10.05 01 Computer security Military training. Computer security (specialty): who to work? Who is the "security officer"? What should be able to know the information security specialist? To whom and why it is worth going to computer-free specialists
For admission, the exam is taken in mathematics, as a profile subject, Russian language, and physics or computer science and ICT to choose from.
The passage point, according to a survey conducted by HSE and the Analytical Department of the RAEK, the average passing point of the EGE in the regions varies slightly, and between different specialties information security It differs significantly.
The maximum passage point in universities varies from 45 to 86.
You can choose a specific specialty, we can consider the nuances and specifics of the directions: Specialty 10.03.01 "Information Security" - here are the basic knowledge of the installation and operation of the components of the IB security system.
- Specialty code - you can get applied technician protection skills.
- The specialty code gives the skill to identify the channels of information leaks and prevent cases.
- The specialty code is the development of threat models for databases and creating programs to protect them.
- The specialty code is the programming and safety of operating, tax, financial, budget systems.
It can be trained in person, after 4 years, passing training at a specialist. There are magistracy and graduate school in some specialties of information security. The correspondence form of training is provided not everywhere, its deadlines vary in different universities. In the sowas, the passing score is significantly lower, but the choice of specialties is narrow.
Specialty Information Security - Universities and Colleges
In which universities there is a specialty information security?
Training of specialists in Russia is conducted in all regions of the country. The distribution of them, however, is unevenly.
Most a large number of IT specialties in Ugatu, they are 19. Next go MSTU them. AD Bauman and Spbniu ITMO. In general, to get an education in the field of information security in 145 universities of Russia. More than 30% of them are located in the Central Federal District.
Specialty Information Security - Universities in Moscow:
1. Academy of FSB of Russia
2. MFU.
3. FGBOU in MGLU
4. Financial University, Financial
5. FGBOU in NIU "MEI"
6. Miigaik
7. FGBOU in Moscow State Engineering University (Mami), University of Engineering (Mami), University of Engineering
8. National Research University MIET; NiU MIET; MIET.
9. OJSC "IMIVT"
10. Niauia Mafi.
11. Academy of GPS Emergencies Ministry of Russia
12. MSTU G.
13. FGBOU in RGAU-MSHA named K.A. Timiryazev
14. FGBOU VO "Russian State Geological Exploration University named after Sergo Ordzhonikidze", MGRI - RGGRU
15. Motusi.
16. MSTU them. N.E. Bauman
17. Military Academy of RVSN named after Peter Great or WA RVSN
18. Moscow University of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia named after V.Ya. Kikotya, Moscow Moss of Russia named after V.Ya. Kikotya
19. Miera, MGUPE
Students study the multi-level Cisco and Oracle security systems, gain skills to work with specialized equipment, blocking information leaks, practice search for hidden camcorders and radio layers, blocking information transmitters using various Sonata complexes, Curtains, Barhan.
Specialty Information Security - who work
Where to work with specialty information security?
Work in the specialty information security with the acceleration of their knowledge and implementation of the capacity for both students and graduates can be offered in IT companies, government agencies, in operators of telecommunication systems, as well as participating in international tournaments. The major players of the IT market are sent to the events of Head Hunters, and subsequently make suggestions to participants.
Gregory Bakunov, Director of Dissemination of Yandex Technologies and Dmitry Voloshin, Director of the Department of Research and Education Mail. GROUP, are jointly the fact that there is a personnel hunger.
Since August 2016, Cisco has launched a scholarships in which 10 million dollars invested invested. It is designed to increase the number of specialists with the preparation necessary for this area. The program will be implemented in conjunction with authorized training partners, among which there are many Russian universities.
According to the results of a survey conducted by apkit and the WTCIOM, only 13% of IT-university graduates confirmed that education in the university can be applied in real work. But, as Alexey Sokolov said, Deputy Minister of Communications and Mass Communications, the number of budget seats increased by 70% for 2 years, and it is planned to achieve a greater increase in the control digit of the reception.
There is hope that the quality of education in this area will also increase, although, in REC, it is believed that, despite the increasingly active support for IT-education by the country's leadership, the problems of insufficient competence of IT specialists, inertness of curricula, incompetence of theoretical teachers are still relevant.
The competent model is an attempt to create the most adequate model of a specialist who would take into account the needs of the market in specialists in computer (information) security, the requirements of enterprises for such employees, as well as the possibility of the highest educational institution on the preparation of such specialists.
I propose to get acquainted with the idea and make constructive offers.
Introduction
The super-proclaimed race of creatures created the computer "Deep Thought" - the second in terms of performance for the existence of time and the universe - to find the final answer to the greatest question of life, the universe and all this. After seven and a half million years of calculations, "Deep Thougoht" issued an answer: "Forty-two". The reaction was like this:
- Forty two! Lunkool screamed. - And that's all you can say after seven and a half million years of work?
"I am very carefully checked," the computer said, "and with all certainty I declare that this is the answer." It seems to me that if you are absolutely honest with you, then the thing is that you yourself did not know what the question is.
- But this is the great question! The final question of life, the universe and all of this! - Almost overwhelmed Lunkkouool.
"Yes," the computer said the voice of an sufferer who enlightens the round fool. - And what is this question?
DOUGLAS ADAMS "THE HITCHHIKER" S GUIDE TO THE GALAXY "
Following the main postulate of management that we cannot manage the fact that we cannot measure, it is necessary to create the conditions for managing training specialists in the specialty computer security. The main question or purpose that is set in this work is the creation of the most adequate competence model of a specialist who would take into account the needs of the market in such specialists, the requirements of enterprises to such employees, as well as the possibility of the highest educational institution on the preparation of such specialists.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the advanced domestic and foreign experience in the field information technologies, psychology and recruitment of personnel. For mostly, computer security specialist will face the work of modern information systems, as well as to prevent unscrupulous people to take possession of information that makes up commercial value.
This paper is divided into three chapters. The first chapter provides an understanding of what is considered competence, what to consider the competence model, which methods are used in practice to create a qualitative competence model of a specialist.
The second chapter provides a description of the competence model, which was compiled as a result of the analysis, classification and summarization of the material of the Association of Computer and Information Technologies (APPC) on the third generation of the third-generation standard for specialties associated with information technology, as well as competencies that indicate OJSC " Svyazinvest "for information and economic security professionals. It is important to note that the apkit when creating competenced models used the experience of companies such as ABBYY, Intel, Microsoft, Motorola, IBM, Oracle, 1C, EMC, Sun, Cisco, Luxoft, Kaspersky Lab, which are leaders in the information technology industry and their requirements for Training of specialists are based on the real needs of this market.
The third chapter provides a summary of the resulting model of a specialist and assess the existing level of training specialists in the specialty computer security for compliance with the developed model. In addition, further paths are indicated to improve the competence model itself and the improvement of the educational process.
Chapter 1. Basic concepts, types and structure of competencesWireless telegraph is easy to understand. The usual telegraph is similar to a very long cat: you pull the tail in New York, and he meows in Los Angeles. Wireless is the same, only without a cat.
Albert Einstein
Basic concepts from the field of competencies
To begin with, we denote the basic concepts that we will operate, considering competencies. This is necessary for a uniform and clear understanding of the outlined material. Given the diversity of various definitions and interpretations used in theory and practice, it should be remembered that the cited definitions are not true in the last instance, but only the options that are used in the outlined material. The proposed definitions are not standardized, but they allow you to correctly designate the main terms used in the present work.
Unfortunately, several popular and frequently used expressions have been historically stuck in Russian, including single-handed words with the word "competence". This significantly confuses when trying to comprehend the essence of the concept of "competence" in relation to the training of specialists in the university and to business in the field of personnel management. For example, we love to say: "He is not compressed", "this is not included in the area of \u200b\u200bmy competence." "He does not mean at all that a person does not have any competences. As a rule, these expressions hides an assessment of the level of authority of the subject. And there has nothing to do with the terminology used in the competency system.
First of all, we denote the difference between the concepts of "competence" and "competence". At their basis, the Latin Compete root - I am achieving, corresponding to it.
Competence is a certain characteristic of the person necessary to fulfill certain works and allowing it to receive the necessary results of work.
Competence is the ability of an individual with personal characteristics to solve work tasks, to obtain the necessary results of work.
In other words, the competence is the standard of behavior required for certain activities, and competence is the level of possession of this standard of behavior, that is, the final result of its use.
Key competencies - a set of competencies, allowing an employee to fulfill its professional job responsibilities as efficiently as possible.
Zun - Knowledge, skills, skills.
PVC - professionally important qualities: individual qualities of a subject of activity that affect the effectiveness of activities and the success of its development. "Professionally important qualities are quality, important for profession, whatever a company."
Competence model is a structured set of necessary, identifiable and measured competencies with behavioral indicators.
Indicators of behavior are standards of behavior that correspond to the effective actions of a person with a specific competence. At the same time, as a rule, the object is the manifestations of a high level of competence.
Competence clusters are a set of competencies (usually from two to five), interconnected into a single semantic unit. Most often in models, clusters are distinguished as: intelligent (thought) activities, achievement, work with people, work with information.
Types of competence
Speaking about the types of competencies, one significant points should be noted:
- species diversity of competencies in the absence of standards;
- The existence of several classifications, that is, a species diversity (a single classification of the types of competencies does not exist, there are many different classifications on different grounds. To navigate in this variety of species is very problematic. Many classifications are extremely inconvenient and not necessarily, which makes their use in practice extremely difficult. But Anyway, the current situation affects the practice of building a competency model).
In various theoretical and practical materials on competencies, you can find a variety of typology. In world practice, there are examples of attempts to develop universal typologies and models of competencies applying for the status of a global standard. For example, the SHL is a global leader in the field of psychometric assessment and solutions development - in 2004 declared the creation of a universal basic structure of competencies by a group of consultants under the direction of Professor Dave Bartram. Basic structureCreated by the Bartram group included 112 components headed by the so-called "large eight competencies". It is possible that the global tendencies of unification will soon lead to the fact that the standard is universally recognized by everyone. Competence is a rather peculiar tool, so it is almost very difficult to create a single set of competencies that any university and any company can enjoy.
In addition, we should not forget that the competence must be measured. That is, Introducing the competence, it is necessary to check it on the possibility of evaluation. It is important to remember exactly when developing a competency model, because It is often great for their temptation to include personality qualities of a social character. For example, "Justice". Measure the presence of this competence in a person is very problematic, because The concept of "fair" is largely relatively and difficult to identify.
Professional competencies on the scale are localized. But a certain set of professional competencies is inherent in any job position and / or specialty. This type of competence is a set of personal characteristics, as well as knowledge, skills and skills necessary for effective work on a specific job position. Given that our classification of competencies is limited by the university framework, the professional competences of the post and professional competencies of activities or professional regions should be not confused.
Professional competencies of activities and regions are more generalized. And professional competences are limited by the framework of a particular company. For example, there may be competencies of the employee of the pedagogical sphere - they are characteristic of all specialists leading pedagogical activities, regardless of the organization in which they work, and there may be proxy competencies of the teacher of a particular training organization. Speaking about professional competencies as the form of competencies, we are talking about them.
Table 1  Management competencies - the most localized and sophisticated view competences. These are the competences necessary to fulfill the leading responsibilities to those who will occupy managerial positions be it management personnel or system administration. Oddly enough, the development of management competencies is most complex - the temptation is too great to create a model of an ideal supermen player, which is unlikely to be able to implement in practice. Therefore, when developing it is recommended to include the optimal set based on the principle of necessary and sufficient competencies in the list of managerial competencies.
Management competencies - the most localized and sophisticated view competences. These are the competences necessary to fulfill the leading responsibilities to those who will occupy managerial positions be it management personnel or system administration. Oddly enough, the development of management competencies is most complex - the temptation is too great to create a model of an ideal supermen player, which is unlikely to be able to implement in practice. Therefore, when developing it is recommended to include the optimal set based on the principle of necessary and sufficient competencies in the list of managerial competencies.
Competence structure
The competency structure serves as the basis for developing a competency model. About what is the model of competencies, we will talk further.
And now about its own structure of competencies - about which elements are competence and what these elements are represented, see Table. one.
From the table we see that the structure of the competence is quite complex, including many elements, the combination of which does, in fact, the competence of the universal tool, which we are talking about. From the presented structure, it becomes clear why only Zong or PVCs cannot be considered under the competence, which are only an element of competence. 
Figure 1. Full universal structure competencies (start).
It should be noted that in theory and practice of constructing a model of competences there are various types of competencies. For example, it is actively used, the so-called launch is a complete universal structure of competencies (see Fig. 1).
In addition, many do not use ready-made developments, they fundamentally go their own way and develop their own competencies. This is justified and efficiently only if the development of the model is engaged in experienced specialists, since for beginner developers this task is either no forces or threatens to create an incorrect and inefficiently working structure of competences.
Competence model
The model is a logical description of the components and functions displaying the essential properties of the simulated object.
The competency model is a logical description of the elements and functions of competencies. The competency model contains detailed description Human behavior standards holding a specific position leading to the achievement of job goals.
The degree of detail in the competence model depends on the purposes for which the model is applied. Some seek to cover the whole range of information and develop a model for all occasions. Such a model is usually very complex in use and ineffective. In addition, it is very difficult to develop, since, according to experts, the difference between many competencies is extremely small and hardly distinguishable. The experience of the recent years of use of the competency model shows that the competency set should be optimal and include key behaviors.
Our task is to show the logic and technology of development and application of the competency model in simple version.
The role of the competency model in the management system. Areas of use
Competencies are most closely related to the strategy. educational processAccordingly, their purpose is to promote the implementation of strategic goals. This task is the competency model solves through certain functions and the applications of these functions. Application areas are shown below. Functions are a type of specific activity through which the competency model works in a particular area. For example, in the field of training and development of personnel, the competency model works through the evaluation of the zone of the missing competencies from the employee. Consider them in more detail.
As mentioned at the very beginning, the competency model is a multifunctional and almost universal tool, so it works in various fields of management. First of all, in managing human resources.
Contents of the competency model
As it has already become clear from all the above, the content of the competency model includes:
- full set competences and indicators of behavior;
-Education of behavioral standards or standards of actions leading to the fulfillment of the tasks and achieve goals;
- levels of competencies (if provided for and applied).
In itself, the content of the model is not a guarantor of creating a tool to improve the efficiency of the educational and workflow. The efficiency of the model depends on the quality of the content. And the result of using the model is directly related to the quality of organizational activities and the harness of the entire management system. Unfortunately, very often competencies, including all the necessary elements, however, do not give the expected effect, but only spend the resources for their maintenance. Often the reason for such a situation in the poor-quality content of the model.
The quality content of the model must meet the following criteria:
1. Compliance with the strategic objectives of the industry. This means that the desired competencies should contribute to the further activities of graduates in various companies in the profile industry aimed at achieving these objectives, and not include a full conceptionable and unthinkable set of possible competencies.
2. Usefulness for all those involved in its operation (specialists of various companies using a model as a tool, teachers). It should be remembered that the subject of the model are students who also have their own goals, their motives of labor activity and their needs. This means that the model should also be of interest to students and be useful.
3. The optimal set of model elements, no repetition and intersections.
4. Measurement of competencies and the availability of the accounting system of expected changes. The optimal set of competencies and their measurement is aimed at the comfort of operation of the model, the objectivity of measurements and the ability to efficiently use the results obtained. The presence of the accounting system of expected changes makes it possible to obtain the desired spectrum of the application of the system and makes the system useful to all participants. For example, the assessment of students and teachers based on the competency model, with success, replacing certification, in the presence of the accounting system, allows you to competently plan the career development, trace the dynamics of changes and link the results with payroll. It also establishes the relationship between the development of a student and the growth of his future wages, makes his expectations realistic.
5. Easy and transparency of the competency model. Highly an important point The content of the competency model is its volume. Some manage to develop such a bulk model that its description is an imaginary volume with a multi-part-in-room description of hundreds of competencies and multiple examples. Everyone pre-reds know that the more extensive any instruction, the less chances of being at least fully read, and not what studied. This rule is also valid for the description of the competency model, although does not mean that the documentation describing the system should be a miser and extremely brief, but when it is created, it is necessary to comply with the rule of optimality.
Competencies should be not only accurate, but also by politically correct, non-self-taking self-esteem. For example, is it correct to measure the honesty of a person and what to do if its level is insufficient?
The competency model can be simplified (without levels of competencies) and more complex (with levels). A simple model of "competence without a level" contains only basic standards of behavior and, as a rule, the same for all set of behavioral indicators. It does not take into account the levels of preparation. The competency model may contain so-called levels of competence and allows you to cover a wider range of students' training levels and take into account various nuances. And such a model is called "competencies in levels". In this case, the indicators of behavior for the same specialties belonging to different levelswill be different. For example, for the administrator and the manager, some competencies may well be coincided, but the level of their manifestation is different, depending on the level of authority and responsibility.
The structure of the competency model is clearly demonstrated by a schematic image. As an example, the following is a scheme of the so-called format-cluster competency model (see Fig. 2). 
Figure 2. Format-cluster competency model.
Profile competences
Competence profile, in fact, is a set of competencies that the employee must have, relevant position, or a graduate of a specialty that meets the requirements for graduates of the university. But this is not just a set, but a list that includes the necessary level of development of each competence for a specific specialty / position. The competency profile is most often in the form of a diagram that allows you to visually illustrate the required level. After evaluating the level of competencies existing at the employee, the chart is compared. It becomes obvious to the discrepancy of the required level and valid. The difference between them is the area of \u200b\u200btraining and development of the employee.
Thus, the competency profile is a very simple and convenient "visual manual" when using the competency model. An example of such a profile is insulated in Fig. 3. 
It is important to note that the competency profile is not statical, it has a property to change. And the required levels of competencies are changing. This is due to the development of a person with time, as well as changing qualifications requirements. In the development of the competency model, the set of competencies may also change. Therefore, the developed competency profiles cannot be used for a long time, they have a certain "shelf life". But this does not mean that they need to be developed every time. They require verification of relevance before use and, if necessary, actualization.
Chapter 2. Diversified Competitive Computer Security Specialist ModelOpening of order is a difficult task, but if it is found, it is not difficult to understand it.
Rene Descartes
Sources close to the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation propose to initially classify the competence of graduates in two large groups:
- General competences (universal, key, superofessional);
- Specialized competencies (professional).
So, summing up the previous paragraph, let's say that the main task of a competence approach in education is to establish conformity between the capabilities of the educational institution, the requirements of the real sector of the economy and the abilities of the studying.
Since the highest educational institutions are at the stage of waiting for the third generation standards, or they are trying to prove somehow on their own that the third generation standard from the standard of second generation differs only by renaming the subject for competence; Students and applicants are in a state of happy ignorance that they are expecting after the end of the university, and the real sector of the economy is fighting with the consequences of financial and economic crises, it is proposed to consider the requirements of enterprises presented to computer security specialists.
The search for information on open sources (actually on closed too) did not give results precisely on the competence model of a computer security specialist in the new generation. However, an interesting article was found to S. M. Avdoshina. In the article, the author summarizes the experience gained in the design of information standards for the information standards for the information technology industry. So, this project was carried out under the auspices of the Association of Computer and Information Technology Enterprises (APPC) and on the website of this association in free access there are the following competence models of specialists:
1. Programmer;
2. System architect;
3. Specialist in information systems;
4. System analyst;
5. System Administration Specialist;
6. Information Technology Manager;
7. Database administrator.
Why do we need all these, at first glance, not related to the case, competence? The fact is that at the heart of computer and information security lies the postulate that only an integrated approach can bring success in the field of security. Information security is a relatively young, rapidly developing area of \u200b\u200binformation technology, for the successful assimilation of which it is important from the very beginning to assimilate the modern, coordinated with other branches of information technology bases. Those. All of the above competencies in the field of information technologies are necessary as a basis for building a high-quality versatile competence model of computer security specialist.
Created apkit Competent models are divided into qualifying levels from the lowest level 1 (Assistant system administrator, personal computer operator) to the highest level 8 (information technology manager who has a scientist and experience in a senior position of at least 5 years). In addition, according to these qualifying levels, the competence models proposed by the apkit are divided by the training of bachelors, specialists and masters.
According to the current HIP standard for the specialty "Computer Security": "The regulatory term for the development of the main educational program for training a specialist information protection specialty 075200 - computer security with full-time learning is 5 years 6 months." Those. Students pass 6 training courses, therefore, by some competence models developed in the apkit, the qualification levels of masters can be taken as the basis.
Based on the foregoing, choose the following qualification levels:
1. Programmer - 3 Qualification level;
2. System architect - 4 Qualification level;
3. Information Systems Specialist - 3 Qualification Level;
4. System analyst - 3 Qualification level;
5. System Administration Specialist - 5 Qualification Level;
6. Information Technology Manager - 4 Qualification Level;
7. Database administrator - 4 qualification level.
So, if you simply combine the method of addition and skills that correspond to the above list, it will be more than 2,000 positions containing skills and skills, and they will be repeated, because We are talking about one industry. If you allocate only unique skills and skills characteristic of all the above-described basis competence models from the field of information technology, then 673 unique skills and skills that specialists from APCC are considered necessary for the preparation of specialists of the relevant profiles to the standard.
But with a list of more than six hundred skills and skills (not counting), it is enough to work quite problematic for the specifics of the perception of information by the human brain, then it is necessary to somehow classify these skills and skills to reduce the complexity and complexity of work on creating a competence model.
Following the methodology of object-oriented analysis and design, so that the specialist model looks like a model, and not as a pile of difficult and difficult-to-distant competencies based on skills and skills. It is necessary to classify competencies. Since there are no methods for creating an ideal classification, it will have to rely on your own intuition and experience.
The first thing comes to mind is the following classification:
Foreign unit first (subject)
1. Mathematics;
2. Physics;
3. Information technologies;
4. Economics and guidelines;
5. Security in a broad sense.
But how it differs from the State HPE 2 generation, in which it is the meaning model. Perhaps nothing. Therefore, it is better to offer classification based on skills and skills, but not knowledge. Knowledge in the model must be in symbiosis with skills and skills.
The following initial classification of competencies is proposed:
1. Documents and standards (global and domestic standards on informational technologies, protection of information, sanitary and fire safety, CS, Quality Standards, Federal Laws, KZOT, FSTEC Guidelines, Other Regulatory Activities, Internal and Project Documentation)
2. Personally business qualities and motivation (abilities, self-development, stress resistance, the ability to mobilize your strength in a short straight interval, the ability to convince, the ability to listen, the ability to subjugate yourself a crowd, focus on the result, high level of self-motive)
3. Programming (Languages \u200b\u200bProgramming, the process of creating software, methods for ensuring the quality of software products, inspections, etc., etc.)
4. Operating systems, computers and networks (ideology, architecture, design, implementation and maintenance)
5. Databases (creation, administration, protection)
6. System analysis and management (analysis of any information systems, business processes, infrastructure management)
7. Working with people (interaction with customers, personnel management, interaction with users, work with permitting and authorized bodies, work with government representatives)
8. Economic Security (Economics, Basics of Accounting and Audit, Property Forms, Interests of Crime, Physical Safety of Objects, Organization of Security Regime at the enterprise, Understanding the interaction of all company structures, the ability to conduct official investigations, interaction with the Ministry of Internal Affairs, FSB and other power structures, understanding Basics of business analysts, basics of psychology)
9. Instrumental control (preventing information leakage on physical fields, bookmarking and bugs detection, checking equipment for the presence of foreign storage devices in it)
10. Information Security (Encryption, VPN, Firewall, Antivirus, IDS, Sauble, Passwords, Data Recovery, Security Policies).
In the course of further work on the classifications of skills and skills were divided into subclasses, which are given in the subsequent sections of this chapter.
Documents and standards
Development of documentation
Project documents
- Develop project documents
- Develop individual provisions of the project charter
- Main project account
- Develop project documentation using graphic specifications
- Document the results of work
- Develop a package of contractual documents
- Participate in the preparation of a technical task
- Participate in the development of technical task
- Make a technical task
- Develop technical tasks in accordance with the requirements of state, sectoral and corporate standards
- Develop acceptance schedules, mounting and testing
- Develop graphs of audit technical documentation, regulations, instructions
- Conduct reports on the results of the functioning of software and hardware
- Develop reports and documentation
- To form reporting documentation on the results of work
- Develop reporting documents in accordance with the requirements of state, sectoral and corporate standards
- Drawing up information reports on availability software
- Draw up and execute reporting documentation
- Compile terminological directories on the subject area
- Develop documentation for the operation of the information system
- Develop technological documentation
- Form technological documentation on the results of work
- Develop fragments of information system documentation
Coordination of documentation
- Justify decisions on adjusting and making changes to regulatory operational documents, instructions and technical documentation
- Prepare proposals for adjusting and making changes to regulatory materials, instructions and technical documentation
- Provide an inventory schedule
- Coordinate and approve the regulations and procedures for maintaining and updating the documentation
- Coordinate technical documentation
- Make decisions on adjustment and amendments to regulatory materials, instructions and technical documentation
- Update operational and technological documentation
- Maintain the relevance of project and technical documentation
- Turn the correctness and timeliness of filling the necessary documentation
- Check the developed documentation for the compliance of the organization standards
- Make conclusions to the documentation of related organizations
- Analyze the results of work on reporting documentation
- Analyze the content of the documentation
- Approve graphs of technical documentation checks, regulations, instructions
State and sectoral standards
- Develop documents in accordance with the requirements of state, sectoral and corporate standards
- Develop regulations in accordance with the requirements of state, industry and corporate standards
- Register technical tasks in accordance with the requirements of state, industry and corporate standards
- Comply with fire safety rules
- Comply with the rules of work
- Ensure respect for the ergonometric requirements and norms of industrial sanitation when organizing jobs
- Apply International, National and Corporate Standards
- Comply with environmental requirements
- Work with reference and regulatory documentation
- Apply regulatory and project documentation
- Apply regulatory and technical documentation in the field of information technology
- Work with reference and regulatory documentation, patent search
Teamwork
- Lead
- Spend the culture of interpersonal communication
- Clarify the formulation of tasks
- Work in a team
- Defend and argue your position
- Take responsibility for the decisions made in the framework of professional competence
- Rationally organize your work in the workplace
- Plan and organize your own work
- Plan your activities
- Assess the borders of one's own competence
- Responsibly approach working tasks
- Develop research plans - practical work
- Maintain and raise professional and personal image
- Observe the rules of time
- Show innovation and creative approach in professional activities
- Produce self-control of the quality of work performed
- Forming accuracy, discipline, responsibility, operational
- Comply with the cost of material resources and time
- Show a creative approach and initiative in professional activities
- Apply standards
- Cope with a variety of job tasks
- Make decisions in the framework of professional competence
- Qualitatively perform the task
- Make decisions in competence
- Exercise a creative approach
- Be responsible for the result of your professional and administrative activity
- Own practical methodologies to manage project and process activities
- Own business applications
- Own business applications
- Work with various types of source data in the subject area for surveying
- Read technical documentation in English
- Work with various types of source data on the information system
- Work with various types of source data on the subject area
- Read project documentation for the development of the information system
- Follow the novelties in the field of network software
- Read professional literature
- Work with documentation and technical literature
- Read the documentation and technical literature in English
- Read the models described using specialized formalized languages \u200b\u200band notations
- Improving the knowledge of a foreign language
- Work with various sources of information
- Monitor new literature on system administration
- Work with various types of source data in the subject area
- Read vocational literature in English
- Follow the innovations of domestic and foreign professional literature
- Read project documentation designed using graphic language specifications
- Evaluate the prospects for the development of information and communication technologies
- Own practical methods for managing project and process activities
- Analyze domestic and foreign experience of working out failures
- Adapt advanced domestic and foreign experience
- Own tools express enterprise survey
- Be responsible, disciplined, neat, executive, initiative, attentive, capable of learning, develop analytical abilities
- Analyze your own professional experience and improve your activities
- Own office and system-wide software
- Master new methods and technologies in the field of information systems and project management
- Develop stress resistance, systemic thinking, tolerance, logical thinking discipline, accuracy, responsibility, demanding, sociability, ability to convince
- Master new technologies
- Develop the flexibility of thinking, systemic thinking, initiative, self-confidence
- Develop Analytical Thinking, Responsibility, Communication, Creativity, Initiative, Emotional Restraint, Leadership and Organizative Qualities
- Improve the objectivity of perception, flexibility of thinking, systemic thinking, focus on the result, initiative, learning, the ability to take others, self-confidence, responsibility, adaptability, accuracy, discipline, goodwill, sociability, stress resistance
- Develop responsibility, discipline, accuracy, durability, initiative, attentiveness, learning, analytical thinking
- Raise professional level
- Develop accuracy, analytical thinking, methodological, responsibility, discipline, sociability, creativity, operational, organization, initiative
- Follow the development of new information technology
- Organize self-study and increase your qualifications
- Develop an analytical thinking, methodological, responsibility, discipline, sociability, creativity, organization, initiative
- Develop in themselves stress resistance, systemic thinking, tolerance, logical thinking, discipline, accuracy, responsibility, demanding, communicability, learning, ability to convince
- To determine the topics of research
- To master new methods and technologies in the field of information systems and networks
- Develop new methods and technologies
- Continuously improve qualifications
- Follow domestic and foreign developments in the field of information and communication technologies
- Participate in scientific and practical conferences and seminars
- Hold presentations
- Follow the schedule for holding exhibitions, conferences, seminars
- Writing and verbally to express your suggestions and the results obtained for various audiences.
- Participate in conferences, seminars, symposia
- Prepare and conduct technical presentations
- Participate in scientific conferences, seminars, symposia
- Own the skills of the presentation
- Own presentation technology
Programming languages
- Own modern programming languages
- Own the basics of modern programming languages
- Use programming languages \u200b\u200band software development tools
- Optimize program code Using specialized software
- Find coding errors in the information system being developed
- Software development in modern programming languages
- Own versions control systems
- Selection of software and storage and storage of information on acquired and developed software
- Analyze source information to describe processes, data, subject area objects
- Own the main methods of software development processes
- Own integrated development media
- Own methods of abstraction of specifications to the level of requirements
- Own basic software development methods
- Own technology integration of design components and subsystems and supporting tools
- Use funds and methods for developing requirements and specifications
- Describe system architecture
- Use methods and technologies for the development of formalized requirements and specifications for generating an executable code and tests according to formal descriptions.
- Use methods and technologies for using development tools to obtain code with specified functionality and quality
- Use methods and technology testing and reviewing code and project documentation
- Apply formalized languages \u200b\u200band notations to build models of processes, data, objects
- Apply specialized methodologies to build models of processes, data, objects
- Apply specialized methodologies for building software systems architecture
- Construction of models of processes, data, objects
- Develop experienced test programs
- Describe system use scenarios
- Apply effective development methods
- Determine the composition and amount of information necessary and sufficient to build adequate, complete and consistent software architecture
- Create modeling stands and experienced technological sites for working out typical design solutions
- Collect information for describing processes, data, subject area objects
- Apply Specialized Project Development Software
- Conduct object-oriented analysis
- Evaluate the feasibility of requirements
- Use methods and development technologies to generate tests for formal descriptions
- Use methods and technology verification formal specifications
- Apply effective design methods
- Evaluate the compliance of the program code of the computer system architecture
- Develop requirements for software
- Use specialized software to build models
- Design software using specialized software packages
- Use methods and means of developing test scenarios and test code
- Use methods and technology testing and reviewing code and project documentation to control the achievement of specified functionality and quality in the program project
- Conduct analysis of existing approaches, methods and tools solving the selected task class
- Apply specialized software to build models of processes, data, objects
- Apply methods and technologies for using development tools to obtain a code with a given functionality and a degree of quality.
- Exercise object-oriented design
- Apply the methods of testing developed information systems
- Simulate systems based on finished architecture
- Develop architectural software design
- Develop and implement advanced design technologies
- Develop technical tasks for work
- Implement object-oriented development
- Make optimization of developed solutions algorithms
- Develop easy applied tasks
- Develop test scenarios on requirements specifications
- Program in accordance with the requirements of the technical task
- Develop recommendations on adjustments computer Systems in the process of developing testing and implementing
- Design software with the use of specialized software packages
- Use methods and development technologies to generate executable code
- Own methods for analyzing software architecture
- Own methods and instruments for analyzing and designing
- Own methods and instruments for analyzing and designing software
- Own reengineering technology
- Make changes to the work of the developed programs
- Analyze the results of expert testing of information systems at the stage of pilot operation
- Use software project metrics to measure its characteristics.
- Make debug program
- Use methods and technologies for the development of formalized requirements and specifications for controlling the ordered functionality and product quality
- Evaluate the quality of the software
- Evaluate the quality of the built model
- Evaluate the quality of the program code
- Organize and conduct expert testing of information systems at the stage of trial operation
- Evaluate the quality of the program code for making decisions to change
- Evaluate the functionality of the software
- Evaluate the laboriousness of development on the basis of a requirement or technical assignment
- Evaluate the program code for compliance with standards
Software
Monitoring the current status of
- Establish restrictions on the use of resources
- Compare characteristics of software and hardware
- Present the presentations of new software and technical means
- Determine the compliance of technical means and software
- Conduct the calculation of indicators of the use and operation of software and technical means
- Carry out an inventory of software and technical means of the system
- Maintain server software operating status
- Choose program technical means monitoring
- Install updates to server operating systems and software
- Install, configure and configure monitoring software
- Install and customize backup system software
- Customize software
- Configure specialized software
- Install information systems
- Install and configure new hardware and software
- Install / customize software
- Establish complex application information systems on servers and workstations
- Install network software on servers and workstations
- Install and configure system software on user computers under the guidance of a system administrator
- Justify the need to purchase software and hardware
- Make a schedule for the modernization of software and technical means
- Conduct a feasibility study of the introduction of new software and hardware
- Formulate recommendations for updating or replacing software
- Develop proposals for modernizing software and hardware
Fixing events and documentation of various procedures related to the operation of the equipment
- Fix and analyze the files in the server and network equipment
- Check equipment labeling
- Comparison inventory numbers
- Fix the results of acceptance, installation and testing
- Register applications for the purchase of equipment and materials
- Mark computers and peripherals
- Monitor the implementation of the schedule of inventory
- Plan work on deployment, configuration and operation of the computing complex
- Fix in log Calls to eliminate office equipment
- Develop standards on the status of software and hardware parameters
- Develop the rules of acceptance, installation and testing of new hardware, software and communications
- Dismantling damaged peripheral devices
- Inform the system administrator when the equipment is detected and the following orders
- To bring to the attention of the system administrator questions about the emergence of freelance situations in the framework of job responsibilities and the relevant classifier
- Apply equipment diagnostics and equipment testing
- Timely perform small repair of equipment
- Control the quality of repair and restoration work
- Check the service component
- Check the functioning of the device
- Conduct the necessary test checks and preventive inspections
- Detect the causes of the peripheral equipment malfunction
- Pick up components to execute applications
- Carefully selection and replacing cartridges, fax paper
- Analyze the programming facilities program
- Operate equipment in accordance with service specifications and service standards
- Manage server resources
- Provide timely execution preventive work
- Identify outdated equipment and software
- Maintain a corporate web server and internal web servers
- Check power
- Control operation of software and hardware for compliance with technical conditions and maintenance regulations
- Install components in a personal computer
- Organize transportation of components
- Provide monitoring compliance with the rules of acceptance, installation and testing of software and equipment
- Determine the optimal hardware configuration
- Control the technical condition of the equipment
- Control operation of server and network equipment in accordance with the technical conditions and service provisions
- Monitor server performance
- Install the device according to the instructions
- Configure Systems and Software on Servers
- Administer servers
- Analyze the results of monitoring the functioning of software and hardware
- Implement and exercise technical support Server solutions
- Analyze the status of software and hardware parameters
Monitoring and monitoring the status of ICIS
- Monitor the status of the information system
- Ensure control of the technical condition of communication objects of network infrastructure
- Monitor use computing network
- Monitor the performance of the computing network infrastructure
- Count Indicators of networking resources
- Determine the purpose of monitoring
- Evaluate the status of information resources
- Analyze Indicators Using Computer Network
- Accompany postal system
- Perform regulations for updating and technical support of the information system
- Ensure the availability of data collection and technical means for analyzing the indicators of the use and operation of the computer network.
- Ensure information sharing with other organizations using email
- Setting the information system
- Make optimization of developed information systems
- Ensure the smooth operation of the computing network
- Provide data collection for analyzing computer network software and technical
- Test new hardware, software and communication components entered in the network configuration
- Maintain the relevance of network infrastructure
- Develop and implement advanced system administration technologies
- Maintain network equipment
- Installation of the information system
- Apply new system administration technologies
- Maintain and update knowledge in the field of system administration
- Select the information system in accordance with the functional requirements for it
- Install the information system
- Check the ability to install and connect to the network
- Operate equipment included in the system and hardware system configuration
- Identify and analyze the causes of problems in information systems
- Give an accurate technical wording of problems
- Identify and analyze the causes of problems in computer systems
- To identify technical problemsarising during the operation of the system
- Perform preventive work
- Make a plan for preventive work together with the system administrator
- Inspection of network infrastructure and workstations in accordance with the approved schedule
- Eliminate technical problems arising during the operation of the system
- Inform database administrator when troubleshooting is detected
- Develop methods of expert testing of information systems at the stage of pilot operation
- Develop regulations on updating and technical support of the information system
- Develop formats and regulations of information systems interaction
- Develop schemes and procedures of the aftervaria restoration of the computer network
- Develop the aftervaria repair schemes of the computer network
- Implement the presentation of infrastructure development plans
- Keep records and analysis of network resource use indicators
- Keep records and analysis of operating conditions
DBMS
- Use software and technical data collection and data processing
- Install and configure the necessary updates for database management systems.
- Analyze the market for modern database management systems and databases
- Update database software
- Install and customize data collection software
- Predicting productivity and required database resources
- Maintain and update knowledge in the database administration field
- Select databases and database supplier
- Identify and troubleshoot in the operation of database management systems
- Organize and ensure uninterrupted operation of database management systems and databases
- Process information
- Analyze information
- Stru's information
- Save data on interchangeable media
- Calculate information
- Restore information
- Own data processing toolkit on a personal computer
- Restore data in the database
- Preparation and save backup data
- Compile data archiving plan
- Development of information collection and storage regulations
- Move the data archiving log and the degree of media use
- Control structural changes in databases
- Monitor the use of databases
- Conduct a feasibility study for the introduction of new database and database management systems
- Apply regulatory and technical documentation using database and database management systems
- Prepare reports on the operation of database management systems
Management of project activities
- Analyze the risks of the project
- Control the content of the project
- Check the compliance of the work performed by the requirements of project documentation
- Project Transition Stages Management
- Project Plan Development Management
- Manage the integration of the project
- Describe the main design solutions
- Manage the project budget
- Own project management tool
- Apply Project Management Toolkit
- Lead operators and technicians entering the duty shift and coordinate their activities
- Define the composition and amount of information for building an adequate, complete and consistent model
- Manage project resources
- Rationally allocate resources during the project
- Manage project risks
- Project development management
- Evaluate the necessary resources for work
- Evaluation and improvement of project execution
- Forming recommendations for adjusting the results of work
- Product Adoption Management
- Manage the quality of the project
- Control the distribution of resources during the project
- Work with various types of source data on the subject area
- Manage acceptance of project work
- Check the compliance of the work performed by the requirements of project documentation
- Manage project contracts
- Develop a list of works on stages
- Develop the project charter
- Manage the project schedule
- Manage project technologies
- Adapt new trends in scientific and technical development
- Evaluate and substantiate the complexity and timing of analytical work
- Analyze the organization's development strategy
- Control the actualization of documentation
- Justify proposals for the implementation of the Information Technology Strategy
- Determine the work of work
- Conduct a comprehensive analysis of problems in organizing the work of the customer's enterprise and identify the reasons for their occurrence
- Evaluate the needs of the organization in information resources
- Control the execution of work transferred to outsourcing
- Control compliance with the cost of material resources and time
- Identify and describe enterprise business processes
- Determine sources of financing scientific works
- Determine the limits of applicability of system analysis methods
- Control the work of suppliers and adjustments
- Control filling the relevant documentation
- Control the quality of the supplied products and services
- Plan the development of the technical base of the organization
- Model organization activities
- To form functional requirements for the information system to solve the business task of the enterprise
- To form recommendations to improve the efficiency of business processes
- Work with various types of source data on the status of the information system market.
- Form scientific units
- Predict the deadlines for the modernization of information infrastructure
- Organize system integration work
- Analyze the causes of problems incidents
- Develop technical and managerial solutions to replace and modernize software and hardware
- Analyze the results of monitoring on the use of the computer network
- Analyze technological and architectural solutions in the field of informatization
- Analyze the quality of work on the compliance of software and hardware instructions
- Analyze the acts of accidents
- Define bottlenecks in the functioning of information systems
- Analyze the protocols of system and network events
- Find ways to improve the efficiency of the enterprise using the capabilities of information systems
- Analyze operating modes and operating conditions
- Analyze failure statistics
- Control the implementation of the procedure for writing off the technical means
- Evaluate the quality of the system built architecture (adequacy, completeness, consistency)
- Formulate tasks in terms of system analysis
- Regularly check reports on the results of inventory and write-off of software and hardware
- Ensure the interaction of information systems with the use of modern technological means and standards
- Control the presence and movement of software and hardware
- Determine the impact of system administration on the processes of other units
- Determine the regulations for modernization, modifications and work on improving reliability and durability
- Evaluate the status of software and technical resources
- Assess the effectiveness of tools
- To generate the required information system for the configuration of local computer networks
- Approve a schedule for the modernization of software and hardware
- Plan technical work
- Control the quality and volume of work performed
- Prepare proposals for making decisions about the purchase of equipment and software
- Control performance of work
- Analyze the dynamics of changes in indicators
- Develop a schedule test inspections and preventive inspections
- Analyze the results of work
- Analyze comments on the results of coordination
- Control the execution of test checks and preventive inspections
- Process statistical data
- Control the execution of work in accordance with the technical task
- Compound reports
- Control graphs of technical documentation checks, regulations, instructions
- Preparing reports to guide the IT division
- Develop a plan-schedule of work on stages
- Compile analytical reports on the review of new hardware and software solutions
- Plan and adjust the performance of work
- Track the approved schedule for preventive work
- Define and formulate priority tasks
- Define necessary parameters Monitoring
- Make analytical reports
- Control the charts of equipment supplies and work
- Draw up and justify the conclusions and make recommendations
Work with the customer
- Coordinate the timing of preventive work
- Develop methods of analyzing customer needs in the field of informatization
- Lead a business conversation with a group of customer representatives
- Make a business conversation with a customer's representative
- Analyze customer requirements for the use of information systems
- Identify and document the conceptual apparatus, basic ideas, methods and processes of the subject area of \u200b\u200bthe customer
- Use terminology, conceptual apparatus, basic ideas, methods and processes by the subject area of \u200b\u200bthe customer
- Evaluate the business task in terms of customer
- To choose with the customer optimal ways to solve problems
- Preparing materials for presenting to the customer
- Negotiate
- Own customer terminology in one or more subject areas
- Negotiate with the management of the customer's enterprise
- Hold meetings and negotiations
- Interview with key customer employees
- Document the results of interaction with stakeholders in the process of developing, testing and implementing computer systems
- Interaction with customers of services inside and outside the organization
- Customer Terminology
- Formulate a commercial offer
- Control compliance with technological, industrial and labor discipline personnel
- Comply with the rules of conduct in emergency situations
- Control compliance with the requirements of industrial sanitation and hygiene
- Comply with labor protection requirements
- Provide working conditions in accordance with the tasks performed
- Control compliance with fire safety requirements
- Analyze the efficiency of working time
- Monitor compliance with labor protection requirements
- Conduct control and analysis of the efficiency of working time use
- Processing the results of the questionnaire
- Structuring and analyze the requests of structural units
- Analyze user reviews
- Check knowledge and user skills
- Develop fragments of methods of learning information system users
- Analyze user needs
- Analyze user requirements
- Interact with the Customer in the Project Implementation Process
- Interact with customer representatives or specialists in the subject area
- Identify user problems
- Advise user information system
- Technical support of the process of learning and certification of users of the information system
- Organize in structural divisions Collect applications for installing software and hardware
- Organize user training with new system facilities
- Answer questions from user information system
- Develop fragments of learning techniques and certification of information system users
- Teach users
- Set the tasks to project performers and control their implementation
- Form a team of project performers
- Distribute work in the project performers
- Select executors of work and evaluate their compliance with the qualification requirements
- Conduct training performers
- Evaluate the results of the work of the project executors and adjust their activities
- Develop qualifying requirements for project executors in accordance with project tasks
- Conduct oral interviews
- Conduct written survey and oral interviews
- Process interviewing results
- Prepare and pursue
- Take part in the development of questionnaire
- Develop questionnaires for interviewing
- Conduct written questionings
- Preparing and conduct oral interviews
- Training and advanced training
- Participate in advanced employee qualifications when implementing new database and database management systems
- Plan the advanced training of specialists and their professional retraining
- Develop a schedule for advanced training of specialists
- Check the knowledge of personnel to fill the required documentation
- Conduct professional retraining in the introduction of new technologies
- Check the knowledge and skills
- Mentoring
- Participate in the development of educational materials
- Transfer knowledge and experience
- Exercise personnel training
- Organize and prepare together with other units technical meetings
- Collaborate with other employees in the working group
- Find and attract experts on adjacent and narrowly profile regions
- Distribute work in the directions between adjacent units
- Explain the algorithm for the interaction of system analysts, programmers and other specialists
- Plan, organize and monitor the work of system analysts, programmers and other specialists
- Analyze the problems of interaction of system analysts, programmers and other specialists
- Personnel Management
- Determine the needs of personnel and their qualifying level
- Plan the work of a group of performers
- Evaluate the work of the staff
- Provide rational placement and staff load
- Define qualifying requirements for work performers
- Maintain a high professional staff
- Organize and prepare technical meetings
- Plan the development of personnel potential
- Organize and control the work of subordinates
- Implement the Working Group
- Participate in the work of qualifying commissions
- Work with staff
- Set tasks to system analysts, programmers and other specialists
- Provide constructive feedback Project performers on the results of their work
- Introduce corporate culture and social ethics
- Create and maintain a microclimate in the team
- Argument and convince interlocutors
- Interpersonal relationship management
- Control conflict situations
- Motivate interaction partners
- Allow conflict situations
- Create and maintain authority in colleagues and customers
- Managing project participants
With competencies on economic security, the situation is much more interesting than with the information. The fact is that only departmental specialists are preparing in the territory of the Russian Federation educational establishments. But some information about the necessary skills can be learned from the leadership of large companies in which there are specialists in this area.
Analytical work and collection of information
- Keeps how to analyze the observed environment or facts: can analyze in particular, so that later you can come to the conclusion (that is, initially repulsted from the signs later to come, minimize the particular to the whole)
- With information and analytical work with sources of information on issues affecting the economic interests of society, the information is able to analyze information: collects significant and reliable information from a variety of diverse sources, determines the type, form and scope of the necessary information. Separates, classifies, sorts significant critical information for analyzing the "noise" information that can be neglected, monitors the quality of primary information so that further prediction methods are reliable. Selects individual topics in essential information, directions. Quickly processes and understands large amounts of information, delves into information. Interprets the information, the situation, given the context. Calculates the moves and options for the development of the situation
- When analyzing those facts that hit the spot, it is able to evaluate information for authenticity (understand the type of information: registered or true), without yielding to the momentary moods or judgments or the effectiveness of the data, can choose the correct version. Can find information about companies, people who are headed by companies (who are behind them, whose capital)
- Conduct analytical work
- Careful information: collects significant and reliable information from a variety of diverse sources, defines the type, shape and scope of the necessary information. Separates, sorts significant critical information for analyzing the "noise" information that can be neglected, monitors the quality of primary information so that further forecasting methods are reliable. Interprets the information, the situation, given the context.
- Consolidates, synthesize, grows and summarizes the data obtained during the analysis, conducts systematization of information. Saves necessary information In a convenient format
- Organize and conduct examination
- Organize conducting expertise
- Carry out expertise
- Optimize business processes
- Analyze the effectiveness of business processes
- Model business processes organization
- He knows the organizational structure of the company, the principles of interaction between units, the responsibility zones of a unit, the scheme of the organization of information, understands the structure of the organization of communication networks and possible sources (internal and external) threats of fraud on communications networks
- Demonstrates possession of the methodology for developing confidential information protection measures, fully represents possible paths Confidential information leakage capable of harvesting the company's economic situation is developing effective ways to prevent information leakage, including non-sabrmed paths
- It has an idea of \u200b\u200bthe forms of unfair competition, owns the methods of identifying unfair competition
- Knows how to work in the mode not a clearly formulated task or hypothesis, or with a minimum number of information
- Knows how to be attentive and observant to details of information, in situations in order not to miss possible facts or signs of threats to the enterprise
- When considering the violation, not only fixes the fact of violations, but is able to analyze and assume possible other non-obvious causes or goals
- Determines, including foreseen in advance, what violation of security protection will entail which financial (for example, a decrease in the company's capitalization) loss or other risks
- Owns the interview skills, including an interview when admission to work: can arrange to a conversation and to himself, it is able to establish contact with various types of people, owns the skills of accurate perception of the non-verbal language of communication (gestures, body position in space, intonation, facial and physiognomy and others), knows how to ask different types Questions and quickly respond to answers to get the necessary information, for example, the foundations of dismissal, can listen and direct the conversation. When working with people, it is extremely correct in its behavior and the use of received information (does not give other opportunities to suspect a person with whom he communicated, nothing that will be able to substitute him or put an interlocutor in an unsightly light, especially in the case of unverified information)
- Knows the organization of work in the law enforcement system, who in the structure of law enforcement agencies can respond to the request and provide information as information from law enforcement agencies can be renounced
- Owns a detailed idea of \u200b\u200bhow the employees of the departmental, private security and employees of private security enterprises are carried out by the service (which the employee should know what rights has the procedure for his work, which may have to ask for office visitors or regime objects)
- Knows the organization of work in the law enforcement system
- Knows internal regulatory documents of the industry and documents regulating security activities, the main provisions of law enforcement documents, the current Russian legislation on private detective activities, the basics of civil and criminal law, the rules of the internal labor regulation
- Owns knowledge of the constituent documents of the enterprise and other documents necessary to establish commercial relations with counterparties (license, etc.), knows where to make an official request for information about the counterparty
- Owns the basics of legal regulation of contractual relations: the skills of checking commercial documents, understands what a contract, the main points of the contract, how contractual relations are built, owns the general ideas about banking activities.
- When purchasing real estate, as well as when working on the company's property complex, the company knows how to check the history of the object, knows which documents should have the object of sale of real estate, which procedures for checking the history of the object exist
- Knows the main provisions of antitrust laws, criminal law, the legislation on the protection of intellectual property, the basics of civil and criminal law, is able to quickly find information in the desired chapter this documentprepare reference information
- Owns the basics of secret office work and confidential office work
Physical security of objects and alarm device
- Demonstrates systemic and complete ownership of the methodology of security activities and engineering -echnic aspects of the organization of protection and protection of facilities (for example, such as office buildings, cable farms, etc.), owns information on how the operated technical systems are organized and how physical protection is organized on Specific facility company
- Knows how to form a TK or attract specialists of contracting organizations to form technical specifications on the organization of engineering - technical system Protection of objects. Knows how to successively plan and organize the implementation of the system
- He knows various types of equipment, their comparative performance, the latest trends and modern developments in the field of engineering and technical protection of objects. Regularly monitors changes and innovations through exhibitions, receiving information with the help of established professional contacts with experts in these areas
- Knows operating systems and equipment, technical data and characteristics of equipment used (for example, fire detectors, receiving and control devices, automatic installations fire extinguishing), in addition to operated systems, has an idea of \u200b\u200bnew developments and their advantages
- Conditions to develop and create a fire safety system, fully represents the level of equipping existing objects, can lead weighty arguments in favor of strengthening one or another object.
- Knows technology and engineering - technically means of implementing and providing special communication
- It knows the mechanism of interaction and appeal to the controlling authorities (the principle of information transfer, the form of its provision, etc.)
- Understanding the physical foundations of interception of information on physical fields of side electromagnetic radiation
- Detection of side electromagnetic emissions
- Detection of mortgage devices (bugs, microphones, voice recorders)
- Check printed circuit board Devices for detecting foreign logical elements that are not part of the initial design of the device
- Give conclusions about the events held in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation and the regulatory documents of FSTEC
- Knows the technology of protecting information from leakage on technical channels (glasses, doors, etc.), methods of their liquidation, technology counteraction tools for technical intelligence
Following information security instructions
- Perform the requirements of information security instructions
- Control the execution of the requirements of the information security instructions
- Participate in the preparation of project documentation for the development of the information system
- Apply technical means of providing information security
- Develop safety system settings
- Set security systems
- Provide perimeter information security
- Control security system settings
- Can establish additional protection tools, maintain and operate these tools (protection systems from unauthorized PC access to delimit and limit access to the system), can adjust the perimeter protection systems (firewall), security analysis systems (specialized software products), can configure the intrusion detection systems (all for PC networks and data networks), SCJ systems (systems cryptographic protection information), antivirus means (agree correct settings with administrators, to issue recommendations to system administrators, do not forget to carry out control - whether the settings are made correctly, whether the settings did not change)
- Sign acts to write-off equipment
- Participate in the selection of software for monitoring the functioning of information systems
- Control information redundancy integrity
- Analysis of the main indicators of IT activities in accordance with the corporate business strategy
- Organize the process of auditing information systems organization
- Analyze the business processes of organization in the field of information security
- Configure anti-virus protection systems
- Fill the magazines of viral attacks
- Control the regular update of anti-virus protection software
- Develop Rules for Update Anti-Virus Protection Software
- Regularly update anti-virus protection software
- Establish restrictions on the use of time
- Participate in the development of policies to limit users to resource use
- Develop policies to limit users on access rights and the degree of resource use
- Establish workstation or servers
- Control Using the Internet and Email
- Organize access to local and global networks, including on the Internet
- Control the performance of the computing network servers during the absence of a system administrator
- Comply with information security policies
- Participate in the formation of information security policies
- Participate in developing information security policies
- Participate in formation and comply with information security policies
- Analyze the software and hardware market
- Follow the software and hardware market
- Work with various types of source data on the state of the computer systems
- Assign identifiers and passwords when registering users
- Create and maintain up to date user accounts
- Delimitation of access rights and keep registry users
- Logging Resource Access Events
- Detect the causes of emergency situations
- Approve a system of response to critical events
- Protection to attacks
- Control the settings of the alert about critical events
- Develop a system of response measures to critical events, at the attacks of hackers
The Bookmaker Association hired a biologist, mathematics and physics to develop a method for predicting the results of the race. Each to study was given a million dollars and one year.
Gone year, hear reports.
Biologist: "I developed a technique with the help of which, knowing pedigree horses and taking their blood tests, you can predict the result with a probability of 90%."
Mathematics: "I developed a methodology with which, knowing the statistics of race for the year, the number of viewers in the podium, the amounts of bets and the relationship between men and women among those who made bets - you can predict the result with a probability of 96%."
Physicist: "I can give a method that allows with 100% probability to predict the results of the race, but I need another 10 million dollars, the laboratory, the staff of the assistants and five years of time, and now I have a model of a spherical horse in vacuum ..."
Collection of the best jokes of all time on anekdot.ru
In order to associate a model with reality, it is necessary to carry out an experiment on real people, which quantitatively will show the quality of the compliance of a separate person of the adopted competency model. There is a sufficiently large number of methods that make an assessment of competencies. The most complete and widespread methods for assessing competencies are Assessment Center methods and 360 degree techniques.
These methods are quite complex and require sufficiently large human and financial resources, so they are used mainly only in large companies. Within the framework of this work, these methods will not be applied in connection with rigid temporal restrictions. Although their application is necessary for a high-quality and quantitative assessment of the model.
As it was said to the epigraph in the introduction of this work, we needed to set the main goal of the work or the main question and try to answer it. The main goal is to create a model of a specialist in this work.
Perfect computer security specialist.
As a result of the work done, 67 competencies were obtained:
1. Project documents
2. Technical tasks
3. Reports
4. Technological documentation
5. Coordination of documentation
6. Amendments to Documents
7. Check documents
8. State and sectoral standards
9. Other regulatory acts
10. Using the documentation
11. Teamwork
12. Self-control and responsibility
13. Ability to correctly read
14. Self-development
15. Public speaking skills
16. Programming languages
17. Understanding the process and methods for creating
18. Ensuring the quality and safety of the
19. Monitoring the current state of
20. Installation and configuration
21. Modernization of PO
22. Fixing events and documentation of various procedures related to the work of the equipment
23. Troubleshooting equipment
24. Operation of equipment
25. CONTROL AND MONITORING THE STATES OF ICIS
26. Operation and maintenance of ICIS
27. Detection and elimination of causes of ICIS fault
28. Development of documents and regulations for work with ICIS
29. DBMS
30. Information processing
31. Backup
32. Implementation of control and documentation of working with databases
33. Management of project activities
34. Understanding the organization's strategy
35. Management of Information Systems Administration
36. Management of planning and reporting activities
37. Work with the customer
38. Ensuring labor protection standards
39. Working with users of information systems
40. People and projects
41. Questioning and interviews
42. Ensuring interaction between people
43. Personnel Management
44. Maintaining a positive working atmosphere
45. Analytical work and collection of information
46. \u200b\u200bConducting examinations
47. Optimization of business processes in terms of economic security
48. Methodology for protecting confidential information
49. Work with security violations: Localization, prevention, investigation, foresight.
50. Interview with people: Candidates for work, workers, partners, competitors.
51. Work with law enforcement agencies
52. Work with the constituent documents, treaties, property rights, laws and other NPA
53. Physical security of objects and alarm device
54. Fire Alarm Sensors and Fire Safety System
55. Means and methods for providing special communication
56. Specifications, special tests, special surplus
57. Following information security instructions
58. Apply technical information security tools.
59. Control of the functioning of equipment
60. Analysis and audit of information systems and security systems
61. Working with anti-virus protection systems
62. Create restrictive policies and procedures
63. Controlling the use of computing resources
64. Formation of security policies
65. Analysis of the software and hardware market
66. Work with records of information systems and users
67. Response to critical events and elimination of emergency situations
Now, if you take some percentage of the competences of specialists as a certain percentage of the knowledge of the skills, skills, personality and business qualities, responsibility and targeted qualities, the desired result desired, then the ideal option will be 100% compliance for each competence (see Fig. 4 and 5). 
Figure 4 Model for evaluating an ideal computer security specialist.
Figure 5 The model of a specialist, where the name of the competencies is replaced by numbers from the list of 67 competencies for the convenience of perception.
Thus, we got a model of a spherical security officer in vacuum?.
Realistic assessment of computer security specialist.
Since ideal people and preparation processes do not happen, we will try to evaluate how a more or less realistic picture of the compliance of a specialist in such a model of competencies looks.
Immediately we can say that domestic educational institutions do not pay due attention to such competencies that belong to teamwork, self-development, public speeches, competent documentation and work with customers. Based on these assumptions, you can build an estimate shown in Figure 6. 
Figure 6 Evaluation of competencies approximate to reality.
Some terrible painting is obtained. But this is not surprising. For now in educational institutions, the main emphasis is placed on the transfer of knowledge, and, knowledge, as a rule, outdated years to 5, and even 10 in relation to the technologies and requirements of today.
Evolution of the model of a specialist from the course to the course.
All of the above applied to the evaluation of the ready-made specialist, i.e. graduate of the university. But good model Must imply the development of itself, and therefore include submodel. Since the training of a specialist is underway for 6 courses, it is advisable to indicate that the model should evolve together with the student. Figure 7, approximately shows how such a model should evolve. The dependence is not the number of competencies, but the capacity of competencies is because competencies should develop as knowledge, skills and skills in the course of training and from one basic competence, which was given to the student in the first year, may have ten total competencies, some basic competences will be may be combined. But all this must be taken into account within the framework of individual items throughout the entire learning process. But such findings go beyond this work.
In addition, this work does not take into account the value component, because In order to build a complete model, taking into account knowledge, it is necessary to view curricula on each discipline taught on this specialty, which will take time exceeding the execution of this work.

Figure 7 Evolution of the competence model together with the learning process
ConclusionThe goal of the school should always be upbringing a harmonious personality, not a specialist.
Albert Einstein
If we summarize this work, then it can be noted that the competences are a link between the university and the enterprise, which will be going to work as a specialist after release. However, the training of specialists in the university currently does not take into account the real needs of enterprises in those knowledge, skills and skills that are really necessary for work. Preparation of specialists in the framework of educational disciplines shifts mainly towards fundamental scientific items, losing real needs in cooperation with people, working in a team, the skill competently work with documents. Undoubtedly, fundamental training is very important as the base, but it is impossible to stop only on fundamental natural science disciplines. Need to move on. Now, within the framework of the project of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation there is a unique chance to develop and use in the preparation of specialists a comprehensive standard based on a competence model. Universities in the state of the third generation are given great freedom to create such standards for a number of specialties and these opportunities must be used to make a specialist who produced from the university has been closer to the ideal, and not to the terrible formed sea hero, which is currently obtained, if you look at knowledge , graduate skills and skills. The highest school must first take care of the education of a person, and further from a person to make a specialist. 
List of used literature
Draft WCC - National Union Personnel Phone Library-Technology Toolkit "Build a model of competencies in the company", annex to the Journal "Human Resources Directory" №11, 2008.
V.I. Bayenko, Identifying the competence of university graduates, as the necessary stage of designing a new generation (methodological manual), M.: 2006.
Bologna process: middle way / under scientific. ed. Dr. Ped. Sciences, Professor V. I. Bayenko. - M.: Research Center for the Quality of Training of Specialists, Russian New University, 2005. - 379 p.
Avdoszyn S. M., on experience professional standards When forming educational educational programs in the direction of 230400 "Applied Engineering", M.: State University - Higher School of Economics, - 2007.
Development of professional standards for the information technology industry. Committee on IT Education. APKIT site
Who is the "security officer"? What should be able to know the information security specialist?
Who and why it is worth going to computer security specialists?
Concept "Information Security" It became relevant with the development of the Internet. The virtual world has become very similar to the real one: already now people communicate on the Internet, read books, watch movies, buy goods and even commit crimes. And if there are cybercriminals, it means there must be specialists who are engaged in the security of objects on the network. These are specialists in information security.
Why should I pay attention to the protection of information?
Imagine that the hacker knows all credit card data. With this information, he will be able to steal money from the card without leaving his home Computer. Now imagine that the hacker managed to hack the security system of a whole bank. In this case, the forage size grows hundreds of times. Cybercriminals for the sake of financial benefits can fail social networks , Internet services, automated systems in commercial and government agencies. Users will not be able to visit the site, and the site owner will bear financial and reputational losses until the site earns again. Hackers can steal valuable information: personal photos of a famous person, classified military documents, drawings from unique inventions. It becomes clear that no organization or separate person is protected from theft important information for them, so IT companies and large organizations pay great attention to its protection.
Information or Computer Safety Specialist
- This is an employee of a company that ensures the confidentiality of the company's data and individual users, is engaged in strengthening the security of information systems, prevents information leakage.
✎ Sets a multi-level information security system (logins and passwords, identification by phone numbers, on fingerprint, on the retina, etc.)
✎ examines the components of the system (site, service, automated system in the company) for vulnerabilities
✎ eliminates the revealed breakdowns and vulnerability
✎ eliminates the effects of hacking if they occurred
✎ Develops and implements new information security regulations
✎ Holds to work with system users to explain the importance and types of protective measures
✎ Leads documentation
✎ Prepares reports on the state of IT systems
✎ interacts with partners and equipment providers in the field of security
Computer Security Specialist Works in a team, and other IT specialists. According to the security officers themselves, they guard the rear and cover the backs of other departments that are engaged in the development of IT infrastructure.
What universal competencies need a security officer in work?
✔ Analytian mind
✔ skill to see and solve the problem
✔ Patience
✔ Stress resistance
✔ ability to work under pressure
✔ Methodology
✔ curiosity
✔ Permanent self-development
✔ learning
✔ skill work in a team
✔ ability to make decisions
✔ Care for details
Position information security specialist Spends high risks and constant stress. They carry the main responsibility in case of violation of the security system. Due to the fact that the technologies of hacking and methods of work of attackers are constantly changing, an information security specialist has to be engaged in constant self-education, follow the news in their field and for new items in software and hardware protection, read technical literature in English.
And although security officers are, first of all, high-class technical specialists, they need the development of communicative skills. They have to work a lot with other employees of the Organization to raise corporate culture in data protection.
Average wage
The position of information security specialist is paid relatively high due to high levels Responsibility:
✔
50 000 - 150,000 per month

Where to study
To become an information security specialist, it is necessary to deal with both the Hard and Soft, that is, be able to work with components and with programs. Therefore, it is necessary to start your education in school, training to collect and disassemble a computer, install new programs and work the soldering iron.
Get in the direction of "Information Security" (10.00.00) you can both in and in. Colleges are preparing specialists maintenance Security systems. And in universities - more qualified engineers, system architects, information security analysts
Universities:
Academy of Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation (AFSB)
National Research University Higher School of Economics (HSE)
Moscow Aviation Institute (MAI)
Moscow State Linguistic University (MGLU)
Moscow City Pedagogical University
Moscow State Technical University. AD Bauman (MSTU)
Moscow State Technical University of Civil Aviation (MSTU GA)
Moscow State University of Geodesy and Cartography (Miigaik)
Moscow State University of Communications Communications (MIIT)
National Research Nuclear University "MEPHI" (MEPI)
National Research University "MIET" (MIET)
Moscow University of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation named after V. Ya. Kikotya (Mosu MVD)
Moscow Polytechnic University (Moscow State Engineering University "Mami")
Moscow State University of Information Technologies, Radio Engineering and Electronics (Mirea)
Moscow Technical University of Communications and Informatics (MTUCI)
Moscow Physics and Technology (University) (MFT)
Moscow Energy Institute (Technical University) (MEI)
Russian State Humanitarian University (RSU)
Russian Economic University named after G. V. Plekhanova (REU)
University of Technology
Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Colleges:
Western continuing education complex (former PC number 42)
College of Automation and Information Technology No. 20 (Cait No. 20)
College of Urban Planning, Transport and Technology No. 41 (KGTT No. 41)
College of Decorative and Applied Art named Charles Faberge (KDPI. Karl Faberge)
College of Space Engineering and Technologies TU (KKMT TU)
College of International University of Nature, Society and Man "Dubna" (College Muina "Dubna")
College of Entrepreneurship number 11 (KP No. 11)
Communication College No. 54 (COP No. 54)
College of Modern Technologies named after the Hero of the Soviet Union M. F. Panova (former construction technical school No. 30)
Moscow State Educational Complex (former MGTTP)
Educational complex of services (OCS)
Polytechnic College No. 8 named Twice Hero of the Soviet Union I. F. Pavlova (PC No. 8)
Polytechnic Technical School No. 2 (Fri No. 2)
Where to work
Information security specialist in demand:
✔ in major organizations
✔ Banks
✔ IT companies
For example, Kaspersky Lab., Central Bank of the Russian Federation, Crook, FSB RF
Sometimes for work in the field of information security requires a special form of admission to state secrets, which imposes certain restrictions on the employee, including non-market abroad.
Establishment
The demand for information security professionals in the labor market today is extremely high. This is due to the fact that almost every company faces the problem of computer threats.
If you want to receive fresh articles about professions, subscribe to our newsletter.
Who is the "security officer"? What should be able to know the information security specialist?
Who and why it is worth going to computer security specialists?
Concept "Information Security" It became relevant with the development of the Internet. The virtual world has become very similar to the real one: already now people communicate on the Internet, read books, watch movies, buy goods and even commit crimes. And if there are cybercriminals, it means there must be specialists who are engaged in the security of objects on the network. These are specialists in information security.
Why should I pay attention to the protection of information?
Imagine that the hacker knows all credit card data. With this information, he will be able to steal money from the card without leaving his home computer. Now imagine that the hacker managed to hack the security system of a whole bank. In this case, the forage size grows hundreds of times. Cybercriminals for the sake of financial benefits can fail social networks , Internet services, automated systems in commercial and government agencies. Users will not be able to visit the site, and the site owner will bear financial and reputational losses until the site earns again. Hackers can steal valuable information: personal photos of a famous person, classified military documents, drawings from unique inventions. It becomes clear that no organization or separate person is protected from theft important information for them, so IT companies and large organizations pay great attention to its protection.
Information or Computer Safety Specialist
- This is an employee of a company that ensures the confidentiality of the company's data and individual users, is engaged in strengthening the security of information systems, prevents information leakage.
✎ Sets a multi-level information security system (logins and passwords, identification by phone numbers, on fingerprint, on the retina, etc.)
✎ Explore the components of the system (site, service, automated system in the company) for vulnerabilities
✎ eliminates the revealed breakdowns and vulnerability
✎ eliminates the effects of hacking if they occurred
✎ Develops and implements new information security regulations
✎ Holds to work with system users to explain the importance and types of protective measures
✎ Leads documentation
✎ Prepares reports on the state of IT systems
✎ interacts with partners and equipment providers in the field of security
Computer Security Specialist Works in a team, and other IT specialists. According to the security officers themselves, they guard the rear and cover the backs of other departments that are engaged in the development of IT infrastructure.
What universal competencies need a security officer in work?
✔ Analytian mind
✔ skill to see and solve the problem
✔ Patience
✔ Stress resistance
✔ ability to work under pressure
✔ Methodology
✔ curiosity
✔ Permanent self-development
✔ learning
✔ skill work in a team
✔ ability to make decisions
✔ Care for details
Position information security specialist Spends high risks and constant stress. They carry the main responsibility in case of violation of the security system. Due to the fact that the technologies of hacking and methods of work of attackers are constantly changing, an information security specialist has to be engaged in constant self-education, follow the news in their field and for new items in software and hardware protection, read technical literature in English.
And although security officers are, first of all, high-class technical specialists, they need the development of communicative skills. They have to work a lot with other employees of the Organization to raise corporate culture in data protection.
average salary
The position of information security specialist is paid relatively high due to the high level of responsibility:
✔
50 000 - 150,000 per month

Where to study
To become an information security specialist, it is necessary to deal with both the Hard and Soft, that is, be able to work with components and with programs. Therefore, it is necessary to start your education in school, training to collect and disassemble a computer, install new programs and work the soldering iron.
Get in the direction of "Information Security" (10.00.00) you can both in and in. Colleges are preparing security specialists for security systems. And in universities - more qualified engineers, system architects, information security analysts
Universities:
Academy of Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation (AFSB)
National Research University Higher School of Economics (HSE)
Moscow Aviation Institute (MAI)
Moscow State Linguistic University (MGLU)
Moscow City Pedagogical University
Moscow State Technical University. AD Bauman (MSTU)
Moscow State Technical University of Civil Aviation (MSTU GA)
Moscow State University of Geodesy and Cartography (Miigaik)
Moscow State University of Communications Communications (MIIT)
National Research Nuclear University "MEPHI" (MEPI)
National Research University "MIET" (MIET)
Moscow University of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation named after V. Ya. Kikotya (Mosu MVD)
Moscow Polytechnic University (Moscow State Engineering University "Mami")
Moscow State University of Information Technologies, Radio Engineering and Electronics (Mirea)
Moscow Technical University of Communications and Informatics (MTUCI)
Moscow Physics and Technology (University) (MFT)
Moscow Energy Institute (Technical University) (MEI)
Russian State Humanitarian University (RSU)
Russian Economic University named after G. V. Plekhanova (REU)
University of Technology
Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Colleges:
Western continuing education complex (former PC number 42)
College of Automation and Information Technology No. 20 (Cait No. 20)
College of Urban Planning, Transport and Technology No. 41 (KGTT No. 41)
College of Decorative and Applied Art named Charles Faberge (KDPI. Karl Faberge)
College of Space Engineering and Technologies TU (KKMT TU)
College of International University of Nature, Society and Man "Dubna" (College Muina "Dubna")
College of Entrepreneurship number 11 (KP No. 11)
Communication College No. 54 (COP No. 54)
College of Modern Technologies named after the Hero of the Soviet Union M. F. Panova (former construction technical school No. 30)
Moscow State Educational Complex (former MGTTP)
Educational complex of services (OCS)
Polytechnic College No. 8 named Twice Hero of the Soviet Union I. F. Pavlova (PC No. 8)
Polytechnic Technical School No. 2 (Fri No. 2)
Where to work
Information security specialist in demand:
✔ in major organizations
✔ Banks
✔ IT companies
For example, Kaspersky Lab, Central Bank of the Russian Federation, Crook, FSB of the Russian Federation
Sometimes for work in the field of information security requires a special form of admission to state secrets, which imposes certain restrictions on the employee, including non-market abroad.
Establishment
The demand for information security professionals in the labor market today is extremely high. This is due to the fact that almost every company faces the problem of computer threats.
If you want to receive fresh articles about professions, subscribe to our newsletter.
 Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it
Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it Effective job search course search
Effective job search course search The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode
The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF
How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF Why the fired program window is long unfolded?
Why the fired program window is long unfolded? DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT
DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT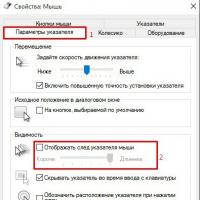 What to do if the mouse cursor disappears
What to do if the mouse cursor disappears