What device is used for long-term storage of information. Detailed characteristics of long-term storage devices. Devices of long-term storage data on PC
A) RAM. B) processor. C) external memory
2. When the computer is disconnected from the information network:
A) disappears from random access memory
B) disappears from a permanent storage device
C) erased on a magnetic disk
3. In each cell of the RAM can be stored binary code length ...
A) 2 signs b) 8 characters c) 4 signs
4. Energy-dependent memory is:
A) Flash-memory b) CD CD) hDD
5. K. internal memory Computer applies:
A) Flash memory b) laser disk c) RAM
electronic computing device for treating numbers;
device for storing information of any kind;
Multifunctional electronic device To work with information;
Device for processing analog signals.
2. Computer performance (speed operation) depends on:
monitor screen size;
Processor clock frequency;
supply voltage;
speed pressing keys;
The volume of processed information.
3. Clock frequency The processor is:
the number of binary operations performed by the processor per unit of time;
the number of clocks performed by the processor per unit of time;
the number of possible processor appeals to RAM per unit time;
information exchange rate between the processor and an input / output device;
The rate of information sharing between the processor and the ROM.
4. Mouse manipulator is a device:
information entry;
modulation and demodulation;
reading information;
To connect the printer to the computer.
5. A constant storage device serves for:
storage of user program during operation;
records of highly valuable application programs;
storage of constantly used programs;
storage of computer boot programs and testing its nodes;
Constantly storage of particularly valuable documents.
6. For long-term storage of information serves:
RAM;
CPU;
magnetic disk;
drive.
7. Storage of information on external media differs from storing information in RAM:
the fact that on external media information can be stored after turning off the power of the computer;
storage amount of information;
the ability to protect information;
ways to access stored information.
8. During execution, applications are stored:
in video memory;
in the processor;
in RAM;
in ROM.
9. When the computer is disconnected, the information is erased:
from RAM;
from the ROM;
on a magnetic disk;
on a CD.
10. The flexible drive drive is a device for:
processing commands of the executable program;
read / write data from external media;
Storage of commands of the executable program;
Long-term storage of information.
11. To connect a computer to a telephone network, uses:
modem;
plotter;
scanner;
Printer;
monitor.
12. Software Management The work of the computer involves:
the need to use the operating system for synchronous operation of hardware;
execution by computer series of commands without user participation;
binary data coding in the computer;
Using special formulas to implement commands in the computer.
13. The file is:
an elementary information unit containing the sequence of bytes and having a unique name;
The object characterized by the name, value and type;
A combination of indexed variables;
A combination of facts and rules.
14. The file extension is usually characterized by:
file creation time;
file volume;
location occupied by a disk file;
type of information contained in the file;
Place creating a file.
15. Full way to file: C: \\ Books \\ Raskaz.txt. What is the name of the file?
Books \\ Raskaz;.
Raskaz.txt;
Books \\ Raskaz.txt;
TXT.
16. The operating system is -
A combination of the main devices of the computer;
Low-level programming system;
Software environment defining user interface;
A combination of programs used for operations with documents;
programs for the destruction of computer viruses.
17. Computer device interface programs are called:
loaders;
drivers;
translators;
interpreters;
compilers.
18. System diskette is required for:
for emergency loading of the operating system;
systematicization of files;
Storage important files;
Treating a computer from viruses.
19. What device has the highest information exchange rate:
CD-ROM drive;
HDD;
Drive for flexible magnetic disks;
RAM;
Processor registers?
energy-dependent.
e) more fast access.
g) slower access.
2. What memory size in bytes will take the next binary
3. Text volume 1024 bits Located in B. random access memorystarting with a byte with the number 10 . What will be the address last byte
4. List at least five known to you devices exterior Memory.
5. What difference Disc CD- ROM, CD- RW and CD- R.?
Urgently needed. Highly. 1. Which of the following characteristics relate to operational, and what are the external memory? but)It is energy-dependent.
b) It is measured with tens and hundreds of gigabytes.
b) Used for long-term storage of information.
d) its volume is measured by hundreds of megabytes or several gigabytes.
e) faster access.
e) Used for temporary storage of information.
g) slower access.
2. What amount of memory in bytes will take the following binary code :? Explain your answer.
3. The text of the volume of 1024 bits is located in RAM, starting from the byte with the number 10. What will be the address of the last byte, which is occupied by this text?
4. List at least five devices known to you external memory.
5. What is the difference cD-ROM discs, CD-RW and CD-R?
Homework number 5 Topic: Computer Memory 1. Which of the following characteristics relate tooperativeand what - to exterior Memory?
a) is energy-dependent.
b) It is measured with tens and hundreds of gigabytes.
b) Used for long-term storage of information.
d) its volume is measured by hundreds of megabytes or several gigabytes.
e) faster access.
e) Used for temporary storage of information.
g) slower access.
2. What memory size in bytes will take the next binary the code: ? Explain your answer.
3. Text volume 1024 bits Located in B. random access memorystarting with a byte with the number 10 . What will be the address last byteWho is engaged in this text?
4. List at least five known to you devices exterior Memory.
Many are thinking: what does it serve for long-term storage of information? So, the structure of my story is as follows:
- what serves for long-term storage of information;
- types of information.
What serves for long-term storage of information
The main information process is the process of saving information, that is, a method, due to which it is possible to transmit data on space and time. In order to save information, devices or devices that depend on the type of stored information are used. In order to ensure the ordering of this process, the presence of information systemsequipped with a search procedure, placement, as well as editing information. Main distinctive feature of information systems - data Key procedures.
Programmers are determined by: in order to save information, external storage devices should be used. It can be a drive or a carrier of all sorts of types, which may be imagined to yourself.
Types of information
In addition to the foregoing, it should be said about what information types are. So information may be as follows:
- textual;
- visual;
- numerical;
- sound recorder;
- video.
The most common in today the method of saving information is the text type. Truth, this method Storage is not reliable and durable. Graphic, or the pictorial type - the most ancient storage method of information, these are all sorts of schemes, graphics and drawings.
In order to store information for long-term time and transfer from one data media to another, devices on hard drives, DVD, CD-equipment, flash drives, drives on flexible disks are used.
Winchester is a means of constant saving information, programs in the computer.
Flexible magnetic disk is the principle of data recording on magnetic tapes. Such a device can accommodate information up to 600 pages of a text document.
CD - this is the principle optical recording. You can write even the encyclopedia that contains many volumes. Flash memory is a device that does not need food from electricity.
Introduction
Information storage devices (external memory) are computer components that allow virtually unlimited time to maintain large amounts of information without electricity consumption (non-volatile).
The first such devices for PCs were floppy drives (FDD) and replaceable floppy disks - at the beginning of the five-year (5.25 ") capacity of 360 KB and 1.2 MB, then three-tie (3.5") capacity of 1, 44 MB. Currently, it is rarely applied due to the wide distribution of flash memory devices with a container of several gigabytes.
A characteristic feature of the external memory is that its devices operate with blocks of information, but not by bytes or words, as whether the RAM allows. These blocks usually have a fixed size, multiple degree of number 2. The unit can be rewritten from the internal memory into external or back only only, and to perform any exchange operation with external memory required. special procedure (subroutine). Exchange procedures with external memory devices are tied to the device type, its controller and method of connecting the device to the system (interface).
External memory is used to long-term storage of large amounts of information. In modern computer Systemsah as external memory devices most often apply:
* storage drives magnetic disks (NGMD)
* Drives on flexible magnetic disks (NGMD)
* Drives on optical disks
* Magneto optical media.
Basic concepts
External memory is the memory implemented in the form of external motherboard, devices S. different principles Storage of information and types of media intended for long-term storage of information. In particular, everything is stored in external memory software Computer. The external memory devices can be placed both in the computer's system unit and in separate cases. Physically, the external memory is implemented in the form of drives.
Drives are storage devices intended for long (which does not depend on power) storage of large amounts of information. The capacity of the drives hundreds of times the capacity of RAM or is generally unlimited when it comes to drives with interchangeable media.
The carrier is a physical storage environment, appearance It may be disk or tape. According to the principle of memorization, magnetic, optical and magneto-optical media differ. Ribbon carriers can only be magnetic, in disk carriers use magnetic, magneto-optical and optical methods for recording-reading information.
Classification of devices of long-term storage of information
As information storage devices, external memory are used, which are implemented in the form of the relevant technical means For storing information. All drives used in PCs are unified in constructive execution. Their sizes are standardized: the width and height of the devices are most rigid, the depth is limited only to the maximum allowable value. Such standardization is necessary for the unification of structural compartments of PC cases.
External memory can be with arbitrary access and consistent access. Random Access Memory Devices allow you to access an arbitrary data block in approximately the same access time. Memory devices with allegant access allow access to data sequentially, i.e. In order to read the desired memory block, you need to consider all previous blocks.
Allocate the following main types of memory devices:
1. Hard magnetic drives (Winchesters, HDD) - non-removable hard magnetic discs. They relate to external memory with direct access to data and are divided into internal, installed in system unit Computer and external (portable) relative to the system unit.
2. Drives on flexible magnetic disks (floppy drives, NGMD) - devices for recording and reading information from small removable magnetic disks (floppy disks) packed in a plastic envelope (flexible - 5.25 inch diskettes and hard 3.5 inch ). Reference to external memory with direct (arbitrary) access to data stored on a magnetic disk and are intended for long-term storage relative to small amounts of information.
3. Information drives on optical disks are external (arbitrary) access to the data and are intended for long-term storage of relatively large amounts of information (hundreds of megabytes and tens of gigabytes).
4. Flash-memory-based information storage devices refer to external memory with direct (arbitrary) data access and are intended for long-term storage relative to small amounts of information (gigabyte units).
5. Magnetic tape drives (NML) - data reading devices from magnetic ribbons, which belong to external memory with sequential access. Such drives are sufficiently slow, albeit a large tank. Modern devices To work with magnetic ribbons - streamers - have an increased recording speed of 4-5 MB in sec. There are also devices allowing you to record digital information on video tapes, which allows you to store on 1 magazine 2 GB of information. Magnetic ribbons are usually used to create data archives for long-term storage of information.
6. Perfoocards - Dense paper cards and Perflectors - Coils with a paper tape, in which the information is encoded by penetrating (perforation) holes. Sequential access devices are used to read the data.
Currently, devices with sequential access to the NGMD data are morally outdated and do not apply, therefore we will not consider them in detail.
With the advent of computers, the issue of storing information was very sharply staging, which was originally fed digitally. And now this problem is very relevant, because the same photos or video want to save on long Memory. That is why it will be initially necessary to find the answer to the question of, for long-term storage of information, which devices and carriers are served. Also should fully appreciate all their advantages and disadvantages.
The concept of information and methods for its storage
Nowadays, you can find several basic types of information data on computers. The most common forms are text, graphic, audio, video, mathematical and other formats.
In very simple version For storage of information, serve hard disks of computers to which the user saves the file initially. But this is just one side of the medal, because in order to view this information (extract), you need at least operating system And the relevant programs that by and large are also informational data.
Interestingly, in schools in informatics lessons, when choosing the right answer, such questions are often found, the statement is often found that, they say, the RAM is served for long-term storage. And schoolchildren who are not familiar with the specifics and principles of her work, consider it the right answer.

Unfortunately, they are mistaken, since only information about the processes running at the moment is currently stored, and when they are completed or rebooting the system, the RAM is fully cleaned. It looks like the principle of the operation of once popular children's toys for drawing, when on the screen you could first draw something, and then shake the toy, and the drawing disappeared, or when the teacher erases with the blackboard text written by chalk with the blackboard.
How information remained earlier
The very first method of preserving information in the form of rock paintings (by the way, graphics) is known since time immemorial.

Much later with the advent of speech, the preservation of information has become a process, so to speak, transmission from mouth to mouth (myths, legends, epics). Writing led to the fact that books began to appear. Pictures or pictures were not forgotten. With the advent of photography photos, sound recordings and video, the corresponding media appeared on the information field. But all this turned out to be short-lived.
Device for long-term storage of information: basic requirements
As for computer systems, it should be clearly understood that modern carriers must be complied with that the information is kept for them as long as possible.
The most important requirement is durability and resistance to wear and physical or other damage. And in relation to any type of carrier on time intervals, you can speak very relatively, because, as you know, "nothing is always under the moon."
For long-term storage of information, what carriers are
We now turn directly to devices on which any type of data can be stored, if not forever, then at least long enough. So, for long-term storage of information serve what types of storage?

Among the most commonly used in relation to computer technician Select the following:
- domestic and removable hard and zip-disks of computers;
- optical CDs, DVD- and Blu-Ray carriers;
- flash memory of any type;
- dakes (now used extremely rarely).
Benefits and disadvantages of carriers
As can be seen from the list, only the hard drives are built into computers relate to internal devices storage. All other carriers are external.
But all of them are one of them are susceptible to aging or external influences. In this sense, the floppy disk or the same CDs or carriers of another format are the most unsafe, although optical media in this regard look more wear-resistant. But how much can they serve? 5-10 years old? But if the information on them is stored, viewing very often, the service life is reduced.
Flash drives and hard drives have more long-term exploitation, but they are not insured against wear, damage and aging.

Winchesters begin to "draw" (this is a natural process), flash drives can be exposed to the same sunlight, moisture, or even delete data when extracting or software failures. In addition, there are many more additional factors that can lead to the inoperability of devices.
Nevertheless, speaking that for long-term storage of information, the devices listed in the list should be borne in mind that such a classification is provided solely for the current state of affairs in the computer world. Who knows, maybe even in the already foreseeable future, completely new carriers using other technologies will be invented, because it is alleged, the creation of quantum computers is not far off.
Introduction
Modern society is characterized by the intensive development of technical and software. Based on timely replenishment, accumulation, recycling of the information resource, rational management is possible and the adoption of certain solutions. This is especially important for the sector of the economy. Permanent growth of information flows places increased requirements for the application of storage devices. In this regard, the consideration of the issue concerning the means of long-term storage of information is very relevant.
In this paper, attention is paid to a separate element of the architecture of a personal computer, known as "external memory". The presentation of the material begins with the formation of a general understanding of the subject of study. Next follows the lighting of the most important components of the selected topic. Each section sequentially reveals the features of these devices, in particular, the essence of the means, its functions, specifications, sphere and conditions of application.
The practical part of the work provided is devoted to the decision of the economic task. According to the above data, the total amount of the return on the loan agreement was calculated. Similar calculations can be applied in a number of economic and financial and credit organizations. Calculations are accompanied by comments to the assignment algorithm, the construction of the corresponding tables and the graphic element.
The work was performed on an IBM standard configuration PC, including a system unit, monitor, keyboard, mouse with the following characteristics: 64-bit Celeron 2.4 GHz microprocessor, 1024 MB RAM, SAMSUNG hard disk with a volume of 80 GB, 3.5 "samsung drive, CD-RW LG 52x32x52, Acer 17 monitor with a resolution of 1280x1024. The work was carried out in Windows XP using the Microsoft Office Word Text Editor 2003, tableware processor Microsoft Office Excel 2003, which are included in the integrated Microsoft Office 2003 PPP.
1. Devices of long-term storage of data on PC
Introduction 4.
1.1. Classification of external memory devices PC 5
1.2. Descriptions of specific species 6
Digile 6.
CD 7
Hard disk 12.
Flash memory 18
Conclusion 20.
Introduction
Personal computer is designed to automate the process processing process. In this case, the data in the computer is entered using input devices and are subject to further processing. However, quite often the need for storage and transferring large amounts of information. The constant storage of such information arrays in the computer's memory is irrational. When taking into account such factors, wide use of long-term storage devices are found, which are also called external memory.
External (long-term) memory (waiv - external storage device) is intended for long-term storage of pro-grams and data not used at the moment in the RAM of PC, and is non-volatile, i.e. The integrity of its content does not depend on whether the computer is turned on or off. In particular, all software PC software is stored in the external memory. Unlike RAM, external memory has no direct connection with the processor. External memory carriers, in addition, provide data transport in cases where computers are not combined on the network (local or global).
Classification of PC External Memory Devices
Foreign memory devices or, otherwise, external storage devices are very diverse. They can be classified for a variety of features: by type of wear, the type of construction, on the principle of recording and reading information, the access method, etc.
One of the possible options for classifying the paragraph is presented below in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Classification
To work with the external memory, it is necessary to have a drive (device that provides the record and (or) reading information) and storage devices.
Depending on the type of media, everything can be divided into drives on the magnetic ribbon and disk drives.
Magnetic tape drives, in turn, there are two species: storage devices on a bobbin magnetic tape (NBML) and storage devices on a cassette magnetic tape (NKML - streamers). Only streamers are used in the PC.
Drive drives - devices for recording / reading from magnetic (optical) media. Purpose of these drives: storing large amounts of information, recording and issuing stored information on request to an operational storage device. Discs relate to engine media with direct access. The concept of direct access means that the PC can "contact" to the track on which the site with the search for information begins or where the new information needs to be recorded, wherever the recording / reading head / reading is.
Thus, the main durable storage devices include:
storage devices on flexible magnetic disks (NGMD);
storage devices on rigid magnetic disks (NGMD);
drives on optical disks (CD, CD-RW);
drives on recording magneto-optical disks;
magnetic tape drives (streamers), etc.
1.2 Description of specific species:
D.  takere
takere
Diskettes - portable magnetic media used for multiple recording and storage of data relatively small volume. This type of carrier was especially common in the 1970s - early 2000s. Instead of the term "floppy", an abbreviation of GMD is used - "flexible magnetic disk" (respectively, a device for working with floppy disks is called NGMD - "Drive on flexible magnetic discs", a slang version - flopoveod, flopic, flopparch from English floppy-disk).
Typically, a floppy disk is a flexible plastic plate coated with a ferrimagnetic layer, hence the English name "FLOPPY DISK" ("Flexible Disk"). This plate is placed in a plastic housing that protects the magnetic layer from physical damage . The shell is flexible or durable. Recording and reading floppy disk is carried out using a special disk drive (floppy disk drive).
Dissars typically have a write protection function by which you can provide access to data only in read mode.
Currently, the floppy disks are virtually overwhelmed with more applicants and having a much smaller specific value of the types of drives. These include, first of all, the storage drives on flash memory recorded by CD and DVDs (especially DVD-RAM).
CD
( "CD", "Shape CD", "CD-ROM", "CD ROM") - an optical medium of information in the form of a disc with a hole in the center, information from which is read with a laser. Initially, the CD was created for digital storage audio (T.N. Audio-CD), however, is currently widely used as a wide-purpose storage device (T.N. CD-ROM). Abbreviation "CD-ROM" means "Compact Disc Read Only Memory" that in translation indicates a CD with the ability to read. "CD ROM" means "CD, constant storage device". CD-ROM often erroneously called CD-drive for reading CDs. The CD was created in 1979 by Philips and Sony.
"CD", "Shape CD", "CD-ROM", "CD ROM") - an optical medium of information in the form of a disc with a hole in the center, information from which is read with a laser. Initially, the CD was created for digital storage audio (T.N. Audio-CD), however, is currently widely used as a wide-purpose storage device (T.N. CD-ROM). Abbreviation "CD-ROM" means "Compact Disc Read Only Memory" that in translation indicates a CD with the ability to read. "CD ROM" means "CD, constant storage device". CD-ROM often erroneously called CD-drive for reading CDs. The CD was created in 1979 by Philips and Sony.
CDs are made from polycarbonate with a thickness of 1.2 mm, covered with the finest aluminum layer (gold) with a protective layer of varnish, on which a graphical representation of the disk content is usually applied. Therefore, contrary to a common opinion, a CD, one should never put up the legs (down label), since the reflective aluminum layer on which the data is stored, it is shown below, as mentioned above, 1.2 mm polycarbonate layer, and From above - only a thin layer of varnish. In addition, on the reflecting side there is an annular protrusion with a height of 0.5 mm, allowing the disk laying on a flat surface, does not touch this surface. In the center of the disk there is a hole with a diameter of 15 mm (if desired, the disk can be transferred, putting on a finger, without touching its surface).
The information on the disk is written in the form of a spiral track of the so-called peit (recesses), extruded on the aluminum layer (as opposed to CD-ROM recording technology where information is recorded cylindrically). Each pit, has about 125 nm in the depth and 500 nm in width. Pita, varies from 850 nm to 3.5 μm. The distance between the adjacent spiral tracks is 1.5 microns. Data from the disk is read using a laser beam with a wavelength of 780 nm, which shines the polycarbonate layer, reflected from aluminum and is read by photodiode. The laser beam forms a decrease in a reflective layer with a diameter of about 1.5 μm. Since the disk is read from the bottom, each pit looks like a laser as an elevation. There are no places where such elevations are not called platforms.
To make it easier for you to imagine the size of the disk size, and the pit: If the CD is the value from the stadium, the pit would be the size of approximately the sand.
Light from the laser entering the pad is reflected and catches the photodetector. If the light falls on the elevation, it is experiencing an interference with light, reflected from the site around the elevation and is not reflected. This is because the height of each elevation is equal to the quarter of the laser light wavelength, which leads to the difference in the phases half the wavelength between the light, reflected from the site and the light reflected from the elevation.
CDs are stamped at the factory (CD-ROM), CD-R for a single record, CD-RW for multiple recording. The disks of the last two types are designed to record at home on special writing drives. In some CD players and music centers Such discs may not be read (recently all manufacturers of household music centers and CD players include the support for reading CD-R / RW).
The read / write speed of CD is indicated by multiple 150 Kb / s (i.e. 153 600 bytes / s). For example, a 48-speed drive provides a maximum read speed (or recording) of CDs, equal to 48 * 150 \u003d 7200 Kb / s (7.03 MB / s).
The weight of the disk without a box is ~ 15.7 gr. The weight of the disk in the usual (not "slim") is equal to ~ 74 gr.
Shape CD (Figure CD) - optical media of digital information type CD-ROM, but not strictly round, but with an outline of an external circuit in the form of a variety of objects, such as portraits, cars, airplanes, Disney characters, hearts, stars, ovals , in the form of credit cards, etc.
There are also disks intended for recording at home: CD-R (Compact Disc Recordable) for a single record and CD-RW (Compact Disc Rewritable) for multiple. In such disks, the reflective ability of the pit and the gaps between them should be mimicified by another method. This is achieved by adding a dye between the gold (aluminum) surface and a layer of polycarbonate. In the original condition, the dye level is transparent and allows a laser beam freely through it and reflects from the gold (aluminum) coating. During recording, the laser goes into high power mode (8-16mW). When the laser enters the dye, he heats it, destroying chemical bonds, and forms dark, opaque stains. When reading a Laser Laser with a capacity of 0.5 MW, a photodetector notices the difference between famous stains and intact regions. This difference is interpreted in the same way as the difference between the excavations and smooth surfaces on ordinary CDs.
 Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference
Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare?
Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare? Social polls work on the Internet
Social polls work on the Internet Sending mail is blocked, how to unlock?
Sending mail is blocked, how to unlock? Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments
Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens
Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens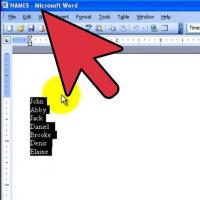 How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips
How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips