New features of the documents inspector for Excel, PowerPoint and Word. Screenwar dispatcher scripts. Remove personal data from documents
Personal data preservation is worth paying special attention, since since last year the legislator has tightened responsibility for the employer for non-compliance with the obligation to protect them. The article will tell you what is considered personal data, what responsibilities for their protection are established for employers and how to organize the correct accounting and storage of personal data of employees.
Systematize or update knowledge, get practical skills and find answers to your questions on at the school accountant. Courses are designed to meet the "Accountant" professandard.
The employer, accepting an employee to work, should request certain information from him, which are necessary within the framework of labor, tax and accounting legislation. Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ "On Personal Data" requires from the employer, which in this case is a personal data operator and performs their processing, ensure the safety of this information.
What data are personal
Personal data is any information, directly or indirectly related to the subject of personal data - a specific or defined physical lick (Art. 3 Federal Law dated July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ "On Personal Data", hereinafter - the Law on Personal Data).
The following information can be attributed to public personal data:
- full Name;
- date and place of birth;
- address (place of registration);
- education, profession;
- an image of a person (photography and video), which allows you to identify and for this purpose is used by the operator (explanation of the Roskomnadzor dated August 30, 2013 "On issues of classifying photo and video images, dactylocopical data and other information to biometric personal data and their peculiarities of their processing ");
- marital status, the presence of children, relatives;
- facts of biography and previous labor activities (place of work, conviction, service in the army, work in elected positions, in public service, etc.);
- financial position. O. Information wages Also are personal data (a letter of Roskomnadzor from 07.02.2014 No. 08km-3681);
- business and other personal qualities that are evaluated;
- other information that can identify humans.
In addition, the law on personal data is mentioned:
- special personal data (relate to racial, national affiliation, political views, religious or philosophical beliefs, health, intimate life). By general rule Processing of this data is not allowed. Exceptions - cases provided for by part 2 of Article 10 of the Law on Personal Data;
- biometric personal data (characterize the physiological and biological features of a person, on the basis of which one can identify his personality). For processing such information, the consent of the subject of personal data is necessary. Exception - cases established by h. 2 tbsp. 11 of the Law on Personal Data.
The employer has the right to receive and use only those information that characterize a citizen as the side of the employment contract (for example, information about the social and property status of a person is not related to its labor process). This information is contained in the following documents presented by the employee when admission to work:
- in the passport or other document certifying the identity;
- labor book;
- documents on military accounting, education, family composition;
- certificate of income from the previous job;
- profile filled with employment;
- personal employee card (form T-2);
- certificates of marriage, the birth of a child;
- medical certificates, etc.
The employer keeps copies of the listed documents, with the exception of questionnaires, labor books and personal cards.
Processing personal data
Processing personal data - any action (operation) or a set of actions (operations) committed using automation tools or without the use of such funds with personal data, including the collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, refinement (update, change), extraction, Use, transmission (distribution, provision, access), depersonal, blocking, deletion, data destruction (Article 3 of the Law on Personal Data).
The law on personal data obliges the employer to comply with certain requirements for processing these data. For example, personal data processing is carried out only with the consent of the employee (clause 1 of Article 6, Art. 9 of the Law on Personal Data). In order to avoid litigation, it is better if this consent is issued in writing. The same rule is valid for applicants.
In some cases, the written form of consent is directly provided for by law (Part 4 of Art. 9 of the Law on Personal Data). For example, the written consent of the employee for the processing of its personal data is required:
1) in obtaining personal data of the employee in the third party (paragraph 3 of Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But in this case, the employee must first notify this and receive his written consent (paragraph 3 of Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The notification must be specified (clause 3 of Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- goals of obtaining personal data of the employee from a third party;
- estimated sources of information (persons who will be requested by data);
- methods for obtaining data, their character;
- possible consequences of refusal to the employer in obtaining personal data of the employee from a third party. If the employee fails to familiarize himself with the notice of the estimated receipt of his personal data from another person it is advisable to compile the corresponding act.
If the worker has changed his mind, then at any time has the right to withdraw agreement to process personal data (part 2 of article 9 of the Law on Personal Data).
In such a situation, the continuation of the processing of personal data of the employee without its consent is possible in the presence of good reasons. They are listed in paragraphs 2 - 11 of Part 1 of Article 6, Part 2 of Article 10, part 2 of Article 11 of the Law on Personal Data (Part 2 of Article 9 of the Law on Personal Data).
Certain information (which is not related to the objectives listed in paragraph 1 of Article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the employer is not entitled to request from third parties even if the employee agrees.
2) when the employee's personal data is transferred to third parties, except for those cases when it is necessary to prevent the threat of life and the health of the employee (para. 2 Article 88 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
3) to process special categories of personal data of the employee directly related to the issues of labor relations (clause 4 of Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 1 of Part 2 of Article 10 of the Law on Personal Data). These data include information on racial, national affiliation, political views, religious and philosophical beliefs, health, intimate life.
With the incapacity of the employee, written consent to the processing of its data gives his legal representative (parent, guardian) (Part 6 of Art. 9 of the Law on Personal Data). And in the event of the death of the employee, such consent issues his heirs, if only it was not received from the employee himself under his life (part 7 of Art. 9 of the Law on Personal Data).
Not in all cases requires the consent of the employee for the processing of personal data. For example, if the data was obtained (p. 2 h. 1, Article 6, paragraph 2.3 of Part 2 of Article 10 of the Law on Personal Data, para. 1 of the explanations of Roskomnadzor):
- from documents (information) imposed on the conclusion of the employment contract;
- according to the results of the compulsory preliminary medical examination of the state of health (Art. 69 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 3 of the explanations of Roskomnadzor dated December 14, 2012 "Issues related to the processing of personal data of workers, applicants for filling vacant posts, as well as persons in personnel reserve" further - explanations of Roskomnadzor dated December 14, 2012);
- in the volume stipulated by the unified form No. T-2, including the personal data of close relatives, and in other cases established by the legislation of the Russian Federation (obtaining alimony, registration of admission to the state secret, the design of social benefits) (clause 2 of the explanations of Roskomnadzor dated 14.12. 2012);
- from the personnel agency acting on behalf of the applicant (paragraph 12 of paragraph 5 of the explanations of Roskomnadzor dated December 14, 2012);
- from the applicant who himself posted his resume on the Internet, making it an affordable unlimited circle of persons (paragraph 10 of Part 1 of Art. 6 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-ФЗ, para. 12 p. 5 explanations of Roskomnadzor dated 14.12.2012 ).
The employer with the consent of the employee can entrust the processing of its personal data to another person (Part 3 of Art. 6 of the Law on Personal Data, para. 2 of paragraph 5 of the explanations of Roskomnadzor dated December 14, 2012). But at the same time, it is the employer that is responsible to the employee for the actions of this person (part 5 of Art. 6 of the Law on Personal Data).
In the contour. Shkol: changes in legislation, specifics of accounting and tax accounting, reporting, salary and personnel, cash transactions.
Organization of accounting and storage of personal data
The employer must protect the personal data of the employee from unlawful use or loss at the expense of its funds (paragraph 7 of Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
We will analyze step-by-step actions of the employer for accounting and storing personal data in the organization.
Step 1. The employer must publish a local act that will regulate the procedure for the storage and use of personal data. Such an act is usually the provision on personal data of employees, with whom employees must be familiar with the signature (paragraph 8 of Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To familiarize yourself with the Regulations on Personal Data, as with the rest of local regulatory acts, the employee must prior to the signing of the employment contract (Art. 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Find out an employee with a document by sending it to e-mail it is impossible, this will not be considered a signature. In the absence of a signature of the employee, the employer will not be able to prove that the employee was familiar with this document.
The provision on personal data, as well as any other local regulatory act, is published and approved by the order, which signs the head of the Organization or other Commissioner to this person.
In the case of a check of an organization that verifies the authorities can request this document and check if employees with him are familiarized. The absence of such a document or the non-known employees with it can be the basis for attracting the employer to justice in accordance with Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Code of the Russian Federation, and in the case of a similar disorder, according to part 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Such a conclusion is also confirmed by judicial practice (the resolution of the FAS of the Moscow District of October 26, 2006 No. CA-A40 / 10220-06 No. A40-20745 / 06-148-194).
Step 2.. The employer approves a document containing a list of personal data that is used in the organization's activities. This document includes all the information that the employee reports in writing about himself upon admission to work, as well as those used in the future when making personnel documentation.
In addition, the list should indicate the documents containing the information about employees who the organization submits to various government agencies (tax and labor inspection, statistical authorities).
Step 3.. The Employer must appoint responsible for working with personal data and responsible for ensuring personal data. Such responsible can be both a specific person and a division. In the latter case, personal responsibility is responsible for the head of such a unit. This order must be brought to the attention of all employees specified in it, which must be confirmed by their signature.
Step 4.. In case of checking in order to avoid disputes with verifying, it is better to prepare the following documents:
- statements of workers about the consent to the processing of personal data;
- personal data accounting magazines, their issuance and transfer to other persons and representatives of various organizations, government agencies;
- magazine checks availability of documents containing personal data of the employee.
Step 5.. By order of the head of the organization to establish a list of storage sites of documentation, which is the carrier of personal data of employees, as well as a list of measures necessary to ensure the safety of personal data, the procedure for their adoption. All documents containing personal data of workers, such as personal affairs, files, credit magazines, should be stored in specially equipped cabinets or safes that locked and sealed. Labor books of workers need to be stored in a safe separately from personal affairs.
Let's summarize
- all employees have received consent to the processing of personal data;
- whether employees with local acts, establishing the procedure for processing such data, and with their rights and obligations in this area;
- due reference to storage and protection of personal data;
- does the documentation on their processing of the requirements of the legislation, etc.
When using the electronic copy of certain Office documents with clients or colleagues, it is recommended to check the document for hidden and personal data. This hidden information can be removed before providing overall access to other people. Document Inspector Function in Word, Excel, PowerPoint or Visio helps find and delete hidden data and personal data in the documents you plan to provide sharing.
Hidden information may include:
hidden data or personal information that may not be provided in Word documents
excel data is added to the book when working with other people.
hidden data and personal data in PowerPoint, which can be stored in the presentation or in its metadata.
document Information and File Properties in Visio Documents
Note: Unless you send your Microsoft document, no data from it will be available.
This article describes data types that are usually stored in Office documents so that you can choose what you need to save and what you want to delete in the document or metadata. Some information that the document inspector cannot delete, see tables that lead to additional information about Word, Excel and PowerPoint.
An electronic copy of the Word document to which you want to provide access to customers or colleagues often contains hidden data or personal data stored in the document itself or in the properties of the document or metadata.
Tip: If you just want not to print Notes, go to the page file _GT_ Print, Select Print all pages And uncheck the checkbox print corrections.
Word Documents may contain hidden and personal data of the following types:
Notes, fixes for recorded corrections, versions and handwritten notes If you work together with other users to create a document, the document may contain elements such as corrections with corrections, notes, handwritten notes and versions. This information allows other people to see the names of people who worked on the document, comments from reviewers and changes made to the document, which may not be required for collaboration outside the group.
Properties of the document and metadata: information about the document, such as the "author", "theme" and "name". The properties of the document also include information automatically served by Office programs, such as the username that the user has last saved, and the document creation date. If you used specific functions, the document may also contain additional personal information, such as email headers, sending and checking, routes and template names.
Persecutors I. Substrate Word Documents may contain information in footers. In addition, you could add a substrate to Word document.
Hidden text Word Documents may contain text formatted as hidden text. If you do not know whether the document contains the hidden text, you can use the document inspector to find it.
Properties of document server If the document has been saved in the location on the document management server, for example, on the website of the Workpiece for documents or the library created on Windows SharePoint Services, the document may contain additional document properties or information associated with this location on the server.
Custom XML data. Documents may contain custom XML data not displayed in the document itself. These XML data can be detected and deleted using the document inspector.
With the help of the document inspector
With the help of the document inspector, you can find and remove hidden and personal data from word documents. Inspector of documents makes sense to run before providing overall access to electronic copies of Word documents, for example, in the form of investments in email messages.
Search and delete documents inspector in Word documents
In Word, the document inspector includes several different modules that allow you to find and delete hidden and personal data specific to Word documents. The list of different types of hidden or personal data that can be detected and deleted from Word documents using the document inspector is presented in the table below.
Notes:
Inspector | Finds and deletes |
|---|---|
|
Notes, corrections, versions Note: In Word Starter 2010, the document inspector removes only the versions and notes. |
Notes Marked the correction mode Document version information Handwritten notes |
|
Properties of the document and personal data |
General, Statistics and Others dialog box Properties of the document Email Message Headers Document routes Properties of document server Content Type Information Username Template name |
|
Circiers and "Watermarks" |
Document headlines Information in the columns of the document "Water marks" |
|
Hidden text |
Text formatted as hidden (font parameter available in dialog box Font) Note: This inspector Cannot detect text hidden by other methods (for example, white text on a white background). |
|
Customizable XML data |
Custom XML data that can be stored in the document |
|
Invisible content |
Note: This inspector does not find objects blocked by other objects. |
When using the electronic copy of the Excel book, make sure that you are viewing a book as hidden data or personal data that can be stored in the book itself or in its properties of the document (metadata).
Using the document inspector in Excel, you can find and delete hidden and personal data.
Note: Although from books sent to other users, you can delete hidden and personal data if the Excel book has been saved as common, it is impossible to remove notes, notes, document properties, and personal data. To delete this data from the general book, first copy it and cancel the total access to it.
Search and delete hidden and personal data
Using the document inspector, you can delete hidden and personal data from Excel books. Inspector of documents makes sense to run before providing general access to electronic copies of books, for example, in the form of investments in email messages.
Types of hidden and personal data in Excel
The following lists some elements that can be the source of hidden and personal data in Excel books.
Notes and handwritten notes. If the book was created in conjunction with other users, it may contain ordinary and handwritten notes. This information allows other users to find out the names of people working on this book, view the notes of the reviewers and see the changes made to the book.
Properties of the document and personal data Metadata or document properties in Excel, as in other office applications, including information about the author, theme and title. Office automatically saves the username that last saved the book, the document creation date and the location of the document (Excel 2013 or later). Additional information (PII) may be available, such as email headers, sending, view, routes, printer properties (for example, the path to the printer and secret code secure printing), as well as information about the path to the publication file. Web pages.
Footers. Excel books may contain data in footer.
Hidden rows, columns and sheets. The book can hidden strings, columns and whole sheets. When distributing a copy of a book containing hidden strings, columns or sheets, other users can display them and view the data contained in them.
Properties of document server. The book stored on the document management server, for example, on the website of the workspace for documents or in windows Library SharePoint Services may contain additional document properties or location information on the server.
Custom XML data. Excel books may contain custom XML data not displayed in the document itself. These XML data can be detected and deleted using the document inspector.
Invisible content. Books may contain objects formatted as invisible.
Implemented files or objects. In the books there may be embedded files (for example, Office documents or text files) or embedded objects (for example, diagrams or equations) containing invisible data.
Macros based on VBA code. In the books there may be macros, VBA modules, COM and ActiveX elements, user forms or user functions that may contain hidden data.
Elements with cached data. In the books there may be cached data of summary tables, summary diagrams, sections, timelines and formulas of cubes that may not be displayed.
Excel polls The books may be hidden Excel survey issues that were introduced in Excel Online and are stored in the book, but are not visible in it.
Screenwar dispatcher scripts. In books, there may be scripts defined using the script manager. They may contain cached or hidden data.
Filters. In the books there may be active autofilters or table filters that can lead to saving cached or hidden data in books.
Hidden names. The books may have hidden names that can be a source of hidden data.
Search and delete documents inspector in Excel documents
In the document inspector displays the found items that may contain hidden and personal data related to Excel books. The table below lists the types of data such that can be removed from books using the document inspector.
Notes:
Not all excel functions l listed in the table are supported in Microsoft Excel. Starter 2010.
If configurable modules are added to the organization to the inspector of documents, additional type data can be detected.
|
Inspector of documents finds and removes |
|
|---|---|
|
Notes |
Notes Handwritten notes Note: In Excel Starter 2010, the document inspector removes only notes. |
|
Properties of the document and personal data |
Properties of the document, including information from tabs General, Statistics and Others dialog box Properties of the document (Excel 2013 and later versions). When choosing a team delete everything The current location of the document will be deleted from the file. It is added while saving only after closing and re- excel opening 2013 or later. Email headlines Document routes Data sent to verification Properties of document server Document Management Policy Information Content Type Information Username Printer path information Notes to scenarios Notes for specific names and table names Inactive connections to external data |
|
Persecutors |
Information in sheets of sheets Information in notes to sheets |
|
Hidden lines and columns |
Hidden string Hidden columns with data Notes: |
|
Hidden lists |
Hidden lists Note: If the hidden sheets in the book contain data, their removal can lead to a change in the results of the calculation of the formulas contained in the book. If it is not known what data is contained in hidden sheets, close the documents inspector, display the hidden sheets, and then browse their contents. |
|
Customizable XML data |
Custom XML data that can be stored in the book |
|
Invisible content |
Objects formatted as invisible Note: Document inspector does not detect objects blocked by other objects. |
The document inspector finds the elements listed below that may contain data not displayed in the book. It is not able to remove them, as this can lead to the wrong work of the book. You can view each element found and decide whether to delete it manually or replace it with an element without hidden data, such as a static pattern.
|
Inspector of documents finds |
|
|---|---|
cells of sheets; |
|
|
Implemented files or objects |
point drawings; visio documents objects; word documents objects; text OpenDocument. |
|
Macros based on VBA code |
Macros or VBA modules that may contain hidden data in the book. These include: macros, including Excel 4.0 macros sheets (XLM); vBA modules; cOM or ActiveX elements. Custom forms, including Form Excel 5.0 custom functions. |
|
Components of business analytics with cached data |
Business analytics components that may contain cached data stored in the book, including invisible data. The document inspector checks the presence of the following elements that may contain consolidated cache, seplosion cache or cache cubes: summary tables and summary charts; sections and timelines; formulas cubes. |
|
Excel polls |
Excel survey issues that were created in Excel Online and are saved in the book, but are not visible in it. |
|
Script Scenarios Scripture |
Scripts that are defined using the Script Manager and can lead to the preservation of cached or hidden data in the book. |
|
Filters |
Filters that can lead to saving cached or hidden data in the book. The document inspector checks the presence of autofilters and filters of tables applied to the data. |
|
Hidden names |
Hidden names that can be a source of hidden data in the book. |
You can search and delete hidden information in PowerPoint presentations using the document inspector.
Tip: If you just want not to print notes, open the tab file _GT_ Print, Click Slides in size all Page And uncheck the checkbox print Notes.
Search and delete hidden and personal data
Types of hidden and personal data
Hidden data may consist of data that PowerPoint add to provide collaboration on creating a presentation with other people. It can also contain the information that you intentionally indicate as hidden.
PowerPoint presentations may contain hidden and personal data of the following types:
Notes and handwritten notes If you work together with other users to create a presentation, your presentation can contain elements such as notes and handwritten notes. This information allows other users to view. changes made And the names of people who worked on the presentation, as well as comments from the reviewers.
Patch tracking data. When working on a general document, which is stored in the cloud, PowerPoint 2016 for Office 365 saves data on who and when introduced into a change document.
Properties of the document and personal data. Properties of the document (metadata) include information about the presentation as the name of the author, theme and title. In addition, they contain data automatically saved by Office programs, such as the name of the user who saved the document last, and the document creation date. If you used specific functions, the document may also contain additional personal information, such as email messaging headers, sending data for verification, document routes, paths to printers, as well as way information to the file to publish web pages.
Invisible content on the slide. The presentation may contain objects formatted as non-renovable.
Content outside the slide. PowerPoint presentations may contain objects that are not displayed because they were moved beyond the slide. Such objects can be inscriptions, pictures, graphic elements and tables.
Notes to the presentation. Section notes to PowerPoint presentation may contain text that may undesirable to provide other users, especially if these notes were created exclusively for the Rapporteur.
Properties of document server. If the presentation has been saved on the document management server, for example, on the website of the workspace for documents or in the Windows SharePoint Services library, it may contain additional properties or location information on the server.
Custom XML data. Presentations may contain custom XML data not displayed in the document itself. They can be detected and deleted using the document inspector.
Information that finds and deletes the inspector of documents
The document inspector in PowerPoint includes several different modules that allow you to find and delete hidden and personal data specific to PowerPoint presentations. A list of various types of hidden and personal data that can be removed from the presentations using the document inspector is presented in the table below.
If additional modules have been added to the organization in the inspector of documents, you can check the presence in the presentations of other types of information.
Inspector | Finds and deletes |
|---|---|
|
Notes |
Notes Handwritten notes |
|
Properties of the document and personal data |
Properties of the document, including information from tabs General, Statistics and Others dialog box Properties of the document Email headlines Document routes Data sent to verification Properties of document server Document Management Policy Information Content Type Information File path to publish web pages |
|
Move tracking data |
Data on who and when the file has been changed. This feature is available only to Office 365 subscribers, which take part in the Office Preliminary Evaluation Program. If you have a subscription to Office 365, make sure that you have the latest version of Office. |
|
Invisible content on the slide |
Objects formatted as non-refined This inspector does not detect objects blocked by other objects. |
|
Content outside Slide |
Content or objects that are not displayed in the presentation, as they are located outside the Slide area |
|
Notes to the presentation |
Text added to the section notes to the presentation The document inspector does not remove the pictures added to the section notes. |
|
Customizable XML data |
Custom XML data that can be stored in the presentation |
Information that the document inspector finds but cannot delete
The document inspector finds the elements listed below that may contain data not displayed in the presentation. It is not capable of removing them, as this can lead to improper presentation. You can view each element found and decide whether to delete it manually or replace it with an element without hidden data, such as a static pattern.
|
Inspector of documents finds |
|
|---|---|
|
Implemented files or objects |
Implemented files (for example, Office documents or text files) or embedded objects (for example, diagrams or equations) that may contain invisible data. Here are some examples of object types: point drawings; microsoft Equation 3.0 objects; objects microsoft Charts Graph; powerPoint presentations objects; visio documents objects; word documents objects; text OpenDocument. |
|
Macros or VBA code |
Macros or VBA modules that may contain hidden data. These include:
|
Inspector of documents and personal data
Correction tracking data that appeared in the assembly of 8403 PowerPoint 2016 for the participants of the Office 365 preliminary assessment program are an example of restrictions inherent in the document inspector. For example, we assume that March and Regina work together on the presentation A in Office 365. Presentation is added to the correction tracking data (i.e. user names and information about the time of expansion). If Gleb will subsequently open a presentation A in PowerPoint 2013 and launches the document inspector to delete personal data, the inspector in this version of PowerPoint will not be able to find and delete pattering tracking data added to the presentation in a later version of PowerPoint (Office 365), which regina and Martha. To remove this data, Gleb will need to go to last version PowerPoint, and then run the document inspector.
You can delete hidden information in Visio as well as in other Office applications. Before you provide other users a copy of the Visio document, you may need to remove certain data from the document and its properties.
You can easily delete the following personal data in Visio:
Notes inserted on document pages
Names, Reviews initials and accumulated by them
Paths to sets of elements
Ways to templates and names of their files
Note: If the document is published on a shared server, then when it opens information about who opened it, and the name of the computer on which the file is stored is displayed. To protect this data, provide access to documents only to those users you trust.
You can search and delete hidden information in Visio presentations by performing the steps below.
On the menu File Click Delete hidden information.
If you use Visio Premium 2010 or later, you will find this command in the section File > Intelligence > Delete Personal Information.
Open tab Personal information.
Check the box Delete the following elements from the document.
Tip: Check the box Prevent in the event of a re-insertion of this dataIf you want to receive a warning while trying to re-insert personal data.
To delete confidential data from external sources, Check the box Delete data from external sources stored in the current document.
Note: This flag not Allows you to delete data related to the figure. It deletes the data source from the circuit, but if the data from it is already in it, they must be deleted manually.
Feedback
This article is updated January 8, 2019.g. As a result of your notice. If you have found this article useful and especially if you do not have, use the reviews in the feedback controls in order to give us a number of proposals for constructive.
The easiest way to grab the tail of a negligent employee or a student who gave his report or coursework "on outsource" is to see the author or co-authors of the document. This information is stored along with other metadata files and can later be viewed by anyone. The case acquires a particularly delicate position if a familiar performer is familiar for the inspection person: an employee of the same company or a student from the same stream. Of course, a multi-storey lie will find a way out of the situation, but as it were, then she did not get into the light. Pay attention to the associated document users in the lower right corner
Banal, of course, an example, but it is usually pierced on it.
What information can leak
The official help of Microsoft gives the same to represent the potential threat to your reputation. I will give her squeeze here:
- Traces of the presence of other users, as well as directions made by them and added comments, if you work on a document in collaboration.
- The discolored information contained in the upper and footers, as well as the substrate (watermark).
- Hidden text Word., invisible PowerPoint objects, hidden rows, columns and Excel sheets.
- Content, located outside the PowerPoint slide area.
- Additional properties of the document and other metadata, such as the path to the printer or the headlines of the electronic letters.
Inspector documents
"Document Inspector" is a convenient tool for checking files for unwanted information. It is convenient for both the sender and the recipient of the document. Just need to go to the "information" and launch the check. Couple of clicks and five seconds will be turned out to be out of all possible.

The Contractor remains to be deleted, and checking - to explore a document based on the existing evidence.
Prohibition of maintaining personal data
Delete personal data
from metadata files
Files created in most popular programsThese properties are automatically completed from the computer and the program itself. Due to the production necessity for files overlooking the organization, this data should be deleted. For example, in MS Office documents, you must remove the name of the company, the name of the author of the document and the user, the last preserved the document. How to do it?
Solving the task of removing metadata from documents can be divided into several stages:
- Delete data from already created documents.
- Non-preservation of such data into newly created documents.
- Control of sending such data through E-mail funds.
For already created files, the task is solved by the built-in means of modern operating systems. Starting with Windows 7, it is enough to call the properties of the file and at the bottom of the tab "Details" select "Delete Properties and Personal Information". Select several files of the same type at once, you can erase the data directly from several documents.
For mass deletion of information from files you can use special applications. For example, Batchpurifier allows you to automatically remove the metadata 60 values \u200b\u200bof 24 file types, including office applications And graphic files (PNG, JPEG).
For new documents in the Microsoft Office application, users must apply the "Inspector of Documents" from the "Details" menu - "Search for problems", which is scanning a not yet saved document for personal data and their removal.
In earlier microsoft versions Office (XP or 2003) You must set the Office 2003 / XP Add-in: Remove Hidden Data, RHD_TOOL extension, after which the Remove Hiden Data option will appear in the File menu.
In order for the registration data of Microsoft Office applications for newly created documents, it is possible to identify the user, the following changes in the registry can be made:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
"COMPANY" \u003d "_"
"CompanyNAME" \u003d "_"
"UserName" \u003d "_"
"Userinitials" \u003d "_"
To change apply, MS Office applications must not be launched.
The next step is to control sending via e-mail of hidden data or personal information.
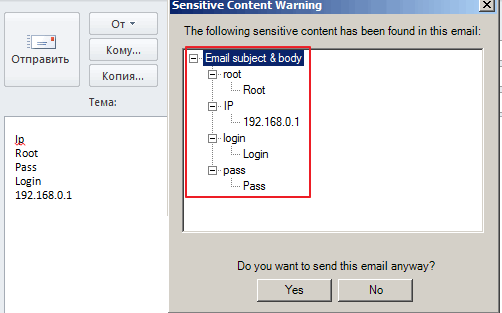
Unfortunately, the solutions are built into Microsoft Outlook. You can use the ConfidentSend application to automatically monitor and clean the documents, which can be cleaned in manually or automatically clean the metadata of attachment files. ConfidentSend also browsing a message to a match with a predetermined user text templates and, if possible, it issues a warning (see Fig. 2).
There is no doubt that secret, confidential information needs protection. Throughout its existence, humanity has invented various ways that could prevent or at least make it difficult to access this information, as well as encryption systems. In the 20th century, new digital technology of accumulation, storage and information transmission appeared. Computer systems made it possible to recruit, edit, check spelling and spelling, convert and transmit information in electronic form, understandable for almost all computers. From this point on, the problem of confidentiality and protection of personal information has become particularly relevant. Hackers, industrial spies, competitors and other detractors are constantly developing new ways to gain access to individual individuals and companies.
Most currently existing software products in the market information referred to as metadata is saved in the same files with which the users and which are used to save the history of file editing, as well as to help search and to extract information from files. The characteristic examples of the metadata are the name and surname of his author, the company, the name of the computer, the version of the document, the version of the document, various hidden information, etc. These metadata are also used to universalize the procedure for saving all the file information in one predetermined place.
At the same time, most of this confidential information is saved as if by default, sometimes unknown for the user in the manner and in an unknown place and form. It's no secret that even harmless to the type of setting in software products There may be information that inquire the persistent user about the owner of the product or its company. An example is the Word text editor from microsoft. or any other software applicationworking electronic documents and allowing you to save various versions of the document in the same file using different modes. Consider a simple but very characteristic case. Suppose our reader, being the head of the marketing department, worked for several weeks with his team to create a document describing the characteristics of the latest development. At the same time, the parcel of this document was planned to the sales department to start a new marketing campaign. At the last moment, it was decided to remove several characteristics from the product description in order to further verify and clarify. However, it was known that these characteristics will necessarily enter the final version of the marketing document for this product. Excluding that the version of version is activated for this document and that every change, including new version With remote characteristics, will be saved in the file, this document has become the widespread. Suppose that after sending a letter with specified file In the sales department, it fell to the competitor. The latter, viewing various versions of the document, can easily estimate your current level and expected results, and also timely transfer information to your developers. In addition, the property properties may contain the name and email address of the author of the document, so it will be considered that he voluntarily provided a document for the use of competitors.
How to organize protection of private information and protect it from unwanted access? We will try to answer this question in this article. We also consider places in the document where metadata can be stored, and we describe the ways with which this data can be deleted, thereby protecting the document. Before turning to business, we note that as a tested object in this article discusses the English versions of a widely known and popular text editor. Microsoft Word. - Word 2000 and Word 2002 - included in the Microsoft Office package. It should be emphasized that, despite the generality and continuity of these versions of this editor, they still have some differences in their functionality. This is primarily worth paying attention to readers who immediately sit for their personal computer.
How to access personal information
achnyne from the simplest - we will show how without special tricks to get to personal information. This is done using the only Microsoft Word feature, which allows you to view the text without formatting it. It turns out this feature It can be used to view metadata associated with a specific document. Everyone can get access to this data. For this you need:
- Run Microsoft Word Editor.
- At the File Main menu item, click Open.
- In the dialog that appears in the Files of Type section, set the Recover Text from Any File, select Microsoft Word format document and click Open.
At the same time, an unformatted document will open, which allows you to easily find information containing the name of the author of the document and the path where you can find a saved document.
Considering all the above, we recommend: before providing a document to other users, view the hidden information in order to decide whether it is worth it to be left in this document for universal review. For example, selecting Track Changes in the main menu of the Microsoft Word editor, and then the Versions item from the Files menu or setting the Allow Fast Saves mode using the Flag button to the Options menu of the Tools menu, can be traced for any hidden or remote information that could potentially Stay in edited document.
As you can see, it is quite simple to access personal information. Naturally, there is a reasonable question about what ways there are ways to protect confidential information from prying eye. Next, the attention of readers will offer several of the most common techniques.
Remove personal data from documents
Current version Word Editor provides the user to the most wide opportunities In working with personal data, starting with manual and ending with the programmable way to remove information. Due to the fact that within the framework of this article we do not address the issues of writing specialized programs, we will focus on the most simple and accessible ways of readers.
First of all, it is necessary to make sure that some personal information has been deleted during the preservation of the document. To do this, you must perform the following actions:
- In the main Word menu, select the Tools item, and in it the Options submenu. In the dialog that appears, open the Security tab.
- In the Privacy Options section, activate the Remove Personal Information from This File On Save and press the OK key.
- Save document.
At the same time, the document is deleted, for example, the following personal information:
- file properties: author, head, company and name preserved the latest version of the document;
- user names related to comments and changes tolerance (Track Changes);
- the name SAVED BY is replaced by Author;
- the e-mail message header is generated by the E-mail button on the toolbar.
It should be emphasized that the specified operation is not installed in the Word editor by default. And even if such a flag is set, it will only relate to the current activated window with the document. Therefore, this mode must be installed for each document separately.
Another way that deserves attention is the method of removing personal information manually. In the properties of the document (inside the file structure), information about the document itself is stored: the name of the document file, the location of it, the date of creation and other file attributes. At the same time, other metadata, such as the name of the author, the name of the company, and the document editor can be stored in the properties of the document. You can delete this information from the properties of the document using the following sequence of actions:
- Open document in Word Editor.
- In the File Main menu section, select Properties.
- In the multi-page dialog that appears on each SUMMARY, STATISTICS, Contents and Custom bookmark may contain confidential information. To remove unnecessary or unwanted information, it is necessary to select it and remove it with the Delete key.
Of course, the above procedures can be automated and programmed by making this process rapid and convenient. However, the description of the Principles of Programming in Word is beyond the scope of this article and we send the reader to specialized literature.
Where information is hidden
the bottom-up rule is guided by practical people, says: "Several times will die - once". This vital principle can be successfully applied to work with documents. Do you always have to rush to part with personal information? Where is the hidden information stored? What are the ways to view hidden information? These questions will be given in this section.
Hidden information can be found in the tracking tracking features (commenting functions), which are for the Microsoft Word editor for the most part of the service. They allow you to maintain intermediate information on formatting, text inserts, deletes, remarks, etc., in other words, can be actively used in the process of working on a document by one or more authors. In this case, by selecting the playback mode of all service functions, you can see all the changes made with the names of the authors. This is done using the Show menu item.
It should be borne in mind that when working on any document it is desirable to adhere to two simple rules. The first rule states that before removing any information it is useful to print edited document together with comments. Thus, at any time it will be possible to make this information into a new version of the document. In order to visualize changes or comments, you need to select Markup in the Main Menu.
The second rule mainly concerns those who forget to follow the presence of auxiliary information in the document sent or transmitted. For such users, an automatic analyzer is provided for the enabled track change mode, which will display a prevention in the edit information document when you try to print it, save or send e-mail from Word Editor. To enable this mode, in the Tools Main menu section, in the Options dialog box, you need to select the Security tab and in it using the WARN Before Containing, Saving, OR Sending A file with the Flag button, Saving, OR Sending A File. So, the meaning of the second rule is: always keep the track Changes analyzer enabled.
The second place where confidential information can be stored is Hidden Text Microsoft Word. This mode allows you to show or hide the specified text using special procedure Formatting characters making them invisible. For example, in the process of editing text in Hidden Text mode (hidden text - special non-reducible characters in the document file) can be made for yourself any mark. To view the hidden text, in the Tools Main Menu section, you need to select Options, and in the View tab - Hidden Text mode in the Formatting Marks section (Fig. 2).
In this case, Word will mark the hidden text using a dotted underscore. Unfortunately, the developers of the editor did not provide for an automatic analyzer in the document of the hidden text. However, there is a very simple procedure for its removal of the document when printing. To do this, in the Tools Main Menu section, select Options, then bookmark the Print and activate the Hidden Text flag button in the Include WITH Document Area section. In all other cases, you will have to delete text manually.
The third source of unwanted leakage of information may be unsuccessful previous versions of the document. The Word editor provides for the ability to save in the same file of several versions of the document. These versions are present in the file in the hidden text mode and can be deleted as needed. They are available to all users, and remain in the document, even if it is saved in another format. Therefore, such versions should be deleted in time, for which there are several ways.
The first way provides to preserve previous versions Document. In this case, the current version is saved as a separate document. To do this, select Versions item in the main menu. Then select the version of the document you want to keep in the form separate file.. Next, press the Open key and in the Main Menu File Select Save AS. In the dialog that appears, set the file name and press the SAVE key.
The second way is to remove unwanted versions from the document, which will require the following steps. In the Main Menu, the File needs to select Versions, then the version of the document it is assumed to be deleted (to select more than one version, you must hold the Ctrl key). Next, click the Delete button.
Silent keepers of hidden information
foot readers and do not suspect that some procedures in Word retain the default metadata. And certainly do not realize that blocking these procedures allows you to remove unwanted metadata from documents. Tell about it in more detail.
First, consider the method of quickly saving the document. Note that it works if the FAST FAST SAVES flashes. However, do not everyone know that if you open a document that edited in this mode, in the form of a text file, it may contain the information that was previously removed from the document. This is because fast saving mode adds changes to the end of the document, without taking into account all changes (including remote information), conducted in the document itself. Therefore for complete removal Erased from the document document you need to disable fast saving mode. To do this, in the main menu Word, you need to select Tools, then the Options section and the Save dialog (Fig. 3).
Secondly, consider the procedure for combining documents. When comparing and combining documents Word uses randomly generated numbers for easy tracking for the relevant documents. Despite the fact that these numbers are hidden, potentially they can be used to demonstrate that the documents have a general source. For stopping storage random numbers During the process of combining documents, you must follow these steps:
- In the Tools menu, run the OPTIONS command. In the multi-page dialog that appears, select the Security dialog.
- Deactivate the Store Random Number to Improve Merge Accuracy flag button.
However, it should be noted that the confidentiality will have to pay - the result of the merge of documents will not be optimal: for the Word editor will be problematic to determine the number of related documents.
Knowledge is power
Everyone who read this article will certainly be a personal opinion on the problem of information protection on personal Computer And everyone will be waited to accept their decision. You can follow the rules listed and cannot save information, but it is possible to lose it if you do not make any effort. The article covered the most simple ways Prevent information leaks. In addition, as noted above, there are a number of programs for solving many of the above-mentioned problems that will undoubtedly allow to significantly facilitate the procedure for checking the content in the documents undesirable to disseminate data. However, this is the topic for another article. In conclusion, I would like to note that, preventing personal information, you can not only protect your business, knowledge and experience, but also give a decisive story unclean to people.
ComputerPress 10 "2002
 How to pay a domain name
How to pay a domain name Domain zone of tokelau islands
Domain zone of tokelau islands What is domain what problems may be
What is domain what problems may be Yandex Wordstat: detailed instructions for using the service and grouping operators and a complicated request
Yandex Wordstat: detailed instructions for using the service and grouping operators and a complicated request Editing DBF files
Editing DBF files Xenu Link Sleuth - What is this program how to use the Xenu program
Xenu Link Sleuth - What is this program how to use the Xenu program Methods Copy and insert text from keyboard without using mouse
Methods Copy and insert text from keyboard without using mouse