Windows Server Editorial
With the release of the new version of Windows Server at the end of September 2016, Microsoft has once again changed the licensing rules. You can express your attitude to this step as much as you like, but ignorance of rules does not save from responsibility. Therefore, in order not to get into the unpleasant situation, we recommend all system administrators together with us to understand the subtleties of licensing a new server operating system.
The changes affected not only the rules of licensing, but also the product line. In its main part, three editions are included:
- Standard. - for physical systems and a small number of virtual environments;
- Datacenter. - for systems with a high level of virtualization and cloud environments;
- Essentials. - For small businesses up to 25 users and 50 devices.
There are also editions:
- Multipoint Premium Server - provides for multiple user access to one computer, only an academic license is available;
- Storage Server - Available only in the OEM channel for specialized storage systems.
Let's start with the editorial board for small business. Unlike Server 2012, there is now only one edition - Essentials.which provides up to 25 accounts and access to 50 devices. Client access licenses are not required. At the current license cost of about 25,000 rubles. This, in our opinion, is a very good acquisition for small enterprises.
As for the removed line Foundation.This is practically not affected by users, since this edition was only available in the OEM channel, i.e. The end user could get it exclusively as part of a ready server, while Essentials. You can purchase in the corporate licensing channel and use with the available hardware.
As part of the main editions also occurred. If in Server 2012, the differences between Standard and Datacenter were only in the rights to launch virtual machines, then in Server 2016 there were differences in the functional composition. So users Datacenter. will be available:
- New storage features, including Storage Spaces Direct and Storage Replica
- New shielded virtual machines
- New network stack
As you can see, the separation is quite logical, new opportunities relate primarily to virtual environments, the main editorial office for which it is positioned. Datacenter..
In addition, new features available in both edits appeared in Windows Server 2016:
- Windows Server Containers (based on Docker)
- Nano Server is a trimmed version of Windows Server, without a user interface designed to provide remotely managed services.
Good news: Windows containers are available without additional licensing and have no restrictions on the number of running instances. Containers will also be supported in Windows 10 editions Pro. and Enterprise.starting with version 1607 (Anniversary Update).
Having understood with the editors, we turn to licensing itself. SERVER 2016 key honors from Server 2012 is that now is not licensed physical processors, and physical processor nuclei.

If earlier the acquired license covered physical processors, regardless of the number of cores (one SERVER 2012 license covered 2 physical processors), now each physical core needs its own license. Minimum requirements: at least 8 licenses for the processor and at least 16 licenses on the server.
The transition from licensing processors to the licensing of nuclei is generally understood and logical, modern technologies allow you to put a sufficiently large number of nuclei on one crystal and get very high computational capabilities without increasing the number of physical sockets.
So earlier it was possible to assemble a high-performance system based on 14-nuclear Xeon E5-2660 V4. And license it for quite funny money. The cost of one SERVER 2012 Datacenter license approximately corresponded to the cost of a pair of processors.
 The transition to a new licensing scheme allows several "align" the situation, now the owners of powerful systems will be forced to pay more that in our opinion it is fairly fair. The development of the server software is a complex resource-intensive process and are not right to those who say that the sale of software is money from the air.
The transition to a new licensing scheme allows several "align" the situation, now the owners of powerful systems will be forced to pay more that in our opinion it is fairly fair. The development of the server software is a complex resource-intensive process and are not right to those who say that the sale of software is money from the air.
For the holders of the entry-level servers (up to 8 cores on the CPU) everything will remain. The kernel licenses are sold by pairs, the cost of one license pair is set in size 1/8 of the Windows Server 2012 license cost of the relevant edition.

As for the rights to virtualization, everything remains here: a license Standard. Allows the launch of two virtualized instances, while the host system can only be used to maintain virtual machines. If necessary, increase the number of virtual machines you need to re-license all the processor kernels, taking into account the minimum requirements.
 Thus, for a two-processor server with 4-core processors, it will be necessary to buy another 16 nucleus licenses, which will meet another SERVER 2012 license. This will allow you to run another pair of virtual machines. How profitable it is or makes sense to go to Datacenter.?
Thus, for a two-processor server with 4-core processors, it will be necessary to buy another 16 nucleus licenses, which will meet another SERVER 2012 license. This will allow you to run another pair of virtual machines. How profitable it is or makes sense to go to Datacenter.?
We take into the hands of the calculator and believe. License Cost Standard. and Datacenter. differ by about 7 times, so you can run up to 14 virtual machines on the license Standard. and pay for it less than worth Datacenter.. Taking into account the fact that the appetite comes while eating, we would advise you to be guided by the following considerations: if you are planning to dozen virtual machines, you should buy the right number of licenses Standard.if virtualok will be more than a dozen, then you should think about the acquisition Datacenter..
Licensing of client connections has not changed any changes, and we do not see sense to repeat, all those who are interested in this topic can familiarize themselves with it in our article :.
If short, any connection or use of server services, including indirect, should be licensed by the acquisition of a user license, or on the device. Similarly, all terminal connections are licensed.
In December, Microsoft has released a document describing the main changes in versions, licensing policies and pricing policies on the editors of its new flagship in the server OS Windows Server 2016.who is preparing for exit in the second half of the coming year.
Note. Information about the licensing features of Windows Server 2016 in this article is based on the documentation that was published by Microsoft in December 2015. Most likely, before the release of RTM versions of Windows Server 2016, licensing policies and prices will not change. In any case, before buying a license, we recommend getting current information about prices and rules for licensing from Microsoft or partners.

Licensing of server cores
The main innovation in the licensing policy of Windows Server 2016 is the transition from licensing physical processors () to licensing processor cores. Now the license cost will be calculated not by the number of processors, but by the number of system cores (similar to the Microsoft SQL Server licensing).
One Windows Server 2016 license will cost eight times cheaper than Windows Server 2012 license for two processors, but one The new license will cover only two physical nuclei.
This MICROSOFT step is in general we expect, because Processor developers over the past few years have significantly increased the number of cores (and actually performance). In particular, Intel already offers to customers 60 Intel® Xeon PHI nuclear processor worth $ 2500. Microsoft presented how much they lose money when licensing over the old model in case of mass introduction of such systems and quickly developed a new licensing policy.
The procedure for licensing physical server cores is as follows:
- All physical server kernels should be licensed (kernels with Hyper-Threading are considered one nucleus)
- The minimum number of purchased licenses on the kernel of one processor: 8 pcs
- Minimum number of licenses for kernels of one server: 16 pcs
- If the processor is disabled at the system level, its kernel is not needed.
Thus, to licensing one physical server with two four-core processors, you need to purchase 8 kits of dual-core licenses (which will be equal to the cost of one two-processor license of Windows Server 2012). To licensing a single-processor 16-nuclear server, you will also need a set of eight 2-nuclear licenses.

Note. Thus, in comparison with Windows Server 2012, the cost of licenses for low-power servers will not change, but for high-performance systems with several 10-nuclear processors, licensing costs will increase by 25%.
Windows Server 2016 Editor
To date, two editions of Windows Server 2016 are known (as it was with Windows Server 2012/2012 R2):
- Windows Server 2016. Datacenter.
- Windows Server 2016. Standard.
Unlike Windows Server 2012 R2, in which the difference in the editors of Standard Edition and Datacenter Edition consisted in the number of supported virtual machines (2 and unlimited quantity, respectively) and in stock capabilities. In addition to differences in virtualization capabilities, other functional differences appeared in Windows Server 2016.
In particular, Windows Server 2016 Datacenter supports the following technologies:
- - Expansion of Storage Spaces technology to create HA storage facilities for clusters
- - Technology block synchronous multisite replication between clusters
- Shielded Virtual Machines. - Technology for creating protected virtual machines, whose content is protected from the Hyper-V host administrator
- Host Guardian Service. - Server role to support protected virtual machines (Shielded Virtual Machines) and data on them from unauthorized access
- Network Fabric
- Microsoft Azure Stack - SDN Azure-based stack
Note. Information about other editions of Windows Server 2016 and Windows Storage Server 2016 will appear in the first quarter of 2016.
Client Access License (CAL) license
Windows Server Standard and Datacenter are still required to purchase Windows Server Cal licenses for all devices or users using the server.
Client CAL licenses for Remote Desktop Services and Ad Rights Management Services also need to be purchased separately.
Prices for Windows Server 2016 Editor
- Windows Server 2016 Standard - 882 $
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter - 6155 $

Windows Server 2016 Licensing FAQ
In this section I will collect and respond to frequent licensing issues Windows Server 2016
- How is Nano Server licensed?Nano Server This is the installation option Windows Server 2016 and does not require additional licensing.
- How to license processors with Hyper-Threading?In Windows Server and System Center 2016, only physical cores are licensed. From this point of view, the kernel with support for Hyper-Threading technology is one core.
- If the processor / core is disabled and Windows does not use, do you need to buy licenses for it?Disabled processors and kernels are not required to license.
- How Licented Virtual Containers (Hyper-V Containers)Hyper-V Containers Containers are licensed as well as ordinary Hyper-V virtual machines. On the Standard editor, you can run 2 virtual machines, on Datacenter - an unlimited number
The Windows Server 2016 platform uses all the achievements of modern technologies and provides IT specialists with new features that increase the flexibility and reliability of server infrastructures. The new product has a number of innovations, allowing to protect and optimize the operation of data centers, and simplifies the process of building and administering the company's cloud infrastructure.
New features Windows Server 2016
- Nano Server. A new version of Windows Server 2016, which requires even less resources than Core mode. Nano Server supports only 64-bit applications and does not have the capabilities of local control (only the control over the network is supported). This option has limitations on use scenarios, but will be useful for solving specific hosting tasks.
- Containers. A new way of isolating applications for Core and Nano installation modes. Containers are presented in 2 options: Windows (isolation of applications in the physical operating environment) and Hyper-V (insulation of applications in virtual machines running Hyper-V). Container control is available via PowerShell or Docker.
- Rolling Upgrades. Ability to add Windows Server 2016 node to Windows Server 2012 R2 clusters. Cluster Management should be managed with Windows Server 2016.
- Hot Aadd & Remove RAM / NIC. The ability to add RAM and connecting network adapters to working virtual machines, without the need to stop them. This technology works on both generations of virtual machines.
- Nested Virtualization. Virtualization inside virtualization. The ability to "raise" Hyper-V inside the virtual machine.
- PowerShell Direct. The ability to manage virtual machines via PowerShell without network access. The administrator passes authentication, selects the virtual machine you need and writes that command to be performed on this virtual machine.
- Host Guardian Service and SHIELDED VMS. Protection of virtual machines from the HYPER-V administrator. The administrator has the ability to enable and disable virtual machines, make a limited list of actions, but does not have access to the data on VHD.
- Storage Space Direct. The ability to aggregate local disks on the nodes of the cluster using SSD to work with the cache.
In more detail with innovations, you can read the link.
There are 3 main editions of Windows Server 2016:
- Datacenter. - Contains full functionality with unlimited rights to launch virtual instances.
- Standard. - Editorial office with full features and running rights up to two virtual instances.
- Essentials. - OS edition for small businesses (supports up to 25 users or 50 devices).
Scenarios for sales
Safety
- Remote Credential Guard Technologies include the ability to administer with time limit and exposure area, almost eliminate the ability to disclose credentials over the network and restrict administrators access to resources.
- From the moment the OS boot is allowed to perform only allowed binary files.
- Active protection against well-known malware without reducing workload performance.
- Protection against unknown vulnerabilities by blocking the main directions of attacks.
Optimal use of servers
- Run more applications on the same server.
- Simple management, cost reduction.
- Convenient movement of loads for new servers without interruptions in the work.
- Improving security through the use of shielded VM.
Hybrid cloud
- Flexibility of control methods, safety loads.
- Reducing the advance costs of IT.
- Fast and less labor costs providing IT services.
- Improving performance, reducing the delay in the local environment.
Remote Desktop Services
- Access to all (or some) Windows applications in a virtual environment, including applications with intensive graphics.
- Managing scalability for resource-intensive applications.
- Creating virtual work areas through the use of hybrid cloud benefits.
Flexible and affordable storage
- Storaging, scalable in accordance with the growing requirements in the amount of data.
- Flexible storage options allow you to restrain the growth of storage costs.
Emergency recovery
- Real-time emergency recovery with high availability, both in the local environment and in the cloud, - using the Storage Replica replication technology.
- Reducing risk for business and cost reduction due to the efficient use of network bandwidth during periods of reduced loads in various locations by Azure Backup service.
The main or only server in the organization
- Simplify everyday tasks thanks to a convenient shared access to files and programs.
- Protection of data critically important with low-cost backup tools.
- Improving safety through centralized management of users and the use of virus protection and malware protection.
Failover clustering
- High availability of critical loads even when updating or transition to the cloud.
- Distribution of risks in different physical offices and sites.
- Adding resources locally and on remote sites.
Licensing
We released 3 editions of Windows Server 2016:
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter.
- Windows Server 2016 Standard.
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials.
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter and Windows Server 2016 Standard
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter and Windows Server 2016 Standard are licensed on the model "on the kernel" / client licenses. The technical differences of editing are indicated in the table above.
First of all, you must purchase a license to a server where Windows Server will unfold. The required number of licenses of Windows Server is equal to the number of physical cores on a licensed server, and the minimum number of licenses for the physical processor is 8, and the minimum number of licenses to the server - 16. It should be remembered that in the price list of the position with server licenses go to 2 package Licenses "on the kernel". Those. One purchased position closes 2 processor cores.
The specified license value in the table is given of the fact that one position closes 2 physical cores.

Editing Windows Server 2016 Standard allows you to deploy two virtual instances of Windows Server on a licensed hardware server by one license, and the Windows Server 2016 Datacenter is entitled to unlimited virtualization rights on the server to which the license is attached.
To licensed client connections, you need to purchase client access licenses (CAL) for all users or devices that will access Windows Server. Cal licenses are two types: "to the user" and "on the device". The customer can choose any type of license based on the economic feasibility of acquisition.
Windows Server 2016 Essentials
To licensing Windows Server 2016 Essentials you need to purchase a license to a server. Client access licenses are not required.
Windows Server 2016 Essentials offers the customer a simplified interface, a preset connection to cloud services and the right to launch one virtual instance of Windows Server Essentials. Windows Server 2016 Essentials is significantly inferior to standard and datacenter editing capabilities, but it is quite suitable as the first server for organizing small businesses (up to 25 people).
For changes in licensing conditions, you can follow in the appropriate document
In this article, we will consider the installation process, settings and activation of the role of the remote desktops licensing server ( Remote Desktop Licensing) on the basis of Windows Server 2016 or 2019, as well as the installation procedure and activation of client terminal ( Cal.).
Let me remind you that after installing the role of the terminal server Remote Desktop Session Host, users can use it only for a trial period of 120 days, after which the possibility of connecting to the remote RDS server disappears. According to Microsoft's licensing scheme, all users or devices that use RDS capabilities should be licensed. For accounting and issuing terminal licenses (RDS CAL) there is a separate role in the RDS - Remote Desktop License Server service.
Installing the Role Desktop Licensing in Windows Server 2019/2016
You can deploy the Remote Desktop License component on any domain server, not necessarily install it on one of the RDSH farm servers.
RDS Licensing Server Related Installation You need to add (or make sure you have the right to add a new server to the domain group Terminal Server License. ServersOtherwise, the server will not be able to give CAL type RDS PER user to domain users.
You can install the Remote Desktop Licensing service through the Server Manager console. To do this, select a role in the Add Roles and Features wizard. Remote Desktop Services.
As a component, you need to choose a service Remote. Desktop. Licensing..

It remains to wait for the end of the role installation. 
Additionally, install the utility for diagnosing licensing problems on RDS servers - Remote Desktop Licensing Diagnoser (lsdiag.msc) that can be installed using Server Manager: Features -\u003e Remote Server Administration Tools -\u003e Role Administration Tools -\u003e Remote Desktop Services Tools -\u003e Remote Desktop Licensing Diagnoser Tools (by default when installing the RDS-Licensing service installed only Console Remote Desktop Licensing Manager - Licmgr.exe).

You can also install the RDS and RD Licensing Diagnoser licensing component using PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature rds-licensing -includeallsubfeature -includemanagementtools
RDS license server activation in Windows Server
In order for the RDS licensing server to issue licenses to clients, it must be activated. To do this, open the console REMOTE DESKTOP LICENSING MANAGER (Licmgr.exe )
, Click PCM by the name of your server and select Menu. Activate Server.
The RDS Licensing Server Activation Wizard will be launched, in which it will be necessary to select the desired activation method. If your server has access to the Internet, it can automatically connect to Microsoft servers. If there is no access to the Internet from the server, you can activate the server via the web browser or by phone. 
Next, you will need to fill out a number of information about your organization (part of the fields is mandatory). 
It remains to click the button FINISH..

Now, if you click the PCM in the console by the server name and select the item, you can make sure that this RDS license server is activated and can be used to activate RDS clients in the domain. 
Types of client terminal licenses (RDS CAL)
Each user or device that connects to Remote Desktop Session servers must have a client license ( Cal. - Client Access License). There are two types of terminal Cal.

Note. Note that 2016 RDS CAL can only be installed on the licensing server running Windows Server 2016 or 2019, setting new CAL to previous Windows Server versions on supported. Those. You will not be able to install2016 RDS CAL on the licensing host Windows Server 2012 R2.
Installing client licenses RDS CAL in Windows Server 2016/2019
Now you need to install the Terminal License Package (RDS CAL) to the Licensing Server.
In the Remote Desktop Licensing Manager console, click PCM on the server and select Install Licensees..

Select the activation method (automatically through the web or by phone) and the licensing program (in our case Enterprise Agreement). 
The following wizard steps depend on what type of licensing is selected. In the case of Enterprise Agreement you need to specify its number. If licensing type License Pack (Retail Purchase) is selected, you will need to specify a 25-character product key received from Microsoft. 
Product Type (Windows Server 2016/2019), license type (RDS PER User Cal) and the number of licenses to be installed on the server. 
After that, the server can issue licenses (RDS CAL) to customers.
You can convert the USER CAL RDS license in Device Cal (and vice versa) using the Convert Licenses context menu in the RD LICENSING MANAGER console.

If you have ended free licenses, you can withdraw previously issued RDS Device Cal licenses for inactive computers using the following PowerShell script:
$ Revokedpcname \u003d "MSK-PC2332"
$ Licensepacks \u003d Get-WMiobject Win32_TSlicenseNseKeyPack | Where ((($ _. KeyPackType -ne 0) -and ($ _. KeypackType -ne 4) -and ($ _. KeyPackType -ne 6))
$ licensepacks.totallicenses
$ TslicenseSasSigned \u003d GWMI Win32_TSissuedLicense | Where ($ _. Licensestatus -eq 2)
$ Revokepc \u003d $ TslicenseSasigned | ? SissuedTocomputer -EQ.
$ RevokedPCname $ revokepc.revoke ()
Deleting RDS CAL from licensing server
If you want to transfer your RDS CAL license set from one Remote Desktop license server to another, you can delete the installed licenses from the licensing server using PowerShell.
Using the next cmdlet, you can display a list of RDS license packages installed on the server:
Get-WMiobject Win32_tslicenseKeyPack | Select-Object Keypackid, ProductVersion, Typeandmodel, AvailableLicenses, IssuedLicenses | FT
Find the KeypackID value for the RDS CAL package to be deleted and populate the command:
wMIC / Namespace: \\\\ root \\ CIMV2 Path Win32_tslicenseKeypack Call UninstalllicenseKeyPackWithid Keypackid
You can also completely delete all CAL sets by re-create the RDS license database. To do this, stop the Remote Desktop Licensing service:
You can check the license server status and the number of licenses issued using the RD Licensing Diagnoser console.
If there are no warnings, and you see the message " RD Licensing Diagnoser Did Not Identify Any Licensing Problems For The Remote Desktop Session Host Server"So the RDSH server can receive RDS CAL licenses for users.

Note. In our case, after specifying a new licensing server, when connected, an error "The Remote Session Was Disconnected Because Therase Servers Available to Provide a License" began to appear on the RDP clint. Solution - removal of the key from the registry.
The editions of Windows Server Standard and Windows Server Datacenter are now licensed in physical nuclei. To comply with licensed cleanliness, it is required to assign licenses to all active physical processor nuclei; Disabled and virtual kernels implemented by Hyper-Threading licenses are not needed.
It is necessary to assign a minimum of 8 licenses for each socket at multiprocessor server, and at least 16 with a single-sided server configuration. It should be noted that the cost of 16-nuclear licenses Datacenter and Standard for Windows Server 2016 will be approximate as the cost of 2-sockets in the relevant editions of Windows Server 2012 R2. Higher licenses will be supplied with packages of two licenses in the package.
In addition, the scheme with cover licenses of Guest instances of the OS is now distributed on the Hyper-V containers. In general, nothing has changed here: you want to have two virtual machines or two Hyper-V containers - licensing it over Standard and use the basic OS solely to maintain virtual machines running on this server. The Datacenter Edition license gives the right to launch an unlimited number of virtual machines or Hyper-V containers. Naturally, all server kernels must be covered with licenses. Mix the Standard and Datacenter licenses on one server is also prohibited.
The procedure for licensing physical server cores is as follows:
- All physical server kernels should be licensed (kernels with Hyper-Threading are considered one nucleus)
- The minimum number of purchased licenses on the kernel of one processor: 8 pcs
- Minimum number of licenses for kernels of one server: 16 pcs
- If the processor is disabled at the system level, its kernel is not needed.
Thus, to licensing one physical server with two four-core processors, you need to purchase 8 kits of dual-core licenses (which will be equal to the cost of one two-processor license of Windows Server 2012). To licensing a single-processor 16-nuclear server, you will also need a set of eight 2-nuclear licenses.
Open in full size "href \u003d" / iarticle / img / 38911_63905753.jpg "Target \u003d" _ blank "\u003e
The official release of Windows Server 2016 has already taken place at the moment, except Standard and Datacentter know about another 4 editions. Thus, Windows Server 2016 is available in 6 editions:
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter - edition for virtualization media;
Windows Server 2016 Standard - edition for media without use or with a low degree of virtualization;
Windows Server 2016 Essentials - edition for small businesses, is limited to 25 users and 50 devices;
Windows Server 2016 Multipoint Premium Server - edition specifically designed for multiplayer connection;
Windows Storage Server 2016 - Special edition for the organization of disk storages;
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 - Free version of the hypervisor.
The Standard and Datacentter editions are licensed on the kernels, the rest (except free Hyper-V Server) are licensed on processors.
Unlike Windows Server 2012 R2, in which the difference in the editors of Standard Edition and Datacenter Edition consisted in the number of supported virtual machines (2 and unlimited quantity, respectively) and in the presence of automatic activation of virtual machines in the Datacenter edition. In addition to differences in virtualization capabilities, other functional differences appeared in Windows Server 2016.
In particular, Windows Server 2016 Datacenter supports the following technologies:
- Storage Spaces Direct. - Expansion of Storage Spaces technology to create HA storage facilities for clusters
- Storage Replica. - Technology block synchronous multisite replication between clusters
- Shielded Virtual Machines. - Technology for creating protected virtual machines, whose content is protected from the Hyper-V host administrator
- Host Guardian Service. - Server role to support protected virtual machines (Shielded Virtual Machines) and data on them from unauthorized access
- Network Fabric
- Microsoft Azure Stack - SDN Azure-based stack
Edition Essentials is based on the Windows 10 kernel and has a trimmed functionality. License to a server (no more than 2 physical processors). Does not require additional client licenses, but is rigidly limited by the number of users' devices.
The MultiPoint Premium Server edition includes the MultiPoint Services (MPS) functionality and is specifically designed to work as a terminal server, positioned for use in curriculum and organizations where there is no heavy load. The peculiarity is that the MPS server can be connected both using thin customers and directly (so-called zero client). You need licenses to the server and each client. The editorial office is only available state. and educational organizations on an academic license.
Windows Storage Server 2016 has a specific functionality and is specifically sharpened to create disk storages. There are versions of Standard and Workgroup, distributed by OEM channels and is available only for OEM Microsoft partners.
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 is a free edition of the operating system, intended exclusively for use as a HYPER-V host.
Client Access License (CAL) license
Windows Server Standard and Datacenter are still required to purchase Windows Server Cal licenses for all devices or users using the server.
Client CAL licenses for Remote Desktop Services and Ad Rights Management Services also need to be purchased separately.
Microsoft Server 2016 Product Licenses
Open License Pack license: OLP 2 Licenses No Level Corelic
License for 2 server processors. The minimum number of 4 licenses per server, that is, for example: one server / two processors, the minimum purchase of 4 licenses (2 licenses in one), total 8 licenses. For placement of the order less than 5 pcs. According to the Open License program, you must provide the valid authorization number of the agreement or the order must include other names of the Open License products program, that is, 5 (name or licenses) of anything.
License License / SoftwareAssurancePack
License for 2 server processors, which includes technical support and updates within 2 years. Software Assurance Customers receive the right to use any new versions of products that will be released during the license agreement (Open License - 2 years), as well as operational access to improvements and new functionality, which the product will be supplemented within the current version.
License Software Assurance
The extension of the Software Assurance is possible within 90 days from the expiration date of the Open License agreement (the validity period of the authorization number). As part of the Open License program, the Software Assurance action ends simultaneously with the expiration of the authorization number, regardless of the time of payment of Software Assurance. Software Assurance - 2 years.
For state organizations ACADEMIC OLP:
Microsoft Academic Open License is a flexible and effective program that provides the ability to purchase permanent licenses to Microsoft at much lower prices than prices for commercial software or on academic versions of boxed products.
This program is intended for a wide range of preferential categories of participants acquiring licenses for use on 5 or more PCs. Its advantages can take advantage of:
- Public and private host educational institutions, educational institutions of secondary and secondary special education, courses and institutions of advanced training, training centers that have licenses for conducting educational activities issued by the Ministry of General and Vocational Education or other authorized state authority.
- Administrative bodies of educational institutions working in the regional, regional and state level.
- Research institutions that are in the structures of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS) and the Russian Academy of Agricultural Sciences (RASH).
- Hospitals and clinics with higher educational institutions.
- Public libraries.
- Museums.
- Charity organisations.
ACADEMIC license OLP. - Microsoft Open License Government - License for state or municipal organizations. Price in level A, minimal count for first purchase Specify in itShop.
Academic. - Software Assurance Customers get the right to use any new versions of products that will be issued during the license agreement (Open License - 2 years).
License Software Assurance Academic - The extension of Software Assurance is possible within 90 days from the expiration date of the Open License agreement (the validity period of the authorization number).
For government organizations Governmentnmen OLP:
License Government Olp. - Microsoft Open License Government provides the opportunity for state and municipal organizations to acquire corporate licenses for Microsoft products at special prices.
License License / Software Assurance Pack Government.- Microsoft Open License Government provides the opportunity for state and municipal organizations to acquire corporate licenses for Microsoft products at special prices. Software Assurance Customers get the right to use any new versions of products that will be released during the license agreement (Open License - 2 years).
License Software Assurance Government.- Microsoft Open License Government provides the opportunity for state and municipal organizations to acquire corporate licenses for Microsoft products at special prices. The extension of the Software Assurance is possible within 90 days from the expiration date of the Open License agreement (the validity period of the authorization number).
 Error appearance during program launch
Error appearance during program launch FRIGATE plugin for Firefox
FRIGATE plugin for Firefox How to show hidden folders and files in Windows
How to show hidden folders and files in Windows Ways how to make a screen on a laptop brighter or darker
Ways how to make a screen on a laptop brighter or darker How to format a flash drive, disk protection
How to format a flash drive, disk protection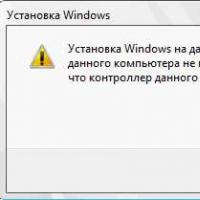 If installing Windows to this disc is not possible
If installing Windows to this disc is not possible During installation of Windows "Make sure that the controller of this disc is included in the computer's BIOS menu.
During installation of Windows "Make sure that the controller of this disc is included in the computer's BIOS menu.