drives and use passive system Cooling This type of MP is aimed at creating inexpensive compact and quiet multimedia home systems.
The video shows below short review one of the MP form factor Mini-ITX where its advantages and possible scope are considered.
System boards formats for server systems
Extended ATX (EATX)
The dimensions of the MP form factor EATX are 30.5 × 33.0 cm. This standard More applicable to creating servers, where the motherboard requires the installation of two or more processors, a large number of RAM and various kinds of expansion cards. The second name is SSI EEB.
SSI CeB.
SSI CEB form factor is focused on building workers of high-performance stations and server solutions. The overall dimensions of the motherboard boards of this standard are 30.5 × 25.9 cm.
As you can see, the classification of system boards is quite extensive and includes both obsolete species and newly developed. If they are divided into a similar principle, then the picture simplifies the reflecting reality will be as follows:
- Outdated form factors: LPX, full-size AT, Baby-AT board; Mini-ATX
- Modern standards: ATX; microatx; FlexATX, EATX, WTX, NLX, CEB
- Implemented Size: Mini-ITX, Nano-ITX, Pico-ITX, BTX, Microbtx, Picobtx, DTX and MINI-DTX
Oddly enough, but often before buying a new computer, people do not always think over the size and type of future PC (form factor). Most often it falls on the shoulders of sellers who are not always interested in the needs of the client, simply speaking - what corps caught - both stuck ... however, it is often that this parameter is important for both the user and for the computer itself. How important is it? From the form factor of a PC (and from the correctness of its choice, of course ...), many important parameters depends on the convenience of work, the noise level, the temperature of the housing, and from here it is followed: "Health" of components inside (primarily hard drives - which store your information - And this is as you know the highest value), the convenience of work, etc., etc. ... So, how to choose the right size of the system block of the future PC?
To begin with - I propose to consider them more in turn:
At the beginning it is necessary to say that the sizes of the PC are not only from the size of the hull itself. The size of the housing must match the size of the components - the motherboard first, video cards, power supply and other devices. For example, it is impossible to place the ATX system board in the MinitOwer case, or the GeForce 9800GTX type video card in the same case - it simply does not fit. And if it gets, it will be so warm that small space will not allow to effectively remove heat, and overheating will threaten all devices ...
So let's consider the form factors of the buildings - their size can be said directly proportional to the possibilities of the future PC, because It defines the size of components that can "fit" in it. And modern components are often large sizes (for example - powerful video cards). Therefore, it is possible in a sense to give such advice: the more powerful PC is planned - the greater the case ...
Full Tower (Full Tower): Sizes of such a case: width 15-20cm, height 50-60cm. Such a housing has from 4 to 9 compartments for devices 5.25 inches (example: DVD-ROM drive), has from 6 to 12 compartments under the device 3.5 inches (example: hard disk), has the ability to install seven expansion cards (for example, TV tuner, sound card). Also, such a housing accommodates a full-sized ATX system board (we will talk later about their size). Speaking easier - the buildings of this type are the largest, and the capacity of various "iron" is enormous. But here, of course, it all depends on the motherboard - how much it allows you to connect hard drives, extension boards, (which then find a place in the enforcement of the case), etc. Application: Mostly for powerful computersfocused solely on high performance, because Such systemic blocks contain a lot of fast components, which are known to highlight a lot of heat, and in such a large case, the cooling is not difficult.
Medium Tower: Mid Tower: Perhaps the most common size among home desktop computers. Its dimensions: width 15-20 cm, height 43-45 cm. Such enclosures are able to accommodate a full-sized ATX system board, full-size power supply, several hard drives and a lot of hard drives. Application: You can say - universal. Sizes are acceptable and for high-performance PCs, and for the usual average home Computer. The space inside the housing allows the circulation of air flows inside usually does not make it difficult to cool the housing and devices. I recommend it to build a PC - if your PC requirements are common, and if you do not need a computer "on the shelf".
Mini Tower (Mini Tower): Mainly distributed in the office computers sector. Because of its small sizes (15-20 cm width, height 33-35 cm) they allow you to install a bit: (1-2 optical drives, 1-2 hard disks and about 4 expansion slots) and the device is medium or below the performance. First, due to the size, and secondly, due to heating. Places in such a case are not enough - and therefore the requirements for the temperature of the devices above, in order not to be created the other noise of fans and overheating of the devices. But in such a case, you can fit the components that are quite enough for office work with text, presentations and spreadsheets.
Mini PC (Small Form Factor): With its size (width of 20 cm, height 18-23 cm) they contain a maximum of 2 expansion slots, some hard drives and imply a compact power supply. Here it is understood that the user will mainly use the components built into the motherboard (which is also small) as well as built-in video and sound. In appearance, these corps resemble household appliances. Their use is like office PCs or as the basis of a home theater. About cooling here is not worth the question, because Devices are very little and they allocate a little heat in their destination.
Also there are still form factors. Micro PC (which are even smaller compared to mini-PC with dimensions, but because of their sizes have even greater limitations) and desktop (horizontal buildings on the table), but they are less common and you are unlikely to get involved with them.
So, we reviewed the form factors of the buildings. I hope - you will choose something suitable for yourself. If not - you can apply for individual advice.
In the following articles from the form-factors cycle, we are general Consider the form factors of the component system block and other devices.
 How to pay a domain name
How to pay a domain name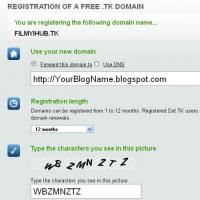 Domain zone of tokelau islands
Domain zone of tokelau islands What is domain what problems may be
What is domain what problems may be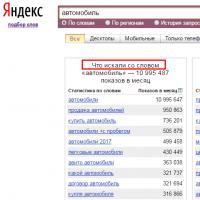 Yandex Wordstat: detailed instructions for using the service and grouping operators and a complicated request
Yandex Wordstat: detailed instructions for using the service and grouping operators and a complicated request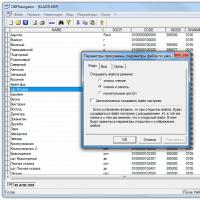 Editing DBF files
Editing DBF files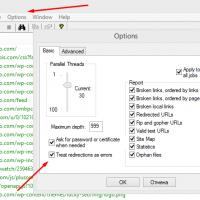 Xenu Link Sleuth - What is this program how to use the Xenu program
Xenu Link Sleuth - What is this program how to use the Xenu program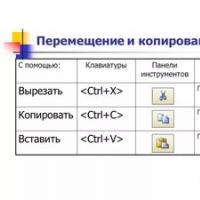 Methods Copy and insert text from keyboard without using mouse
Methods Copy and insert text from keyboard without using mouse