Postgresql connecting to a remote database. PostgreSQL database connection. Changing user roles
A vulnerability (CVE-2019-18634) has been identified in the sudo utility, which is used to organize the execution of commands on behalf of other users, which allows you to increase your privileges on the system. Problem [...]
The release of WordPress 5.3 improves and expands the block editor introduced in WordPress 5.0 with a new block, more intuitive interactions, and improved accessibility. New features in the editor [...]
After nine months of development, the FFmpeg 4.2 multimedia package is available, which includes a set of applications and a collection of libraries for operations on various multimedia formats (recording, converting and [...]
Linux Mint 19.2 is a Long Term Support release that will be supported until 2023. It comes with an updated software and contains improvements and many new [...]
Release submitted Linux distribution Mint 19.2, the second update to the Linux Mint 19.x branch, built on the Ubuntu 18.04 LTS package base and supported until 2023. The distribution is fully compatible [...]
New BIND service releases are available that include bug fixes and feature enhancements. New releases can be downloaded from the downloads page on the developer's site: [...]
Exim is a Message Transfer Agent (MTA) developed at the University of Cambridge for use on Unix systems connected to the Internet. It is freely available in accordance with [...]
After nearly two years of development, ZFS on Linux 0.8.0 has been released, implementing file system ZFS, designed as a module for the Linux kernel. The module has been tested with Linux kernels 2.6.32 to [...]
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), which is engaged in the development of Internet protocols and architecture, has completed the formation of an RFC for the Automatic Certificate Management Environment (ACME) protocol [...]
Let’s Encrypt, a non-profit certification center controlled by the community and providing certificates for free to everyone, summed up the results of the past year and spoke about plans for 2019. […]
PostgreSQL is a cross-platform object-relational database management system with an open source code... This article will show you how to install PostgreSQL in Ubuntu Linux, connect to it and pair simple SQL queries, as well as how to set up a backup.
To install PostgreSQL 9.2 on Ubuntu 12.10, run the following commands:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa: pitti / postgresql
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install postgresql-9.2
Let's try to work with the DBMS through the shell:
sudo -u postgres psql
Let's create a test database and a test user:
CREATE DATABASE test_database;
CREATE USER test_user WITH password "qwerty";
GRANT ALL ON DATABASE test_database TO test_user;
To exit the shell, enter the \ q command.
Now let's try to work with the created database on behalf of test_user:
psql -h localhost test_database test_user
Let's create a new table:
CREATE SEQUENCE user_ids;
CREATE TABLE users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT NEXTVAL ("user_ids"),
login CHAR (64),
password CHAR (64));
Note that, unlike some other DBMSs, PostgreSQL does not have auto_increment columns. Instead, sequences are used in postgres. On the this moment it is enough to know that using the nextval function we can get unique numbers for a given sequence:
SELECT NEXTVAL ("user_ids");
By setting the default value for the id field of the users table the value NEXTVAL ("user_ids"), we have achieved the same effect as auto_increment. When adding new records to the table, we can omit the id, because a unique id will be generated automatically. Several tables can use the same sequence. Thus, we can ensure that the values of some fields in these tables do not overlap. In this sense, sequences are more flexible than auto_increment.
The exact same table can be created with just one command:
CREATE TABLE users2 (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
login CHAR (64),
password CHAR (64));
In this case, the sequence for the id field is automatically generated.
Now with the command \ d you can see the list of all available tables, and with the help of \ d users you can see the description of the table users. If you don't get the information you're interested in, try \ d + instead of \ d. The list of databases can be obtained with the \ l command, and switching to a specific database can be obtained with the \ c dbname command. For command help, say \? ...
It is important to note that PostgreSQL converts table and column names to lowercase by default. If this behavior is undesirable, you can use double quotes:
CREATE TABLE "anotherTable" ("someValue" VARCHAR (64));
Another PostgreSQL feature that can be difficult to get started with is the so-called "schema". A schema is something like a namespace for tables, like a catalog of tables within a database.
Creating a schema:
CREATE SCHEMA bookings;
Switching to the circuit:
SET search_path TO bookings;
You can view a list of existing schemas with the \ dn command. The default is a schema named public. In principle, you can successfully use PostgreSQL without knowing about the existence of schemas. But when working with legacy code, as well as in some edge cases, knowledge about schemas can be very useful.
Otherwise, working with PostgreSQL is not much different from working with any other relational DBMS:
INSERT INTO users (login, password)
VALUES ("afiskon", "123456");
SELECT * FROM users;
If you try to connect to postgres from another machine now, you will fail:
psql -h 192.168.0.1 test_database test_user
Psql: could not connect to server: Connection refused
Is the server running on host "192.168.0.1" and accepting
TCP / IP connections on port 5432?
To fix this, add the line:
listen_addresses = "localhost, 192.168.0.1"
... to the file /etc/postgresql/9.2/main/postgresql.conf as well.
Attention : If you work in Windows and have not yet installed PostgreSQL and Debet Plus V12, then you can download the Debit Plus V12 assembly from the download page with a pre-installed PostgreSQL DBMS and a connected database (with a basic configuration for Ukraine). Otherwise, you need to first install the PostgreSQL DBMS and the Debet Plus V12 software package, after which you can configure the connection and import the PostgreSQL database following this instruction.
To connect the PostgreSQL database, you need to do the following:
Run "Debit Plus V12" and add a new base (context menu "Add new").
Leave the checkbox "Add existing to the list".


"DBMS" - POSTGRE.
"Database Server" - localhost.
"Database name" - specify the name of the database from the PostgreSQL DBMS in lowercase Latin letters (small letters).
Note: Usually one base is used. For special purposes, the database can be split into several, then you need to check the box next to "Use multiple databases", click the "Next" button and specify the correspondence of the "tags" physical bases... This may be necessary, for example, if the databases of several enterprises will refer to the same directories (counterparties, items, etc.). This case is not discussed further.
"Settings directory" - specify the path to the base settings for PostgreSQL (drive \ DebetPlusV12 \ base \ pgdpbase).
Save changes made by clicking the "Finish" button.
Start pgAdmin (PostgreSQL DBMS administrator), add a server (File / Add Server ...) and add a new database (New Database ... menu).

Enter the server name, localhost in the Host field, fill in the rest of the fields as you wish.
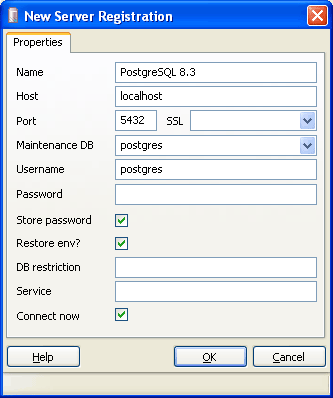
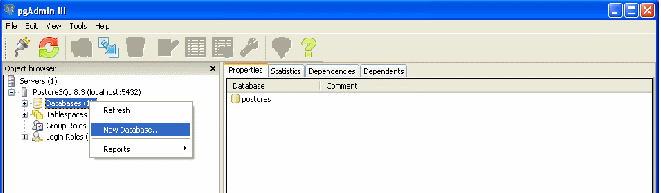
Enter the name of the database in the "Name" field (the same as entered in the "Server" field in the settings for connecting to the "Debit Plus V12" database).

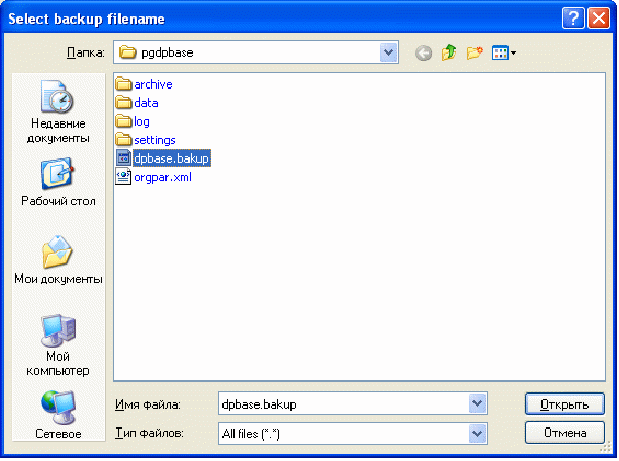
To import the database from the archive, use the "Restore ..." menu.

Specify the path to the dpbase.bakup database archive (drive \ DebetPlusV12 \ base \ pgdpbase).

You can add the dpadmin user, who is the administrator, to Debit Plus V12 by default (no password).

Assign all rights to this user.
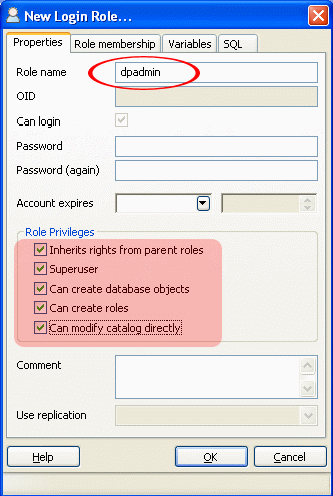
Note : You can not add the dpadmin user, then when activating the database you will need to enter the postgres administrator name.
Refresh the list of bases (menu "Refresh").
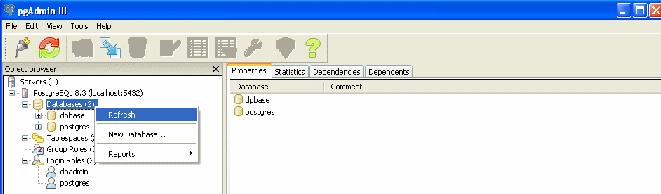
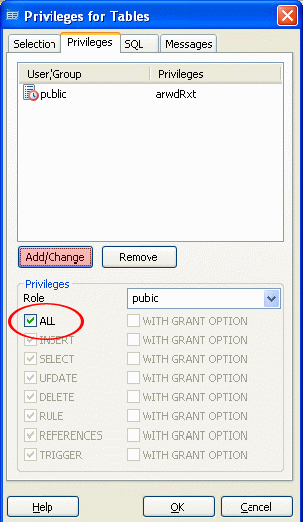
Note : If you do not want to assign the "Superuser" rights to the user, then assign the rights to "Tables" and "Views". To do this, select the appropriate object and select the Grant Wizard context menu item.

On the "Selection" tab, click the "Check all" button, and on the "Privileges" tab, check the "ALL" checkbox and click the "Add / Change" button. Save your changes.

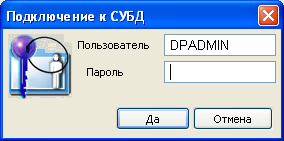
Activate the setting of the connection to the database in the Debet Plus V12 software (context menu "Make active").

The system will ask for a password to connect to the database. Click Yes.
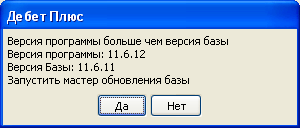
Attention! If such a message does not appear, then start updating the database structures by selecting the menu item "Service" / "Update database structures".
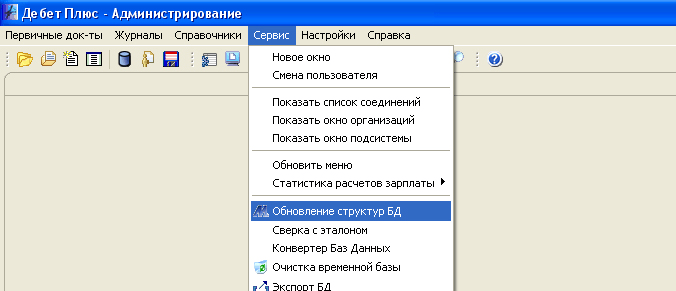
As a result, the following window will appear:

Leave all checkboxes by default (there must be checkboxes in the "Reindex" column for all database tables).
After finishing the modification, you can start working.
Run "Debit Plus V12" and add a new base (context menu "Add new").
Leave the checkbox "Add existing to the list":


In the first field, specify an arbitrary name for the database (the name may be different on each working computer).
"DBMS" - POSTGRE.
Database Server is the name or IP address of the server.
Database server port - specify the port of the database server, by default 5432.
"Database name" - specify the name of the database in Latin letters in lower case.
The "Database Schema Name" is dpbase.
Check the box "Use Debit Plus authorization" only.
"Settings directory" - specify the path to the base settings for PostgreSQL (network path \ DebetPlusV12 \ base \ pgdpbase).
Save the changes made by clicking the "Finish" button, and then make the base active.
Set launch parameters (main menu "Settings" / "Launch parameters")

In the window that appears, in the "Password for changing settings" field, enter the password 150301 and click the "Accept" button.

Specify the path to the JDebet folder on the server and click save. Make the base active and you can get to work.
System AdministrationThis post - short instruction for beginners, for those who first installed PostgreSQL. Here all the necessary information to get started with PostgreSQL.
Connection to DBMS
The first thing to do is to get access to PostgreSQL, access as superuser.Authentication settings are located in the pg_hba.conf file.
- local all postgres peer
We connect:
- $ sudo -u postgres psql postgres postgres
- # TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
- hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
Setting the environment variable PGPASSWORD
I must say right away that it is better not to use this method, because some OS allow regular users to view environment variables with ps. But if you want, then you need to write in the terminal:- export PGPASSWORD = mypasswd
Storing the password in a .pgpass file
If we are talking about Linux, then the file should be located in $ HOME (/ home / username). Only the owner (0600) must have write and read permissions. You need to write lines of the form to the file:- hostname: port: database: username: password
Getting help information
\? - will give all the available commands along with their brief description,\ h - will list all available requests,
\ h CREATE - will display help for a specific request.
DBMS user management
How do I get a list of PostgreSQL users? Or, you can query the pg_user table.- SELECT * FROM pg_user;
Creating a new PostgreSQL user
From the psql shell, you can do this with the CREATE command.- CREATE USER username WITH password "password";
- createuser -S -D -R -P username
Change user password
- ALTER USER username WITH PASSWORD "password";
Changing user roles
To enable the user to create databases, run the query:- ALTER ROLE username WITH CREATEDB;
Database management
Listing databases in psql terminal: Same from Linux terminal:- psql -l
- CREATE DATABASE dbname OWNER dbadmin;
- createdb -O username dbname;
Setting up access rights to the database
If the user is the owner (owner) of the database, then he has all the rights. But if you want to give access to another user, then you can do this using GRANT commands... The query below will allow the user to connect to the database. But don't forget about config file pg_hba.conf, it must also have the appropriate connection permissions.- GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE dbname TO dbadmin;
 Making money for a car How to make money if not 18
Making money for a car How to make money if not 18 Earning money on traffic on the Internet: step by step instructions
Earning money on traffic on the Internet: step by step instructions Yandex Direct doesn't sell?
Yandex Direct doesn't sell? Delivery. Yandex.Delivery Yandex.Delivery
Delivery. Yandex.Delivery Yandex.Delivery Practical lessons: registration at Wildberries, working with a personal account and other important tasks Supply of wildberries
Practical lessons: registration at Wildberries, working with a personal account and other important tasks Supply of wildberries How to enter the personal account of tiu ru
How to enter the personal account of tiu ru How "black" and "white" promotion on Instagram works: interviews with developers of the deferred posting service Parasite service
How "black" and "white" promotion on Instagram works: interviews with developers of the deferred posting service Parasite service