PCI E 3.0 x16 cards. What is the difference between the PCI Express interface from PCI? PCI-E ports and lines may vary
- Hello! Please explain the difference in the bandwidth between the PCI Express 3.0 x16 interface and PCI Express 2.0 x16. Now there are still on sale motherboards with PCI Express 2.0 x16 interface. I S. i lose it in the performance of vidyuhi if I install a new interface graphics cardPCI Express 3.0 on a computer with a motherboard, where there is only a connectorPCI-E 2.0? I think that I lose, because the totaldata transfer ratepCI Express 2.0 is equal to - 16 GB / s, and totaldata transfer rate from PCI Express 3.0 twice as large -32 GB / s.
- Hey! I have a powerful computer, but not a new Intel Core i7 2700K processor and the motherboard on which there is a PCI Express 2.0 connector. Tell me if I buy a new PCI Express 3.0 interface video card, then this video card will work twice as slower than if I had a motherboard with a connector PCI Express 3.0? So I have time to change the computer?
- Please answer such a question. On my motherboard there are two connectors: PCI Express 3.0 and PCI Express 2.0, but in the connector PCI Express 3.0 New Video CardPCI Express 3.0 does not climb, prevents the southern bridge radiator. If I install the video cardPCI-E 3.0 in a slot PCI-E 2.0, then my video card will work worse than if it were installed in the PCI Express 3.0 slot?
- Hello, I want to buy a little used motherboard from a friend for two thousand rubles. Three years ago he bought it for 7,000 rubles, but I was confused by the fact that an interface video card slot PCI-E 2.0, and I have a video cardPCI-E 3.0. My video card on this motherboard will work at full power or not?
Hi friends! To date, you can find motherboards with a connector to install PCI Express 2.0 x16 video cards and PCI EXPRESS. 3.0 x16. The same can be said about graphic adapters, commercial cards with interface are on sale.PCI-E 3.0, as well as PCI-E 2.0. If you look at the official characteristics of the PCI Express 3.0 x16 and PCI Express 2.0 x16 interfaces and PCI Express 2.0 x16, then you will learn that the total data transfer rate of PCI Express 2.0 is equal to - 16 GB / s, and PCI Express 3.0 is two times more -32 GB / s. I will not delve into the debris of the specifics of these interfaces and just tell you that such a big difference in The data transfer rates are visible only in theory, in practice it is very small.If you read articles on this topic on the Internet, thenyou will come to the conclusion that modern PCI Express 3.0 interface video cards work with the same speed in PCI Express 3.0 x16 and PCI Express 2.0 x16 and PCI Express 2.0 x16 anddifference in bandwidthbetween PCI-E 3.0 X16 and PCI-E 2.0 x16, only 1-2% of the performance loss of the video card. That is, it's all the same in which slot you install the video card, in PCI-E 3.0 or PCI-E 2.0, everything will work equally.
But unfortunately all these articles were written in 2013 and 2014 and at that time there were no such games as Far Cry Primal, Battlefield 1 and other new products that appeared in 2016. Also in 2016 saw the light Family of NVIDIA graphic processors of the 10th series, for example, GeForce GTX 1050 and GeForce GTX 1050 Ti video cards and even GTX 1060. My experiments with new games and new video cards showed that the advantage of the PCI-E 3.0 interface overPCI-E 2.0 is already far from 1-2%, but Average 6-7%. What is interesting if the video card is below the class thanGeForce GTX 1050. , then the percentage is less (2-3%) , and if on the contrary, then more -9-13%.
So, in your experiment I used a video card GeForce GTX 1050 Interface PCI-E 3.0 and Motherboard with connectorsPCI Express 3.0 x16 and PCI Express 2.0 x16.
N. articles of graphics in games are maximum everywhere.
- Far Cry Primal game. Interface PCI-E 3.0 showed the advantage overPCI-E 2.0, since Always above 4-5 frames, which in the percentage of approximately4 % %.
- Game Battlefield 1. Out of PCI-E 3.0 from PCI-E 2.0 amounted to8-10 frames that in the percentage ratio of approximately 9%.
- Rise of the Tomb Raider. Advantage PCI-E 3.0 averages 9-10 FPS or 9%.
- Witcher. The advantage of PCI-E 3.0 amounted to 3%.
- GRAND THEFT AUTO V. The advantage of PCI-E 3.0 is 5 fps or 5%.
That is, the difference in bandwidth between the PCI-E 3.0 x16 and PCI-E 2.0 x16 interface is still there and not in favor PCI-E 2.0. Therefore, I would not buy the motherboard at the moment with one PCI-E 2.0 connector.
One of my buddy bought the existent motherboard for three thousand rubles. Yes, once she was fed and cost about ten thousand rubles, there are many connectors on itSATA III and USB 3.0, also 8 slots for RAM, it supports RAID technology, etc., but it is built on an outdated chipset and a video card slot on it PCI Express 2.0! My opinion would be better bought. Why?
It may well happen that after a year or two, the newest video cards will only work in the connectivityPCI Express 3.0 x16 , and on your motherboard there will be moral and outdated and already unused connectorPCI Express 2.0 x16 . You buy a new video card, and it will refuse to work in the old connector. Personally, I have already faced many times with the fact that the video card PCI-E 3.0 did not start on the mat. Panel with connector PCI-E 2.0, and It did not even help to update the BIOS motherboard.I also dealt with video cardsPCI-E 2.0 x16, which refused to work on old motherboards with interfacePCI-E 1.0 x16, although everywhere write about backward compatibility.Cases when the video card PCI Express 3.0 x16 did not start on motherboard withPCI Express 1.0 x16, even more.
Well, do not forget about the appearance of this year the interface PCI Express 4.0. In this case, PCI Express 3.0 will be obsolete.
Introduction
The Moore law states that the number of transistors on a silicon crystal, which is profitable to produce, doubles every couple of years. But it is not necessary to think that the processor speed also doubles every couple of years. Such a misconception is found in many, and users often expect the PC performance to exponentially.
However, as you probably noticed, the top processors on the market are stuck at the level between 3 and 4 GHz for six years. And the computer industry had to look for new ways to increase the performance of computing. The most important of these methods is to maintain the balance between the components of the platform, which use the PCI Express bus - an open standard that allows high-speed video cards, expansion cards and other components to exchange information. And the PCI Express interface is no less important to scaling performance than multi-core processors. If dual-core, four-core and six-core processors can only be loaded using applications optimized for multithreading, any program installed on your computer, one way or another interacts with components connected via PCI Express.
Many journalists and experts expected motherboards and chipsets with support for the next-generation PCI Express interface 3.0 interface in the first quarter. Unfortunately, the problems with backward compatibility were delayed by the PCI Express 3.0 output, and today six months have passed, but we still wait Official information about the publication of the new standard.
However, we talked to the PCI-SIG group (Special Interest Group, which is responsible for the PCI and PCI Express standards), which allowed us to get some answers.
PCI Express 3.0: Plans
Al Yanes (Al Yanes), President and Chairman PCI-SIG, and Ramin Neshati, Chairman of the PCI-SIG Serial Communications Workgroup, shared current plans about the implementation of PCI Express 3.0.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
June 23, 2010 version 0.71 of the PCI Express 3.0 specification was released. Jansen argued that version 0.71 should eliminate all the inverse compatibility problems that led to the initial delay. Naughty noted that the main problem with compatibility was the "DC Wandering" function, which he explained so that the PCI EXPRESS 2.0 devices and earlier "were not given the desired zero and units" to fit the PCI Express 3.0 interface.
Today, when problems with backward compatibility are solved, PCI-SIG is ready to submit a basic version of 0.9 "later this summer." And for this basic version, version 1.0 in the fourth quarter of this year is expected.
Of course, the most intriguing question is when PCI EXPRESS 3.0 motherboards appear on store shelves. Naughty noted that he expects the appearance of the first products in the first quarter of 2011 (the triangle "FYI" in the picture with the plan).
Naughty added that between versions of 0.9 and 1.0 should not be changed at the level of silicon crystal (that is, all changes will affect only software and firmware), so that some products must enter the market before the final specification 1.0 appears. And products can already be certified for the list of PCI-SIG "INTEGRATOR'S LIST" (triangle "IL"), which is an option for the PCI-SIG conformity logo.
Necession Joking called the third quarter of 2011 as the date "Fry's and Buy" (probably referring to FRYS.COM sites, Buy.com or Best Buy). That is, during this period we must expect a large number of products with support for PCI Express 3.0 in retail stores and online stores.
PCI Express 3.0: Designed for speed
For end users, the main difference between the PCI Express 2.0 and PCI Express 3.0 will be to significantly increase the maximum bandwidth. PCI EXPRESS 2.0 signal transmission signal is 5 GT / S, that is, bandwidth is 500 MB / s for each line. Thus, the main graphic slot PCI Express 2.0, which usually uses 16 lines, provides bidirectional bandwidth to 8 GB / s.
PCI Express 3.0, we will receive doubling these indicators. PCI EXPRESS 3.0 uses 8 GT / S signaling speed, which gives 1 GB / s bandwidth per line. Thus, the main slot for the video card will receive bandwidth up to 16 GB / s.
At first glance, an increase in signaling speed with 5 GT / S to 8 gT / s does not seem to be a doubling. However, the PCI EXPRESS 2.0 standard uses an 8B / 10B encoding scheme, where 8 data bits are transmitted as 10-bit characters for the error elongation algorithm. As a result, we get 20% redundancy, that is, a reduction in useful bandwidth.
PCI Express 3.0 passes to a much more efficient coding scheme 128B / 130B, eliminating 20% \u200b\u200bredundancy. Therefore, 8 GT / S is no longer the "theoretical" speed; This is the actual speed, comparable by performance with a signaling rate of 10 GT / S if the principle of coding 8B / 10B was used.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
We asked Yang's about the devices that will require an increase in speed. He replied that they would include "PLC switches, Ethernet controllers 40 Gbit / s, InfiniBand, solid devices that are becoming increasingly popular, and, of course, video cards." He added "We did not exhausted innovations, they appear not statically, it is a continuous stream," they open the way for further improvements in future versions of the PCI Express interface.
Analysis: Where will we use PCI Express 3.0?
Drives
AMD has already integrated support for SATA 6 Gbps to its 8th line of chipsets, and managing manufacturers add USB 3.0 controllers. Intel in this area is a little behind, because it does not support USB 3.0 or SATA 6 Gb / s chipsets (there are already preliminary samples of motherboards on P67 in the laboratory, and they have support for SATA 6 Gb / s, but USB 3.0 in this We will not get generation). However, as we have repeatedly seen in the confrontation of AMD and Intel, AMD innovation often inspire Intel. Given the speed of the next generation and peripherals interface, until it is necessary to transfer any of the technologies to PCI Express 3.0. And for USB 3.0 (5 Gbit / s), and for SATA 6 Gbps (there are no drives that it would come to the limits of this interface) will be enough one PCI Express line of the second generation.
Of course, when it comes to drives, the interaction between drives and controllers is only part of the question. Imagine an array of multiple SSD with SATA 6 Gb / s interface with a chipset when an array of RAID 0 can potentially load one PCI Express line of the second generation, which most manufacturers of motherboards are used to connect the controller. So determine whether USB 3.0 and SATA 6 Gbps interfaces can really require PCI Express 3.0 support, you can after easy counts.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
As we mentioned, the USB 3.0 interface gives the maximum speed of 5 Gb / s. But also as the PCI Express 2.1 standard, USB 3.0 uses coding 8B / 10B, that is, the actual peak velocity is 4 Gb / s. Email bits to convert to bytes, and you will receive a peak bandwidth of 500 MB / s - just the same as one line of the current standard PCI EXPRESS 2.1. SATA 6 Gb / s works at a speed of 6 Gb / s, but here also uses the coding scheme 8B / 10B, as a result of which the theoretical 6 Gb / s is transformed into the actual 4.8 Gb / s. Again, convert this value to bytes, and you will receive 600 MB / s or 20% more than the PCI Express 2.0 line can provide.
However, the problem lies in the fact that even the fastest SSDs today cannot fully load the connection of SATA 3 Gb / s. Peripherals and closely does not suit USB 3.0 interface load, the same can be said about the latest generation SATA 6 Gb / s. At least today, the PCI Express 3.0 interface is not necessary for active promotion on the platform market. But we hope that as the Intel transitions to the production of the third-generation flash memory, the clock frequencies will increase, and we will get a device that can exceed 3 Gb / s level at the SATA ports of the second generation.
Video card
We conducted our own studies of the effect of PCI Express throughput on video card performance - after entering the PCI Express 2.0 market , in early 2010 as well as recently . As we found, it is very difficult to load the bandwidth X16, which is currently available from PCI EXPRESS 2.1 motherboards. You will need a configuration on several GPUs or an extreme high-end video card on one GPU so that you can detect the difference between X8 and X16 connections.
We asked AMD and Nvidia to comment on the need for PCI Express 3.0 - will this high-speed tire need for the disclosure of the next generation video card performance potential? AMD representative told us that he could not give comments yet.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
The NVIDIA representative turned out to be more agreed: "NVIDIA played one of the key roles in the industry in the development of PCI Express 3.0, which must double the access of the current generation standard (2.0). When such significant increases in the bandwidth occurs, applications that may appear. Use them. From the new standard, consumers and professionals will benefit, thanks to the increased performance of graphics and computing in laptops, desktops, workstations and servers, where there is a GPU. "
Perhaps the key can be called the phrase "applications that can use them" will appear. It seems that the world does not decrease anything in the world. Displays are becoming more, the high resolution goes to replace the standard resolution, the textures in games are becoming more and intriguing. Today we do not believe that even the newest top video cards have the need to use the PCI Express 3.0 interface with 16 lines. But enthusiasts from year to year are observing the repetition of history: the progress of technology makes the way for new ways to use "thicker pipes". Perhaps we will get explosive growth of applications that will make calculations on GPU more massive. Or perhaps a drop in performance that is observed when you go beyond the memory of the video card when the swinging from the system memory begins, it will not be so tangible at mass and low-end products. In any case, we have to see innovations that PCI Express 3.0 will make it possible to implement AMD and NVIDIA.
Connecting the components of the motherboard
AMD and Intel are always very reluctant to share information about the interfaces that they use to communicate the components of chipset or logical "bricks" in the North / South Bridges. We know the speed with which these interfaces work, as well as what they are being developed so that, if possible, do not create "bottlenecks". Sometimes we know who made a specific part of the system logic, for example, AMD used the SATA controller based on the Silicon Logic development in the SB600. But the technologies used to guide the bridges between the components often remain "white spots". PCI Express 3.0, of course, it seems a very attractive solution, like the A-Link interface that uses AMD.
The recent appearance of USB 3.0 and SATA 6 Gb / s controllers on a large number of motherboards also allows you to assess the situation. Since the Intel X58 chipset does not provide "native" support for any of two technologies, companies such as Gigabyte, have to integrate controllers on the motherboard, using accessible lines to connect them.
The Gigabyte EX58-UD5 motherboard has no support nor USB 3.0, nor SATA 6 Gb / s. However, she has an X4 PCI Express slot.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
Gigabyte replaced the EX58-UD5 motherboard with a new X58A-UD5 model, which has the support of two USB 3.0 ports and two SATA 6 Gb / s ports. Where is Gigabyte found bandwidth to support two of these technologies? The company took under the same PCI Express 2.0 line for each controller, cutting the possibility of installing expansion cards, but at the same time enriching the functionality of the motherboard.
In addition to adding USB 3.0 and SATA 6 Gb / s, the only noticeable difference between the two motherboards concerns the removal of the X4 slot.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
Will PCI Express 3.0 interface, as standards before it, add future technologies and controllers to motherboards, which will not be present in current generations of chipsets in integrated form? As it seems to us, it will be.
CUDA and parallel calculations
We are entering the era of desktop supercomputers. In our systems, graphic processors with intensive parallel data processing are operating, as well as power supplies and motherboards capable of maintaining simultaneous operation of up to four video cards. NVIDIA CUDA technology allows you to convert a video card to a tool for programmers for calculations not only in games, but also in scientific areas, and in engineering applications. The programming interface has already proven itself to developing a variety of solutions for the corporate sector , including processing images in medicine, mathematics, work on the reconnaissance of oil and gas fields.
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
We asked the OpenGl Terry Welsh programmer's opinion (Terry Welsh) from the company Really Slick Screensavers. What about PCI Express 3.0 and calculations on the GPU. Terry told us that "PCI Express got a good jerk, and I like that the developers double the bandwidth when wanted - as with a version 3.0. However, in projects that I have to work on, I do not expect to see any difference. Most My work is related to airlinters, but they, as a rule, rest in memory and I / O performance of the hard disk; Graphic bus is not a "bottleneck" at all. But I can easily foresee that the Tire PCI Express 3.0 will cause a significant advance forward for The scope of calculations on the GPU; for people who perform scientific work with large data arrays. "
 |
Click on the picture to enlarge.
The ability to double the transfer rate when working with loads, intensively using mathematics, will definitely motivate the development of CUDA and FUSION. And this is one of the most promised areas for the upcoming PCI Express 3.0 interface.
Any gamer with Intel P55 chipset can tell about the advantages and disadvantages of Intel P55 compared to the Intel X58 chipset. Advantage: Most motherboards on the P55 chipset cost more reasonably than the model on Intel X58 (in general, of course). Disadvantage: P55 Minimum PCI Express connectivity features, the main task is assigned to Intel Clarkdale and Lynnfield processors that have 16 second-generation PCIe lines in the CPU itself. Meanwhile, X58 boasts 36 PCI Express 2.0 lines.
For P55 buyers who wish to use two video cards, they will have to connect them through X8 lines each. If you want to add a third video card to the Intel P55 platform, you will have to use the chipset lines - but they, unfortunately, are limited to the first generation rate, and the chipset can highlight, maximum four lines for expansion slot.

When we asked Ela Jans from PCI-SIG, how many lines can be expected in chipsets with support for PCI Express 3.0 from AMD and Intel, then he replied that it was "Private Information", which he "cannot reveal". Of course, we did not expect to receive an answer, but the question still set it out. However, the AMD and Intel, which are part of the PCI-SIG Board of Directors, would be to invest time and money in PCI Express 3.0, if they planned to use the new PCI Express standard simply as a means of reducing the number of lines. As it seems to us, in the future, AMD and Intel's chipsets will still be segmented as we see today, high-end platforms will have enough opportunities to connect a pair of video cards with a full X16 interface, and the chipsets for the mass market will be cut down.
Imagine a chipset similar to Intel P55, but with 16 available PCI Express 3.0 lines. Since these 16 lines work twice as fast as PCI Express 2.0, then we will receive the equivalent of 32 lines of the old standard. In such a situation, Intel will depend on whether it wishes to make a compatible chipset with the configurations of 3-Way and 4-way GPU. Unfortunately, as we already know, the next-generation chipsets Intel P67 and X68 will be limited to support for PCIE 2.0 (and the Sandy Bridge processors will be just as limited to support for 16 lines on the crystal).

In addition to parallel CUDA / Fusion calculations, we also see the growth of systems for the mass market due to increasing the speed of the PCI Express 3.0 components - here, as it seems, there is also a considerable potential. Without a doubt, PCI Express 3.0 will improve the possibilities of inexpensive motherboards, which only high-end platforms have been available in the previous generation. And High-End Platforms, who received PCI Express 3.0, will allow us to put new performance records by innovation in the schedule, data storage subsystem and network technologies that can use the available bus bandwidth.
When it comes to any interfaces in the context of computer systems, you need to be very attentive, in order not to "run out" to incompatible interfaces for the same components within the system.
Fortunately, when it comes to the PCI-Express interface to connect a video card, there will be almost no problems with incompatibility. In this article, we will analyze this in more detail, and also talk about what this most PCI-Express is.
What is necessary PCI-Express and what is it?
Let's start, as usual, with the most azes. Interface PCI-Express (PCI-E) - this is a means of interaction, in this context consisting of a tire controller and the corresponding slot (Fig.2) on motherboard (If we generalize).
This high-performance protocol is used as already noted above, to connect the video card to the system. Accordingly, there is an appropriate PCI-Express slot on the motherboard, where the video adapter is installed. Previously, video cards, connected via the AGP interface, but when this interface, simply speaking, "stopped enough", PCI-E came to the rescue, about the detailed characteristics of which we will talk now.

Fig.2 (PCI-Express 3.0 Slots on the Motherboard)
The main characteristics of PCI-Express (1.0, 2.0 and 3.0)
Despite the fact that the names of PCI and PCI-Express are very similar, the principles of connection (interaction) differ fundamentally. In the case of PCI-Express, a bidirectional sequential connection is used, the point-to-point type, lines data can be several. In the case of video cards and motherboards (do not take into account Cross Fire and SLI), which support PCI-Express X16 (i.e., most), you can easily guess that such lines 16 (Fig.3), quite often on motherboards with PCI- E 1.0, it was possible to observe the second slot X8, to work in SLI or Cross Fire mode.
Well, in PCI, the device is connected to a total 32-bit parallel bus.

Fig. 3. Sample slots with different number of lines
(As mentioned earlier, X16 is most often used)
For the interface, the bandwidth is 2.5 Gb / c. These data are needed to us to track changes in this parameter in various versions of PCI-E.
Further, version 1.0 evolved in PCI-E 2.0. As a result of this transformation, we received two times a large bandwidth, that is, 5 Gbps, but I would like to note that in performance graphics adapters did not really won, as it is just a version of the interface. Most of the performance depends on the video card itself, the version of the interface can only slightly improve or inhibit the data transfer (in this case, "braking" is not, and there is a good stock).
In the same way in 2010, with a margin, an interface was developed PCI-E 3.0At the moment it is used in all new systems, but if you are still 1.0 or 2.0, then do not flaruse - we will talk about relatively backward compatibility of various versions.
In the PCI-E 3.0 version, the bandwidth was increased twice as compared with version 2.0. There was also a lot of technical changes.
By 2015, it is expected to appear PCI-E 4.0That for the dynamic IT industry is absolutely no wonder.
Well, okay, we will end with these versions and numbers of bandwidth, and we will affect the very important question of the backward compatibility of various versions of PCI-Express.
Backup compatibility of Versions PCI-Express 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0
This question worries many, especially when select video card For the current system. Since I am satisfied with the motherboard system, which supports PCI-Express 1.0, doubts arise whether the video card will work correctly with PCI-Express 2.0 or 3.0? Yes, it will, at least so promise developers who provided this compatibility. The only thing that the video card will not be able to fully disclose in all its glory, but the loss of performance, in most cases, will be insignificant.

With accuracy, on the contrary, you can quietly install video cards with PCI-E 1.0 interface, in motherboards that support PCI-E 3.0 or 2.0, there is nothing limited at all, so be calm about compatibility. Unless, of course, with other factors, everything is in order, such a powerful power supply unit can be attributed to such.
In general, we talked quite in detail with respect to PCI-Express, which will allow you to get rid of many ambiguities and doubts about compatibility and understanding differences in PCI-E versions.
I was asked this question more than once, so now I will try the most accessible as possible and briefly answer it, for this I will give pictures of the PCI Express and PCI expansion slots and PCI on the motherboard for a more visual understanding and, of course, will indicate the main differences in the characteristics, T .. Very soon, you will learn what are the interfaces and how they look.
So, for starters, let's briefly answer such a question that is generally PCI Express and PCI.
What is PCI Express and PCI?
PCI - This is a computer input-output parallel to connect peripheral devices to a computer motherboard. PCI is used to connect: video cards, audio cards, network cards, TV tuners and other devices. The PCI interface is obsolete, so finding, for example, a modern video card, which is connected via PCI, will probably fail.
PCI EXPRESS. (PCIE or PCI-E) is a computer sequential I / O bus to connect peripherals to the computer motherboard. Those. This already uses a bidirectional sequential compound that several lines (X1, X2, X4, X8, X16, X2, X4, X8, X12, X16 and X32) are already used, the higher the bandwidth of the PCI-E tire. The PCI Express interface is used to connect such devices as: video cards, audio cards, network cards, SSD drives and others.
There are several versions of the PCI-E interface. This is: 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 (the version 4.0 will soon be released.). Denotes this interface usually, for example, like this PCI-E 3.0 x16What is the version of PCI Express 3.0 with 16 lines.
If we talk about whether it will work, for example, a video card, which has interfacePCI-E 3.0 on the motherboard, which supports only PCI-E 2.0 or 1.0, so the developers say that everything will work, only of course, consider that the bandwidth will be Limited by the capabilities of the motherboard. Therefore, in this case, overpay for a video card with a newer version of PCI Express, I think, not worth it ( if only for the future, i.e. You are planning to purchase a new motherboard with PCI-E 3.0). Also, on the contrary, let's say, you have a motherboard supports the version of PCI Express 3.0, and I will say a video card version 1.0, then such a configuration should also work, but only with PCI-E 1.0 capabilities, i.e. There is no restriction here, since the video card in this case will work at the limit of its capabilities.
Differences PCI Express from PCI
The main difference in the characteristics is, of course, the bandwidth, in PCI Express it is significantly higher, for example, in PCI at 66 MHz bandwidth 266 MB / s, and PCI-E 3.0 (x16) 32 GB / s.
Externally, interfaces are also different, so connect, for example, the PCI Express video card in the PCI expansion slot will not work. PCI EXPRESS interfaces with different amounts of lines are also different, I'll show it all in pictures.
PCI Express and PCI Expression Slots on Motherboards
PCI and AGP slots
PCI-E X1, PCI-E X16 and PCI slots


PCI Express interfaces on video cards


On this, I have everything while!
"Manhunt1908 "The support of the motherboard of the new PCI EXPRESS V.3.0 standard is not a competitive advantage." We mainly get that in PCI Express 3.0, in fact, it does not have any real advantages, and it will not increase the speed in modern games. This is no longer anyone else and not interesting, no increase, it means sucks, but in addition to the game functions of the PCI Express V.3.0 standard, it also has other functions, in particular USB 3.0 direct depends on the motherboard with PCI Express support functions v.3.0, after all, they themselves say that, well, the presence of two-four USB ports 3.0 in the computer, according to today's standards, it is simply necessary, 3.0 Many Quaster 2.0, this is many checked in practice. How do not cool and motherboard with PCI Express V. 3.0 is needed, a lot of the latest technologies are attached to this standard. Someone will refuse to have such a solid list on board their motherboard below!
SUPREMEFX IV.
Perfect sound
This motherboard can boast a high-quality audio system based on the built-in SUPREMEFX IV sound card, marked on a printed circuit board with a special line. Capacitors and electromagnetic shielding contribute to the highest sound quality. In addition, the SUPREMEFX IV includes a highlighted headphone amplifier.
Gamefirst II.
The GameFirst II function based on CFOS TRAFFIC SHAPING technology will help set the priority of using an Internet channel with various applications. Having received the maximum priority, online games will work as quickly as possible, without annoying "lags", and other online applications that have a low priority of using an Internet channel will not interfere with it. To access this feature, there is a convenient graphical interface in the ROG style.
Gigabit Ethernet controller
Intel network controllers are famous for its stable and efficient operation at a low level of loading of the central processor.
Adapter MPCIE COMBO and Wi-Fi / Bluetooth 4.0 controller
To save basic expansion slots, this motherboard is equipped with a special optional slot with the MPCIE Combo adapter to which you can connect devices with MSATA interfaces (for example, a solid-state disc) and MPCIE (Wi-Fi wireless adapters, 3G / 4G, GPS, etc. .). And the package already includes a MPCie map with support for Wi-Fi 802.11 A / B / G / N and Bluetooth 4.0.
Fusion Thermo Cooling System
To cool the batteries of the power system on this motherboard, a special cooler ROG FUSION THERMO is used, which consists of a copper water unit, massive radiators and a thermal tube. Thus, it can be used both as part of a liquid cooling system and for conventional cooling with fans. \u003e Find out more
Rog Connect.
Interface for overclocking and settings ROG CONNECT
Using the ROG Connect function, you can monitor the status of the computer and adjust its parameters in real time using a laptop by connecting the last to the main system via a USB cable.
EXTREME ENGINE DIGI + II
Highly efficient digital power system
The Energy Management System EXTREME ENGINE DIGI + II is distinguished by highly efficient operation due to the variable frequency of latitude-pulse modulation of digital stabilizers of the processor and memory voltage. It also uses high-quality capacitors of Japanese manufacturers. Reliable and powerful power system - the key to the successful functioning of the computer in overclocking mode!
ROG CPU-Z
New face of the famous utility
ROG CPU-Z is an individualized version of the famous information utility from the CPUID. It provides the same functionality and accuracy of data issued on a data system as the original, but has a unique interface in the republic of Gamers style. Using ROG CPU-Z, you can get complete information about the processor and some other components of your computer.
Multi-GPU technologies
LucidLogix Virtu MVP.
High speed in graphic applications
LUCIDLOGIX VIRTU MVP technology is a Windows 7 software that implements automatic switching between the graphics core and discrete video card. Due to the translation of the discrete video card to sleep mode in those moments when its resources are not needed, electricity saving is achieved, the noise level from the computer is reduced and the temperature is reduced inside the system unit, which contributes to a more favorable mode of operation of all components. In addition, you can use the built-in graphics core to accelerate the main video card, which allows you to increase the capacity by 60% (according to the results of tests in 3DMark Vantage). It is also worth noting that this technology is fully compatible with the quick transcoding function Intel Quick Sync 2.0.
 Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it
Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it Effective job search course search
Effective job search course search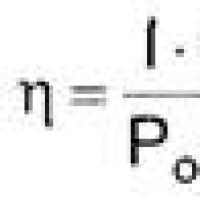 The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode
The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF
How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF Why the fired program window is long unfolded?
Why the fired program window is long unfolded? DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT
DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT What to do if the mouse cursor disappears
What to do if the mouse cursor disappears