The year of release of the AMD processor. What processor is better: AMD or Intel? Intel processor marking
Question: What are the features of the marking of AMD processors?
Answer: Marketing AMD processors is called OPN (Ordering Part Number). At first glance, it is quite complicated and more like a certain cipher, although if you figure it out, you can get enough detailed information about their main technical parameter characteristics:
- The first two letters indicate the processor type:
- AX - Athlon XP (0.18 microns);
- AD - Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 x2;
- SD - SEMPRON.
- The third letter denotes a TDP processor:
- A - 89-125 W;
- O - 65 W;
- D - 35 W;
- H - 45 watts;
- X - 125 W.
- For SEMPRON processors, a third letter has a few different meaning:
- A - Desktop;
- D - ENERGY EFFICIENT.
- Four the following numbers - a processor rating (the one that is specified in all the prices along with the type of processor, for example, Athlon 64 4000+) or, in otherwise, the model number of the model (MODEL NUMBER). It is a number that (from the AMD point of view) characterizes the performance of this CPU in abstract conventional units. Although it did not cost without exceptions, in the Athlon 64 FX processors, for example, instead of the rating numbers, the letter index "FX (Model Index)" is specified.
- The first letter of the three-letter index indicates the type of processor housing:
- A - Socket 754;
- D - Socket 939;
- C - Socket 940;
- I - Socket AM2;
- G - Socket F.
- The second letter of the three-letter index denotes the power supply voltage of the processor core:
- A - 1.35-1.4 V
- C - 1.55 V;
- E - 1.5 V;
- I - 1.4 V;
- K - 1.35 b;
- M - 1.3 B;
- Q - 1.2 b;
- S - 1, 15 V.
- The third letter of the three-letter index indicates the maximum temperature of the processor kernel:
- A - 71 ° C;
- K - 65 ° C;
- M - 67 ° C;
- O - 69 ° C;
- P - 70 ° C;
- X - 95 ° C.
- The subsequent digit indicates the size of the second-level cache (total for dual-core processors):
- 2 - 128 KB;
- 3 - 256 KB;
- 4 - 512 kb;
- 5 - 1024 kb;
- 6 - 2048 Kb.
- Two-letter index indicates the type of core processor:
- AX, AW - NEWCASTLE;
- AP, AR, AS, AT - Clawhammer;
- AK - Sledge Hammer;
- BI - WINCHESTER;
- BN - San Diego;
- BP, bw - venice;
- Bv - manchester;
- CD - Toledo;
- CS, CU - Windsor F2;
- CZ - Windsor F3;
- CN, CW - ORLEANS, MANILA;
- DE - LIMA;
- DD, DL - Brisbane;
- DH - Orleans F3
- AX - Paris (for sempron);
- BI - Manchester (for sempron);
- BA, BO, AW, BX, BP, BW - Palermo (for Sempron).
For example, the AMD SEMPRON 3000+ processor (the manila core) is marked as SDA3000IA3CN. But nothing is always in our world, and AMD in the near future is going to rename the processor ruler by entering a new, much more visual alphanumeric circuit. The new system assumes, along with the traditional designation of the brand and class, also alphanumeric model code
| Brand | Class | Model |
| Phenom | FX. | - |
| Phenom | X4. | GP-7XXX |
| Phenom | X2 | GS-6XXX |
| Athlon | X2 | BE-2XXX. |
| Athlon | X2 | LS-2XXX. |
| SEMPRON. | - | LE-1XXX |
- The first character in the title of the processor model determines its class:
- G - HIGH-END;
- B - Mainstream;
- L - LOW-END.
- The second character determines the power consumption of the processor:
- P - more than 65 W;
- S - 65 W;
- E is less than 65 W (Energy Efficient class).
- The first digit indicates the processor belonging to a specific family:
- 1 - single-core sempron;
- 2 - dual-core Athlon;
- 6 - dual-core Phenom X2;
- 7 - quad-core Phenom X4.
- The second digit will indicate the level of productivity of a particular processor within the family.
- The two recent digits will determine the processor modification.
Thus, the newest two and quad-core processors will become marked as AMD Phenom X2 GS-6XXX and Phenom X4 GP-7XXX. Athlon X2 BE-2XXX Economic Athlon X2 Saders, and Budget AMD Athlon and Sempron will be referred to as Athlon X2 LS-2XXX and SEMPRON LE-1XXX. And the notorious digit 64, indicating the support of a 64-bit architecture, will disappear from the name of the Athlon processor.
Question: What is the difference between the SEMPRON processors from Athlon 64?
Answer: Modern processors of the SEMPRON series, designed for the budget segment of the market, differ from full prototypes - Athlon 64 processors reduced to 128 (or in separate models, up to 256 KB) the volume of the second level cache. In addition, the Hypertransport bus in the SEMPRON processors only works at a frequency of 800 MHz, whereas in Athlon 64 its frequency can reach 1000 MHz; How less significant can be noted the lack of support for Pacifica virtualization technology. Everything else, including a two-channel memory controller, support for 64-bit AMD64 architecture and SSE3 command system - available in full.
At the same time, you should not forget that the SEMPRON so-faced processors are produced mainly in options for Socket AM2 and Socket 939. Older SEMPRON models for Socket 754, for example, have only a single-channel memory controller.
Question: What are the features of the Socket AM2 processor connector?
Answer: Today in the desktop segment, AMD has "Vakhatanalia" when you can find processors at least in four (!) Options: Socket 754, Socket 939, Socket 940 and Socket AM2 (and this is not to mention Rarity Socket A, Which still occasionally occur on store shelves). True, AMD thought on time and with the release of the Socket AM2 platform, returned to the way of unifying the processor jack for desktops, for which she always respected the upgrade lovers.
Socket AM2 connector, which will replace Socket 754 and Socket 939, has 940 legs (as well as server Socket 940, but they are not compatible!), It is used in mass single and dual-core Athlon 64 processors, prestigious Athlon 64 FX and budget sempron. Socket AM2 processors work with DDR2 memory with frequencies from 533 to 800 MHz (PC4200, PC5300 or PC6400) in two-channel mode, the memory of type REGISTERED and ECC is not supported. The rest of the AMD processors for Socket AM2 are fully identical to the Socket 939 processors, the production of which is currently terminated.
Question: Is the future AMD platform for Socket AM2 + and Socket AM3 compatible with existing solutions?
Answer: In the near future, we will have another transition to a new type of memory - DDR3 (see FAQ material on DDR3. In accordance with AMD plans, in early 2008, the modern Socket AM2 will be replaced first on Socket AM2 +, and then on Socket AM3. The only serious Difference Socket AM2 from Socket AM2 + will be the introduction of support for the new high-speed Hypertransport 3.0 bus. Its use will significantly increase the bandwidth of the chipset processor (as well as a processor processor in the case of multiprocessor solutions). Socket AM3 processors, in addition, will acquire support and new DDR3 memory. The characteristic features of new platforms compared to modern Socket AM2 are given in Table:
| Connector | Socket AM2. | Socket AM2 +. | Socket AM3. |
| Number of contacts | 940 | 940 | 940 |
| Memory support | DDR2. | DDR2. | DDR2, DDR3 |
| Hypertransport version | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| release date | May 2006. | 3 square meters 2007. | 3 square meters 2008. |
In this regard, inevitably arises about the compatibility of the promising AMD platforms with existing ones.
So, processors and motherboards Socket AM2 and Socket AM2 + will be fully compatible with each other. Of course, if you install a new CPU with support for HT 3.0 in Socket AM2, it will exchange data with a chipset at the speed of the old HT 1.0. Socket AM3 processors, thanks to its memory controller, working with both DDR2 memory and DDR3, will be most universal and can be installed in Socket AM3, Socket AM2 + and Socket Am2 motherboards (providing the last platform a very worthy service life). And they will not be backward compatibility - in the Socket AM3 board, neither the Socket AM2 processors nor Socket AM2 + will not be installed.
Question: What is Cool "N" Quiet?
Answer: Cool "N" QUIET energy-saving technology came to AMD desktop processors from mobile sphere and reduces heat dissipation and energy consumption in their incomplete workload. At the moment, this technology is implemented in all AMD K8 processors - Athlon 64, Athlon 64 x2, Athlon 64 FX, SEMPRON. Naturally, the motherboard must support this technology (the corresponding item must be activated in the BIOS).
There is nothing radically new in the cool "n" quiet technology. During operation, the operating system monitors the loading of the processor, and, if it is less than a certain threshold, the operating frequency and the processor supply voltage decreases. Reducing the processor operating frequency is carried out by reprogramming its registers (using a special processor driver). Having reduced the frequency and voltage, the processor will consume much less energy, heated less and if the cooler is equipped with a thermal control system, the noise of the system will decrease.
With an increase in the processor load, everything occurs along the same chain (OC-driver-cooler), but on the contrary - the processor will return to the nominal frequency. In a second, there may be up to hundreds of such switches between different modes, for user programs, all this happens completely unnoticed, and on the overall speed of the COOL system "N" quiet if it affects, then slightly.
The degree of response of the system to change the processor loading The user determines itself by choosing a particular policy in the Windows power supply - from a minimum level (transition to power saving mode only with simple) to rigid energy savings (the processor will almost always be in a state of reduced power consumption).
The marking of AMD Athlon 64 processors is so complicated and confusing, which confuses even specialists.
Model rooms, or ratings, were invented by AMD at that time, when she just tried to compete with Intel. The idea underlying the pseudo-frequency processor is to explain to the user, an analogue of which Intel processor he buys. Already then AMD began to promote the thesis that the processor performance depends not only on the clock frequency, but also from other parameters, primarily from the microarchitecture and the volume of the built-in cache. Processory rating ("pseudo-frequency") just takes into account the difference in other parameters and can be used to compare processors of different manufacturers. And AMD began to assign the number "with a plus" to their processors, denoting the clock frequency similar in terms of Intel processors.
The starting point for the processor rating was indeed calculated on the basis of test results. However, further AMD began to assign ratings simply by increasing. And when different options for Athlon 64 appeared, the rating situation finally left due to control: now, with the help of the rating, not only the difference in frequencies, but also different caches, different processor sockets, etc. Therefore, in the pivot table you will find many processors with the same numbers, but different parameters. It is possible to distinguish them only by the labeling line (OPN), which is applied on the processor housing directly under its name.
When AMD put into operation a new production technology, she decided not to change the name nor the method of marking processors. And therefore, Athlon 64 with different audits of the kernel, differing in support of different frequencies and types of memory, supporting the set of instructions, power consumption and overclocking potential, can be distinguished only by OPN. Fortunately, the box "Boxing" packing Athlon 64 has a transparent window through which the processor marking can be easily read. And not to buy a random processor on the old core, which may not support the DDR400 or not accelerate at all.
Note that lately AMD begins to correct. Among the processors on the last modification of Venice kernel, there are no models with the same numbers and different parameters. You can already talk about the unique accordance with the frequency number and the cache volume. Let's say, 3200+ will always have a frequency of 2 GHz and cache 512 KB, and only two numbers - 3700+ and 4000+ were reserved under processors with cache 1 MB.
Especially for overclocking lovers, I will notice that processors on the VENICE kernel (E3, E6), regardless of the number, they usually accelerate to 2.8-2.9 GHz. Therefore, it makes sense to buy the most affordable model - 3000+, since it, with due luck, will achieve the theoretical limit of their nucleus.
Decoding of processor numbers and marking Athlon 64
| Name via |
room | Marking | Core | Hour- Tota |
Cache L2. | Tire | Those- pro- Cess. |
Socket |
| AEP * AP: Processors on Clawhammer Core (130 nm) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 2800+ | ADA2800AEP4AP. | C0. | 1.8 GHz | 0.5 MB | x4. | 130 nm | Socket 754. |
| 3000+ | Ada3000aep4ap | 2 GHz | ||||||
| 3200+ | Ada3200aep5ap | 2 GHz | 1 MB | |||||
| 3400+ | ADA3400AEP5AP. | 2.2 GHz | ||||||
| AEP * AX / AR: Processors on a cut-off NEWCASTLE core | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 2800+ | Ada2800aep4ar | CG. | 1.8 GHz | 0.5 MB | x4. | 130 nm | Socket 754. |
| ADA2800AEP4AX | ||||||||
| 3000+ | Ada3000aep4ar | 2 GHz | ||||||
| ADA3000AEP4AX. | ||||||||
| 3200+ | ADA3200AEP4AX. | 2.2 GHz | ||||||
| Ada3200aep5ar | 2 GHz | 1 MB | ||||||
| 3400+ | Ada3400aep4ar | 2.4 GHz | 0.5 MB | |||||
| ADA3400AEP4AX | ||||||||
| Ada3400aep5ar | 2.2 GHz | 1 MB | ||||||
| 3700+ | Ada3700aep5ar | 2.4 GHz | 1 MB | |||||
| AI * 4BX: Processors on the trimmed Venice kernel (90 nm) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3000+ | Ada3000aik4bx. | E6. | 2 GHz | 0.5 MB | x4. | 90 nm | Socket 754. |
| 3200+ | ADA3200AIO4BX. | E6. | 2.2 GHz | |||||
| 3400+ | ADA3400AIK4BO. | E3. | 2.4 GHz | |||||
| DEP * A *: Processors on the NEWCASTLE kernel (130 nm, two-channel memory controller) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3000+ | Ada3000Dep4aw. | CG. | 1.8 GHz | 0.5 MB | x5 | 130 nm | Socket 939. |
| 3200+ | ADA3200DEP4AW. | 2 GHz | ||||||
| 3500+ | Ada3500dep4as. | 2.2 GHz | ||||||
| ADA3500Dep4aw. | ||||||||
| 3800+ | Ada3800dep4as | 2.4 GHz | ||||||
| ADA3800Dep4aw. | ||||||||
| 4000+ | ADA4000Dep5as. | 1 MB | ||||||
| DIK4BI: Processors on the Winchester kernel (90 nm, cache 512 KB) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3000+ | Ada3000dik4bi. | D0 | 1.8 GHz | 0.5 MB | x5 | 90 nm | Socket 939. |
| 3200+ | Ada3200dik4bi. | 2 GHz | ||||||
| 3500+ | Ada3500dik4bi. | 2.2 GHz | ||||||
| DAA4BP: Processors on the Venice kernel (E3) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3000+ | ADA3000DAA4BP. | E3. | 1.8 GHz | 0.5 MB | x5 | 90 nm | Socket 939. |
| 3200+ | ADA3200DAA4BP. | 2 GHz | ||||||
| 3500+ | ADA3500DAA4BP. | 2.2 GHz | ||||||
| 3800+ | ADA3800DAA4BP. | 2.4 GHz | ||||||
| DAA * BN: Processors on the Sandiego kernel (cache up to 1 MB) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3500+ | ADA3500DAA4BN. | E4. | 2.2 GHz | 0.5 MB | x5 | 90 nm | Socket 939. |
| 3700+ | ADA3700DAA5BN. | 2.2 GHz | 1 MB | |||||
| 4000+ | ADA4000DAA5BN. | 2.4 GHz | ||||||
| DAA4BW: Processors on the VENICE Core (Cash 512 KB) | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3000+ | ADA3000DAA4BW. | E6. | 1.8 GHz | 0.5 MB | x5 | 90 nm | Socket 939. |
| 3200+ | ADA3200DAA4BW. | 2 GHz | ||||||
| 3500+ | ADA3000DAA4BW. | 2.2 GHz | ||||||
| 3800+ | ADA3000DAA4BW. | 2.4 GHz | ||||||
| DKA * CG / CF: Reduced Consumption Processors | ||||||||
| Athlon 64. | 3200+ | ADA3200DKA4CG. | E4. | 2 GHz | 0.5 MB | x5 | 90 nm | Socket 939. |
| 3500+ | ADA3500DKA4CG. | 2.2 GHz | 0.5 MB | |||||
| 3700+ | ADA3700DKA5CF. | E6. | 2.2 GHz | 1 MB | ||||
| 4000+ | ADA4000DKA5CF. | 2.4 GHz | 1 MB | |||||
AMD processor marking is called OPN. Ordering Part Number.
At first glance, it is quite complicated and more like a certain cipher, although if you figure it out, you can get enough detailed information about their basic technical parameter characteristics.
The first two letters indicate the processor type:
AX. - Athlon XP (0.18 microns);
AD - Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 x2;
SD. - SEMPRON.
The third letter denotes a TDP processor
BUT - 89-125 W;
O. - 65 W;
D. - 35 W;
H. - 45 W;
X. - 125 watts.
For SEMPRON processors, a third letter has a few different meaning:
A. - Desktop;
D. - ENERGY EFFICIENT.
It is a number that (from the AMD point of view) characterizes the performance of this CPU in abstract conventional units.
Although it did not cost without exceptions, in the Athlon 64 FX processors, for example, instead of the rating numbers, the letter index "FX (Model Index)" is specified.
The first letter of the three-letter index indicates the type of processor housing:
A. - Socket 754;
D. - Socket 939;
C. - Socket 940;
I. - Socket AM2;
G. - Socket F.
The second letter of the three-letter index denotes the power supply voltage of the processor core:
BUT - 1.35-1,4 V.
FROM - 1.55 V;
E. - 1.5 V;
I. - 1.4 V;
K. - 1.35 b;
M. - 1.3 b;
Q. - 1.2 b;
S. - 1.15 V.
The third letter of the three-letter index indicates the maximum temperature of the processor kernel:
BUT - 71 ° C;
K. - 65 ° C;
M. - 67 ° C;
O. - 69 ° C;
P. - 70 ° C;
X. - 95 ° C.
The subsequent digit indicates the size of the second-level cache (total for dual-core processors):
2
- 128 KB;
3
- 256 KB;
4
- 512 KB;
5
- 1024 KB;
6
- 2048 KB.
Two-letter index indicates the type of core processor:
AX., Aw - NEWCASTLE;
Ap., AR, As, AT. - Clawhammer;
AK - SLEDGE HAMMER;
BI - Winchester;
BN. - San Diego;
BP., BW - Venice;
Bv. - Manchester;
CD - Toledo;
CS., Cu. - Windsor F2; CZ. - Windsor F3;
CN., CW. - ORLEANS, MANILA;
DE. - Lima;
DD, DL - Brisbane;
DH - Orleans F3.
AX. - Paris (for sempron);
BI - Manchester (for sempron);
BA., BO., Aw, BX., BP., BW - Palermo (for SEMPRON).
For example, the AMD SEMPRON 3000+ processor (the manila core) is marked as SDA3000IA3CN.
But nothing is always in our world, and AMD in the near future is going to rename the processor ruler by entering a new, much more visual alphanumeric circuit.
The new system involves, along with the traditional designation of the brand and class, also the alphanumeric model code:
Phenom X4 GP-7XXX
Phenom X2 GS-6XXX
Athlon X2 BE-2XXX
Athlon X2 LS-2XXX
SEMPRON LE-1XXX
The first character in the title of the processor model determines its class:
G. - HIGH-END;
B. - Mainstream;
L. - Low-end.
The second character determines the power consumption of the processor:
P. - more than 65 W;
S. - 65 W;
E. - less than 65 W (Energy Efficient class).
The first digit indicates the processor belonging to a specific family:
1
- single-core sempron;
2
- dual-core Athlon;
6
- dual-core Phenom X2;
7
- Quad-core Phenom X4.
The second digit will indicate the level of productivity of a particular processor within the family.
The two recent digits will determine the processor modification.
Thus, the newest two and quad-core processors will become marked as AMD Phenom X2 GS-6XXX and Phenom X4 GP-7XXX.
Athlon X2 BE-2XXX Economic Athlon X2 Saders, and Budget AMD Athlon and Sempron will be referred to as Athlon X2 LS-2XXX and SEMPRON LE-1XXX.
And the notorious digit 64, indicating the support of a 64-bit architecture, will disappear from the name of the Athlon processor.

More and more details appear on the network of COMET LAKE-S processors.
Speaking Intel LGA1200 for PC processors

Exit processors Intel Core Comet Lake 10th generation for desktop PCs and motherboards based on the 400th series chipsets (Z490, W480, Q470 and H410) is expected in the second half of 2020.
- 1. A bit of history
- 2. Provision policy
- 3. Opportunities for overclocking
- 4. Processor for computer games
- 5. Recent instructions
Each computer, regardless of how it is used, consists of identical basic components. The main element in any PC is a processor that performs all computing operations, and the performance of the system as a whole depends on the performance of this small part. For leadership in the processor market, only two companies are struggling about which we will talk about and try to give an answer to the eternal question - AMD or Intel better?
A bit of history
Both companies began their way to era when computing machines occupied whole rooms, and the concept of a personal computer only began to go into fashion. Intel became the first on this field, created in 1968 and became almost the only developer and producer of processes. The initial products of the brand were integrated chips, but rather soon the manufacturer focused only on processors. AMD appeared in 1969 and was originally aimed at market processes.

At that time, AMD processors became a product that appeared with the active interaction of two manufacturers. The Intel Technical Department in every way supported the young competitor and shared technologies, as well as patents. After the company firmly rose to his feet, the paths of manufacturers were separated into different directions, and today two world producers face foreheads in each generation of processors.
Price policy
Many solutions are presented on the market both from one manufacturer and from the other. Take the side of one company and radically refuse the second is not so easy, because when choosing a processor, many factors should be taken into account. To begin with, it is worth noting that both companies produce processors for all applications and for any budget:
- Office. Such processors have minimal technical indicators and low cost, are intended to launch office applications and are not designed for programs with high computational needs.
- Homemade. This type of processes is usually more powerful of the office option, because it involves the productivity supply for casual gemina, but also the cost of such an element is significantly higher.
- Game or professional. Computer games put forward certain requirements for CPU power, and this processor will cost a round sum.
If you select a processor for work, the AMD company offers low-cost "stones" options with good technical indicators. The budget line from the producer is of a low cost, excellent performance and reasonable energy consumption. However, Intel products, according to all experts, has a much higher power supply. Thus, an AMD processor is great for the budget computer, but to work in resource-intensive applications, gemina and stable operation of the system as a whole, it is better to stop your choice on Intel.
 Opportunities for overclocking
Opportunities for overclocking
Acceleration is a pretty popular way to increase computer performance without having to buy additional equipment. However, for a full overclocking, the processor must have a specific architecture and meet specific requirements.
If the Intel processor is better for games, then for overclocking it is recommended to purchase AMD. Unlike its competitor, AMD has created processors that can work on different clock frequency, which gives ample opportunities for overclocking. At the same time, you can overclock any processor from the line, but the Intel permits experimenting only with some models with an index to the name. Other processors simply do not support overclocking and cannot change the clock frequency. 
Those who plan to overclock the PC platform are better to purchase exactly AMD, which works stable at any frequency. At the same time, such an impact is supported by both expensive eight-core processors and budget options.
Computer games processor
Fans of clear graphics definitely choose Intel Core i5 and I7. The latest models of this manufacturer showed high parameters in the most "heavy" games and perfectly cope with the visualization of any picture. Such processors refer to the category of gaming.
However, AMD does not give positions so simple. Not so long ago, a solution appeared, which is great for the budget game computer - the six-core chipsets Ryzen 5. As a result, it turned out an inexpensive and quite productive working platform. Although the verdict still adheres to Intel products, which is recognized as the best solution for the game computer.
One of the main factors when choosing a processor for games is its energy efficiency. Traditionally, Intel processors are better optimized both in terms of power consumption and in working temperatures. Therefore, if you do not want your computer to "grab like a stove", it is better to join the camp of the blue, or save on the processor and take AMD, but additionally buy a powerful cooling system.
Recent instructions
In 2019, both companies will present a new generation of processors that will have more advanced characteristics. At the moment, the best choice for a home computer in terms of price / quality is two processors - Intel Core i5 and AMD Ryzen 5 1600.
Both stones have approximately the same parameters, but there are several quite obvious differences:
- Both stones have the same number of nuclei, but in the case of AMD there is a notorious possibility of a fairly simple overclocking. Therefore, it will be better for the future, but Intel will work more stable.
- Specific RAM format. The AMD processor fully reveals its potential in the presence of a certain frequency of RAM, which can create some difficulties. Intel processor in this regard is much more interesting because it does not create such strict restrictions.
- The processor from Intel is heated much less, that is, you do not have to spend additional funds for the organization of the cooling system. AMD warms pretty much and for him will have to acquire a powerful cooler.
In any case, the proposals from all manufacturers have their own advantages and sharpened to perform the definition of tasks. If you are forced to keep a strict framework of the allocated budget, the AMD will offer an excellent line of low-cost processors. In the case when you want to assemble a computer that can cope with any task, then the best Intel products for this purpose have not yet been developed.
The question of which processor is better than AMD or Intel, has no definite response, because each component has a number of specific parameters and the choice of one or another should be built on the assignment of the PC itself. An efficient platform will demonstrate high performance only with the correct selection of all components that will enhance each other's performance.
AMD processors compete with Intel, in order to conquer the market offered much more types of processors.
Consider the marking of AMD processors for desktop computers and laptops, laptop marking is almost the same.
In this segment, we have, as of the beginning of 2017, the following categories of processors
- AMD FX ™ CPU
- AMD Athlon ™ X4 CPU
- AMD A-Series Apu
- AMD ATHLON ™ 5000 APU, AMD SEMPRON ™ 3000 APU
Marking of AMD FX ™ CPU Series Processors
FX 8370E.
- FX. - Series of processors
- 8 - The processor model in the series, it also indicates how many physical cores in the processor, there is an exception 9 model in it 8 nuclei but these processors require water cooling.
- 370 - Type of processor
- E. - processors with less energy consumption
AMD Athlon Processor Marking
Athlon processors in their name contain basic information, for example X4 Quad-Core Processors.
Decrypts very simply processor of the X series has 4 kernels type 880K.indicates the model in the series.
Marking of AMD A-Series Processors
This series is designed for games, A series processors have built-in graphic kernels and such a processor will be better handled video or graphics.
A8-7600.
- A. - Series of processor
- 8 - Number of nuclei in the processor 6-6 cores, 8-10 cores, 10-12 cores, usually the main cores 2 or 4 other graphic kernels.
- 600 - Type of processor
AMD ATHLON ™ APUS Series Processor Marking
Low power processors for low productive computers, designation processor marking for example 5350, the greater the number of the more productive processor.
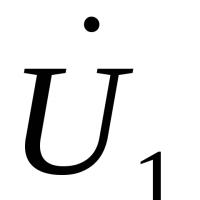 Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it
Magnetometry in the simplest version The ferrozond consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils on it Effective job search course search
Effective job search course search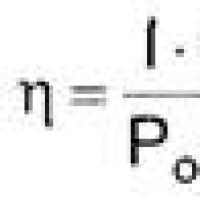 The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode
The main characteristics and parameters of the photodiode How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF
How to edit PDF (five applications to change PDF files) How to delete individual pages from PDF Why the fired program window is long unfolded?
Why the fired program window is long unfolded? DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT
DXF2TXT - export and translation of the text from AutoCAD to display a dwg traffic point in TXT What to do if the mouse cursor disappears
What to do if the mouse cursor disappears