What are smd LEDs. SMD LEDs: marking and characteristics. Pros and Cons of SMD LEDs
LEDs are becoming more and more popular in modern systems lighting. They are actively used in the design, decoration, for and in other areas. LED sources emit pure light, are economical and safe. Currently, SMD LEDs, known as surface mounted devices, are increasingly used, which means a surface-mounted device. Their power and luminous flux are constantly increasing in the same way as traditional light bulbs with long legs and a round plastic lens.
General device and principle of operation of SMD LEDs
The main advantage of such LEDs is their closest location of the crystal relative to the heat sink. This factor is important when emitting a powerful light flux with the release of a large amount of heat. The power of one SMD LED is in the range of 0.01-0.2 W, and from 1 to 3 crystals can be installed on a separate ceramic substrate.
Due to its design, the pads of the LED substrate are directly connected to the circuit board. A wide angle of illumination and other parameters allow with a standard base. These LEDs are widely used in various displays and scoreboards due to the small size of the housing. They are easily mounted on boards, combined into tapes and rulers, convenient for subsequent separation and installation. A wide range of package sizes significantly expands the scope of SMD LEDs.
To grow crystals, a standard technology is used, which is an organometallic epitaxy. The thickness of each grown layer is constantly measured and strictly controlled. Special impurities are added to separate layers - acceptors or donors, which provide a p-n transition when electrons are concentrated in the p-region, and holes - in the p-region.
At a certain stage, films are etched, contacts are created to transition layers, contact leads are covered with a metal film. Such a film is grown on a common substrate, after which it is cut into many chips with an area of 0.06-1.0 mm. In the future, these chips are used to make LEDs.

Finished crystals are installed in special cases. Then contacts are brought to them, and at the end an optical coating is mounted on the crystal to reflect radiation or, conversely, to brighten the surface. For example, in the manufacture of a white LED, a uniform application of the phosphor is performed. In the next step, heat is removed from the housing with the crystal, and then it is covered with a plastic dome to focus the light at the desired angle. The production of LEDs in this way involves the use of new technologies, which make up about half the cost of the entire light source.
There is a special technology for placing SMD LEDs on a single substrate. It is abbreviated as SOB, which means chip-on-board or a chip on a board. When using this technology, several crystals are placed on the board at once, which do not have ceramic substrates and cases. The installed crystals are further covered by a common phosphor layer, which can significantly improve performance and reduce the overall cost of the entire matrix.

Regardless of the manufacturing technology, all SMD LEDs are mounted on a common metal substrate, which often performs a cooling function. If the LED assembly has increased power, it is arranged additional cooling using heatsink and fan.
Thus, low-power SMD LEDs, installed in large numbers in a luminaire, make it possible to obtain high-quality diffused light without using any special optical systems for this. In this case, only protective glass absorbing only 8% of the light flux.
Pros and Cons of SMD LEDs
Despite their lower power compared to fluorescent lamps, LEDs of this type are among the most promising. Due to white radiation, high accuracy in the reproduction of colors and shades is ensured. SMD LEDs, due to their excellent light output, reaching 146 lumens per watt, make it possible in lighting systems.

The designs of these LED light sources are characterized by increased resistance to vibrations and mechanical stress. Therefore, they are actively used in industrial and street lighting. The service life of such LEDs is about 30 thousand hours, with daily operation of at least 8 hours. All types of devices, including SMD 3528, SMD 5050 and others, are able to withstand any number of on and off cycles.
SMD luminaires are distinguished by a wide range of colors, which includes not only the intensity of the radiation, but also shades. In this regard, there is no need to use filters. Many LEDs, such as SMD 5630 and SMD 5730, have low inertia, that is, they immediately begin to work at full power. No need to wait for heating and subsequent glow, as is the case with conventional lamps.

LEDs SMD 3014, SMD 2835 and other similar elements differ in different radiation angles. During operation, a directional light flux is generated, illuminating a specific area, and not the entire surrounding space. The undoubted advantage of such lamps is their absolute insensitivity to cold weather.
As disadvantages, high temperature intolerance can be noted, requiring additional measures for ventilation and heat removal. It should be noted the high cost of these devices, which fully pays off in the process of further operation.
Characteristics of SMD elements
LEDs of this type differ from other products in their own specific characteristics. First of all, their entire design is designed for surface mounting, as a result, there is no need for soldering, fastening and assembly. Most SMD LEDs have low thermal resistance, that is, they do not heat up and can be placed on any surface - ceilings, plastic panels, near stretch fabrics, etc.

Depending on the brand, the sizes of smd LEDs can be very different, and therefore they are successfully used in any place. During operation, the radiation power of these elements remains unchanged.
Many LEDs have a silicone coating to help seal and improve heat dissipation. In order to choose the right product correctly, a special marking of smd LEDs is used, which displays all the main parameters.
More clearly, the technical characteristics are displayed in the table:
|
Options |
3528 |
5050 |
5630 |
5730 |
2835 |
|
Luminous flux (lm) |
100 |
||||
|
Power, W) |
0,06 |
0,2 |
0,5 |
1,0 |
0,2 |
|
Temperature (0 C) |
|||||
|
Current (A) |
0,02 |
0,06 |
0,15 |
0,3 |
0,18 |
|
Voltage (V) |
3,3 |
3,3 |
3,3 |
3,4 |
3,3 |
|
Dimensions (mm) |
3.3x2.8 |
5.0 x 5.0 |
5.6x3.0 |
5.7x3.0 |
2.8x3.5 |
Super-bright LEDs, invented relatively recently, have already firmly entered our lives. Compact and economical, they are successfully used both in portable lighting fixtures, and in stationary systems of illumination and illumination. Particularly popular in Lately powerful and compact smd LEDs began to be used, which we will talk about today. After reading this article, you will find out why they are called that, how they differ from each other and where they can meet.
Features of SMD LEDs
The main visually noticeable difference between smd LEDs and conventional ones is the design of their body:
Conventional with axial leads (left) and SMD LEDs
If a conventional diode has long enough leads for mounting through holes in the board, then their smd counterparts have only small pads (planar leads) and are mounted directly on the board.
 Mounting the LED in the usual way(left) and surface mount
Mounting the LED in the usual way(left) and surface mount This assembly method is called surface mounting, hence the name of the LEDs: smd (eng. Surface Mount Device - a device for surface mounting). Such installation is the simplest, and it can be entrusted to robots.
 Assembly of devices on smd components can be entrusted to a robot
Assembly of devices on smd components can be entrusted to a robot In addition, efficient heat removal from the crystal became possible due to very short but relatively massive leads and the fact that the device is practically lying on the board. Indeed, despite their efficiency, super-bright diodes heat up during operation. This design feature made it possible to produce very tiny but powerful smd LEDs that require good heat dissipation.
Today, the global industry produces many smd types LEDs, which differ from each other in both dimensions and electrical parameters.
How to decipher the marking
Super-bright smd LEDs are usually labeled with four digits, and the line of devices manufactured today looks something like this:
 Sizes and appearance most popular smd led
Sizes and appearance most popular smd led There are, of course, many more types of devices, but these are enough for us to parse the markings. How to understand this marking and what do the numbers mean? It turns out that there is nothing complicated here: the numbers indicate the horizontal dimensions of the smd LED housing - the length and width are in hundredths of a millimeter. For example, the 5050 device has dimensions of 5.0x5.0 mm, and 3528 - 3.5x2.8 mm. The marking does not carry any more information. Specifications you can only find out from the accompanying documentation or take the word of the seller.

Expert opinion
Alexey Bartosh
Specialist in the repair, maintenance of electrical equipment and industrial electronics.
Ask an expertWhen buying LEDs, be sure to read the accompanying documentation - our "friends" from China have a habit of embedding crystals of the most different power(usually smaller). If the seller is silent about this, then you can easily get a LED with a power of, for example, 0.09 W instead of a single watt one, but the marking and appearance will be the same!
Brief specifications
Although their digital marking does not carry any information about the characteristics of smd LEDs, there is still some connection between the standard sizes and parameters of the devices. Consider the parameters of the most common types of light-emitting smd semiconductors:
Main technical characteristics of smd leds
Device type | Housing dimensions, mm | Number of crystals | Power, W | Luminous* flux, lm | Operating current, mA | Operating temperature, °C | Solid angle, ° | Glow color |
| 3528 | 3.5x2.8 | 1 or 3 | 0.06 or 0.2 | 0.6 – 5.0* | 20 | -40 … +85 | 120 – 140 | white, neutral, warm, blue, yellow, green, red, RGB |
| 5050 | 5.5x1.6 | 3 or 4 | 0.2 or 0.26 | 2 – 14* | 60 or 80 | -20 … +60 | 120 – 140 | white, warm, blue, yellow, green, red, RGB, RGBW |
| 5630 | 5.6x3.0 | 1 | 0.5 | 57 | 150 | -25 … +85 | 120 | |
| 5730 | 5.7x3.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.5 or 1 | 50 or 158 | 150 or 300 | -40 … +65 | 120 | cold, white, neutral, warm |
| 3014 | 3.0x1.4 | 1 | 0.12 | 9 – 11* | 30 | -40 … +85 | 120 | cool, neutral, warm, blue, yellow, green, red, orange |
| 2835 | 2.8x3.5 | 1 | 0.2 or 0.5 or 1 | 20 or 50 or 100 | 60 or 150 or 300 | -40 … +65 | 120 | cold, neutral, warm |
* - depends on the color of the glow of the crystal
Now let's look at each of these types in more detail.
smd 3528
smd LED of this type can be single-chip (white, neutral, warm, blue, yellow, green, red) or three-chip (RGB). In the first case, the device has two outputs for connection, in the second - four: one common (cathodes) and three anodes. Crystals for protection from environment are filled with a transparent compound or a compound with the addition of a phosphor that equalizes the color characteristic of the diode.
 The appearance of a single and three-chip LED 3528
The appearance of a single and three-chip LED 3528 As can be seen from the plate, this type of LED has a relatively low luminous flux. But thanks to its small size, moderate cost and the ability to shine in different colors, including RGB, he still found wide application in inexpensive lighting devices and decorative lighting devices.
Very often, 3528 LEDs are part of lcd backlight strips. Such a strip with smd LEDs is most often used for decorative purposes.
 Automotive lamps and LED strip assembled by 3528
Automotive lamps and LED strip assembled by 3528 smd 5050
Unlike the 3528, the 5050 is exclusively 3-chip or quad-chip (RGBW). If the device is single-color, then all three crystals have the same or close (to equalize the color characteristics) color of the light emission. This means that the 5050 diode has three times the brightness of its single-chip counterpart smd 3528. As in the first case, the crystals are protected by a compound with or without a phosphor.
 Three-chip LED 5050
Three-chip LED 5050 This is perhaps the most popular device used for decorative lighting and lighting. It has an optimal cost / power ratio and can provide any backlight color (in the case of using rgb5050), including white increased brightness(four-chip version), by simply changing the power on each of the crystals.
Most often, such LEDs are built into such LED decorative strips as:
- single-channel, where three crystals are connected in parallel and are powered by the same voltage;
- RGB and RGBW, having three and four channels, respectively.
Thanks Enough high power diodes already at their density of 60 pcs. for 1 meter of LED strip, it can be successfully used not only for decorative lighting, but also for interior lighting. At the same time, the user can change the color temperature and even the color of the lighting on their own, for this it is enough to install the appropriate controller.
 5050 LED strip single color (left), RGB and RGBW
5050 LED strip single color (left), RGB and RGBW smd 5630 and 5730
The smd 5630 is a single-chip powerful fixture (see table above) capable of producing up to 57 lumens of light output. Thanks to the built-in protection, assembled on two stabistors, the device is able to withstand an impulse current of up to 400 mA and polarity reversal. The LED has 4 outputs, but only two are involved in the operation of the crystal. The remaining two and the metal substrate are used for better heat dissipation. The color of the LED glow is white of different color temperatures.
 Appearance and internal circuit of the LED 5630
Appearance and internal circuit of the LED 5630 The 5730 instruments can be either single or dual-chip. The former have characteristics similar to the 5630, the latter are twice as powerful (1 W) and are able to create a luminous flux of up to 158 lm.
 Appearance of the LED 5730
Appearance of the LED 5730 Both types of devices emit white light of various color temperatures and can be used to make high-power LED strips, lamps, spotlights.
 car lamp at 5630 and a hundred watt spotlight at 5730
car lamp at 5630 and a hundred watt spotlight at 5730 Single-chip compact device of moderate (0.12 W) power and luminous flux up to 11 lm. Depending on the version, it can emit white light of different color temperatures, as well as blue, yellow, green, red and orange. To protect against the environment and correct the color temperature, the crystal is coated with a compound with a phosphor.
 smd 3014 LED
smd 3014 LED The main scope of smd 3014: LED strips and modules for decorative lighting, spotlights and lamps for them. Often used for the manufacture of automotive lamps.
 Car lamp, table and recessed lamps, strip based on smd 3014 diodes
Car lamp, table and recessed lamps, strip based on smd 3014 diodes smd 2835
Single chip LED increased power. Available in three versions: 0.2, 0.5 and 1 W. It emits white light of various color temperatures, the size of the body coincides with the device 3528, but differs from the latter in a rectangular lens (in 3528 it is round).
 smd 2835 (left) and smd 3528
smd 2835 (left) and smd 3528 Due to the high popularity of devices, a lot of fakes are produced in which crystals of lower power are installed. So, although the Chinese smd 2835 is officially released, it is equipped with a crystal of only 0.09 W. Outwardly, it can be impossible to distinguish it from a single-watt one due to the phosphor added to the compound, since it is opaque; accordingly, it will not be possible to estimate the size of the crystal by eye.
Lighting is an important condition for work and human comfort. For a long time were used as light sources of incandescent lamps, then fluorescent lamps, for powerful spotlights and lanterns, halogen lamps, DRL and HPS were used.
In the 21st century, there has been a change in generations of lighting fixtures, and more than half of the market is occupied by LED lights, they are often called in a foreign manner LED-lamps or lamps. Depending on the design and power, they are either LED COB-matrices, or assembly .
Varieties of LEDs
The first LED fixtures and lamps were built on the basis of. They were not distinguished by high energy efficiency, price and reliability, but this was the first step in the development of a new light source. For a long time, such LEDs were used as indicators for household and industrial equipment and as emitters for portable flashlights.

Later they were replaced by LEDs made in leadless packages, the so-called SMD (surface mounted device, Russian surface-mounted devices).
If 5 mm LEDs were mounted into the board through holes, then SMDs are soldered directly to the surface of the board, which speeds up their assembly and reduces the cost of the lamp. Instead of legs, they have contact metal pads, from 2 or more pieces, depending on the number of colors and crystals in one case.
In general, there are three types of LEDs:
1. Output (3, 5, 10 mm - the diameter of the flask and others).
2. SMD (we will consider their variety in this article).

3. COB LEDs are matrices of crystals located on the board under a single layer of phosphor. Stands for Chip-On-Board, Russian. chips on board. Their appearance is in the picture above.
SMD LEDs are used, spotlights, LED strips, LED table lamps and other lighting fixtures.
Characteristics of SMD LEDs
Initially, the 3528 and 5050 LED models received the greatest popularity, now they are found mainly, they are practically not used in lamps, giving preference to 5630 LEDs and other modern models.

SMD LEDs in their marking contain their overall dimensions - length and width, while in the original LEDs in each type of housing, regardless of whether it is 3528 or 5730, its own type of LED crystal with special characteristics is installed.
Unfortunately, Chinese manufacturers under the guise of modern 5730, they do not disdain selling 3528 crystals in a new case. In the review, I will not indicate the supply voltage, because. for all white LEDs, it usually lies between 2.8 - 3.4V.
SMD3528 specifications
3528 LEDs are something like an analogue of a standard 5mm LED, but in SMD Enclosure. They have characteristics:
current - 20 mA;
power - 0.06 W;
luminous flux - 5-7 lm;
dimensions - 3.5x2.8x1.4 mm;
temperature up to 80 °C;
there is a cut on the front of the case - on this side the cathode (minus).

In LED strips, they are installed in the amount of 30, 60, 120 pcs / m, they are used mainly for lighting, less often for lighting, because. pretty weak. A tape of 120 pcs/m of 3528 consumes 9.6 W/m.
SMD5050 specifications
The 5050 LED contains three of the same crystals as in the 3528, which means it is three times more powerful.

The design is very interesting: on its "belly" you will see 6 conclusions, these are the anodes and cathodes, one pair from each crystal.
current - 3x0.02 A = 0.06 A total current with parallel connection of crystals;
power - 3x0.06 W total up to 0.02 W;
luminous flux - up to 20 Lm
cathodes from the side of the cut at the corner of the case.

On the tape, 30 and 60 diodes per meter are usually installed. A strip with 60 5050 type LEDs consumes 14.4 W / m, can be successfully used for lighting. Often found in RGB and RGBW versions.

SMD 5630 specifications
5630 LEDs are more modern and technologically advanced, they are used in spotlights, lamps, mounted on LED strips. There are 4 pins on the case.

You can see the pinout in the figure above, the cathode from the side of the cut corner.

Characteristics:
Current - 0.15-0.2 A;
Power - 0.5 W;
Maximum crystal temperature - 130 °C;
Luminous flux 40 Lm.
Dimensions 5.6x3x0.75 mm
In tapes, 60 pieces / m are most often supplied, as well as metal rulers with the number of diodes 72 pieces, 12V power supply. Such a tape consumes up to 18 W / m, can be used for the main lighting of a room, or decorative lighting, for example. They come in RGB versions.
SMD 5730 - specifications
Very similar to the previous ones, they are available in versions 5730-05 and 5730-1, at 0.5 and 1 W, respectively. They have a slightly higher luminous flux. Unlike the 5630, the 5730 has two leads, and their length is slightly longer.

Characteristics:
current - 0.15 / 0.3 A;
power - 0.5/1 W;
luminous flux - 55/110 Lm;
dimensions, taking into account the length of the leads - 5.7x3x0.75 mm.
You may have noticed that this and the previous LED, in addition to the terminals for connection, have a metal platform on the bottom part, it is needed for heat dissipation. Such a constructive solution made it possible to successfully use high-power chips. By the way, this will also help determine the pinout of the LED, the heat sink on them is shifted to the ANODE.
SMD 2835 - specifications
This is not a typo, the marking 2835 is often confused with 3528, but this is completely different generations LEDs. LED 2835 is more modern and brighter. The first difference that catches your eye is that the area covered with phosphor is round in 3528, and closer to a rectangle in 2835. The luminous flux of the former is up to 40 Lm / W, and the 2835 has more than 110 Lm / W, which is 2-3 times brighter, with the same power consumption.

The increase in power necessitated better heat dissipation, so the 2835 package was made thinner and the contact pads larger. The industry produces 0.2, 0.5 and 1W. However, do not forget that the greater the power, the more heat is generated, and with such small sizes this is very important.
Characteristics:
Current - 0.06 A;
Power - 0.2 W;
Luminous flux - 25 Lm;
Working temperature - 65 °C;
Dimensions - 2.8x3.5x0.95 mm.
They are also mounted on LED strips in the amount of 30, 60, 120 pieces per meter. For example, a strip with a LED density of 60 pcs/m consumes power of 4.8 W/m, due to its characteristics it is much more efficient in terms of energy saving and lighting than 3528, it can be used as a light source and decorative lighting.
Summary table of characteristics SMD 3014, 7020, 3020
LEDs that are less common, I decided to consider all together in a pivot table.
3014 LEDs are very compact, better suited for decorative lighting, their appearance is shown below.
Personally, I am skeptical about the classic flexible tapes with 7020s due to the high power of the LEDs, but there are 60 pcs / m on sale.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, the quality of most LED products leaves much to be desired. Manufacturers either neglect diode switching circuits, or power supplies, or even buy low-grade fakes for their devices. Therefore, I did not specify such a parameter as . It strongly depends on the quality of the phosphor.
Moreover, there is information on the network that they have learned to deceive the system for determining the CRI color rendering index, the phosphor consists of such components that form a luminous flux with peaks in the spectrum at the required wavelengths to successfully pass the test.
It turns out that with a high index, the real difference in colors of the eye suffers. It is pointless to indicate the service life, for LEDs it is usually from 30 to 50 thousand hours, but it strongly depends on the power source (or rather, the quality of power), thermal conditions and operating conditions in general.
Also, I did not indicate the glow angle, since on all SMD LEDs it lies within 105-135 °, and the most common is 120 °.
As a result, the conclusion is that such a popular product as an LED is actually difficult to find of proper quality. If you want to get decent light, it is better to pay attention to products from trusted manufacturers, such as OSRAM, Philips, CREE.
Alexey Bartosh
LEDs are used in various areas of lighting technology.
The most common SMD LEDs are crystals mounted on the board surface.
This design allows you to get maximum power with minimal dimensions.
This technology has both advantages and disadvantages, which are being eliminated by leading manufacturers continuously.
This type of LED is a board, on the surface of which a crystal is fixed, grown using metal-organic epitaxy technology. The most important stage of production is the creation of contacts and their coating with metal films.
Each diode is mounted in a housing, equipped with leads, covered with a composition that diverts or emits light. White LEDs are coated with a phosphor. A dome is placed on the crystal to focus the light. Heat is removed through the substrate, if the diode is powerful, a radiator is installed. Electric current is converted into light in p-n-junction(same as in any other diode).

The main advantage of the SMD design is the maximum approximation of the crystal to the substrate, which removes heat. One or more LEDs are mounted on one board. If in one lighting device they a large number of, the light is powerful enough without installing additional optical systems. Ordinary glass is enough, losses due to which do not exceed 8%.
SMD packages vary in shape and size and are directly connected to the circuit board using a pad.
Attention! Due to its simplicity, installation can be performed by a non-specialist.
How to decipher the marking
The marking indicates the type of LED (mounted on the surface - from the English "surface mounted device"), and indicates the dimensions of the diode housing in millimeters. For example, the length and width of the SMD 5050 board is 5x5 mm. Surface-mount technology is used in the production of lighting fixtures.
Brief specifications
In the manufacture of lighting fixtures, manufacturers are guided by several characteristics:
- board dimensions;
- the number of crystals;
- voltage and current;
- light stream;
- operating environment temperature.
Table of the most common SMD LEDs:
| SMD type | Number of crystals | Dimensions (mm) | Power, W) | Current (mA) | Light output (lm) | Medium temperature |
| 3528 | 1 | 3.5x2.8x1.4 | 0.02 or 0.06 | 20 | 5-7 | -40 – +85 |
| 5050 | 3 or 4 | 5x5x1.6 | 0,02 | 60 or 80 | 18-20 | -40 – +60 |
| 5630 | 1 | 5.6x3x0.75 | 0,2-0,4 | 150 | 58 | -25 – +65 |
| 5730 | 1 or 2 | 5.7x3x0.75 | 0.5 or 1 | 150 or 300 | 50 or 158 | -40 – +65 |
| 3014 | 1 | 3x1.4x0.75 | 0,1-0,12 | 30 | 9-13 | -40 – +85 |
| 2835 | 1 | 2.8x3.5x0.8 | 0.2, 0.5 or 1 | 60, 150 or 300 | 20, 50 or 100 | -40 – +85 |
These bulbs can be one-, two- and multi-color. From them, you can create rigid and flexible modules of any shape (round, rectangular, linear, with a plinth). A round radiator is used in spotlights.
Reference! The number of diodes in the module is gradually decreasing due to the emergence of high-voltage SMDs (15 and even 45 V).
Led SMD 3528 are rectangular, thanks to them Surface-mount technology is progressing. On the short sides there are 2 contacts, the minus is indicated by a cut. The surface covered with a phosphor is round, the brightness of the radiation depends on the temperature - the higher it is, the lower the brightness (when +80 is reached, a quarter decreases). The main scope of application is the manufacture of tapes consisting of 30, 60 or 120 diodes per meter.
Read also Formula and example for calculating a limiting resistor for an LED

The 5050 has 3 of the same LEDs as the 3528, that is, the power is increased by 3 times. There are 6 anodes on the surface and 6 cathodes on the cut (2 from each crystal). This is a more advanced version of the 3528, allowing the production of colored LEDs (from red, green and blue crystals). Colors can be controlled separately. Voltage 3.3 V, 30 or 60 diodes are installed per meter of tape.

SMD 5630 and 5730
SMD 5630 marked a new stage in the development of technology. In production, other materials are used to increase power and luminous flux, RGB products are available. 60 pieces are mounted in tapes per meter, 72 pieces in metal rulers.
SMD 5730 is structurally similar to 5630, the main differences are an increased light flux and only 2 contacts. Modification with a current of 300 mA can operate in a pulsed mode, the temperature of the crystal can reach +130°C. To increase the power, SMD 5630 and 5730 are installed on a metal board that effectively removes heat.

SMD 3014
SMD 3014 belong to the group of relatively new LEDs operating from 3-3.6 V. The minimum light output for crystals is white, the maximum for colored ones. The anode and 2 cathodes are located on the bottom of the case. Compact dimensions make installation easy. There are 30-120 elements in the tapes, less often - 240 per meter.
Led 2835 has a rectangular area covered with a phosphor, the brightness is 2-3 times higher than 3528. The case is thinner (compared to 5050), the contact areas are larger. 30, 60 or 120 such diodes are installed per meter of tape.

Reference! Led SMD 3528, 2835, 5050 and 5630 is one LED, differing in the number of crystals and the shape of the package. It is these parameters that determine the brightness and power. The 5050 and 5630 (5730) have a wider light output window for higher efficiency per lm/W.
Application of SMD LEDs
Recently, SMD LEDs have been used as elements of general lighting (after reaching a radiation intensity of 120 lm/W). This allowed the production of LED lamps that can replace fluorescent and filament lamps. Manufacturers make sure that when replacing, consumers do not have to change or rebuild the lighting system, buy other lamps and spotlights. From SMD Led, it is easy to assemble any matrices and embed them in standard housings for fluorescent and halogen lamps.
LED lighting is based on the ability of semiconductors to convert electricity into the light stream. According to their purpose, the devices are divided into two groups: indication and lighting. The first type has low power and is used to indicate instruments. The second type is installed in lighting fixtures. SMD LEDs are the most common type of lighting elements.
What are SMD LEDs
SMD LEDs
Semiconductors manufactured using surface mount technology are called smd LEDs. They differ from other devices design features. The electronic chip is going to printed circuit board from copper or aluminium. A crystal is used as a chip. The surface mount method simplifies production and reduces the cost of LEDs.
SMD electronic components are characterized by the maximum approximation of the semiconductor to the substrate, which removes heat. To create white light, the crystal is covered with a layer of phosphor. The main features of the device:
- high brightness;
- a monochrome crystal emits one color - white, red, blue, yellow;
- consists of one or more crystals;
- modules are able to create illumination with a scattering angle from 100 to 160 °;
- smd diodes run on direct current.
For all semiconductor devices characterized by a high working resource.
Manufacturers marking

LED marking
The standard marking of LEDs, the decoding of which gives information about the linear dimensions of the device, is applied by all manufacturers. The digital designation shows the length and width of the LED chip in fractions of a millimeter. In some cases, in addition to the frame size, other parameters are applied - color and power. For example: SMD 2835 UWC 5 - matrix size 2.8 × 3.5 mm, color - white (Ultra White Color), power 0.5 W. For electronic components surface mount there is a special code smd 2l.
Characteristics of LEDs
Device parameters affect the possibility of using them in various fields. The main characteristics of products include: voltage, power, glow angle, color temperature, luminous flux.
Current consumption
 The average current on a chip is 0.02 A. For chips with several chips, the characteristic increases by a multiple of their number. Fluctuations in the parameter negatively affect the intensity of the glow and the service life. An increase in current increases the color temperature of the chip, changes the shade of the glow. To ensure the stability of the characteristics, current-limiting resistors are connected.
The average current on a chip is 0.02 A. For chips with several chips, the characteristic increases by a multiple of their number. Fluctuations in the parameter negatively affect the intensity of the glow and the service life. An increase in current increases the color temperature of the chip, changes the shade of the glow. To ensure the stability of the characteristics, current-limiting resistors are connected.
Light output, glow angle, power
 The luminous flux of an LED matrix differs from the light produced by an incandescent lamp. It is directional, so it is brighter in the central part. Typically, the scattering angle is in the range of 100-120°. Lenses are used to change the parameter. According to the power of the device are divided into 3 groups:
The luminous flux of an LED matrix differs from the light produced by an incandescent lamp. It is directional, so it is brighter in the central part. Typically, the scattering angle is in the range of 100-120°. Lenses are used to change the parameter. According to the power of the device are divided into 3 groups:
- low power - up to 0.5 W;
- medium - 0.5-3 W;
- large - from 3 watts.
The characteristic is necessary when calculating the power supply. It is calculated by the formula - the current strength multiplied by the voltage.
The nominal voltage of the diodes is low, it is 1.1-4 V. The value varies due to the difference in colors and materials of electronic components. The white device has the highest voltage.
Colorful temperature

Types of illumination depending on the color temperature of the light
The intensity of radiation or color temperature is important for the comfortable perception of lighting by the human eye. There are several categories of white light:
- 2700-3500 - warm;
- 3500-5000 - neutral or daily;
- above 5000 - cold.
The color temperature is indicated in Kelvin (K), it is indicated in the marking.
Dimensions and their influence on the properties of LED sources

Illumination difference and illumination angle directivity
Varies depending on the type smd size LEDs. The brightness of the elements increases with the dimensions. The glow area can be round or rectangular. The larger the setting, the brighter the illumination. The light output also depends on the number of crystals. IN various models there are 1 to 4 of them. The power of the device depends on the size of the crystal. The characteristic is indicated by the manufacturer in "mil", 1 mil \u003d 0.0254 mm. For example: 45×45 mil chip - power 1 W, 24×24 mil - 0.5 W.
Color Range
The color of an LED depends on the semiconductor material and dopants. Primary colors: red, blue, green and yellow. White color is obtained by applying a layer of phosphor to a blue glow crystal. Two-color devices are used for indication. Tricolor is used in displays.
Description of the main smd LEDs
The number of standard sizes of LED lighting sources is constantly increasing. The most widespread are several types.
SMD 2835
 The 2.8×3.5 mm model demonstrates high light output efficiency. Its parameters are:
The 2.8×3.5 mm model demonstrates high light output efficiency. Its parameters are:
- current - 60, 150, 300 mA;
- power - 0.2, 0.5, 1 W;
- light flux - 20-100 lm.
The housing is made of heat-resistant polymer, designed for heating up to 240-260°. The radiating area of a rectangular shape is covered with a phosphor.
SMD 5050
 The LED matrix consists of three crystals placed in one housing. Its dimensions are 5.0 × 5.0 mm. The technical characteristics of the LED components are similar to those of the smd 3528 diode:
The LED matrix consists of three crystals placed in one housing. Its dimensions are 5.0 × 5.0 mm. The technical characteristics of the LED components are similar to those of the smd 3528 diode:
- the total current is - 0.02 × 3 = 0.06 A;
- power - 3 × 0.7 = 0.21 W;
- Luminous flux - 18-20 Lm.
The chip is capable of emitting all shades of white, blue, red, yellow, green color or tri-color RGB. Used in flexible tapes, lamps. Lighting mode can be adjusted.
SMD 5630
 A new class of surface-mount devices, its dimensions are 5.6 × 3.0 mm. Models smd 5630 have improved brightness characteristics:
A new class of surface-mount devices, its dimensions are 5.6 × 3.0 mm. Models smd 5630 have improved brightness characteristics:
- rated current - 0.1-0.15 A;
- luminous flux - 32-57 lm;
- voltage - 3-3.6 V.
To prevent overheating of the crystal, the chip is installed on an aluminum substrate. The device is used in street and industrial lighting.
SMD 5730
 The geometrical parameters of the case are 5.7 × 3.0 mm. A large device is one of the super-bright diodes. The semiconductor is made from new materials that increase power. Characteristics:
The geometrical parameters of the case are 5.7 × 3.0 mm. A large device is one of the super-bright diodes. The semiconductor is made from new materials that increase power. Characteristics:
- rated current - 0.15.0.18 A;
- power - 0.5-1 W;
- luminous flux - 45 lm.
The illumination angle is 120°. The device is resistant to vibration, moisture, has a long service life.
SMD 3014
 A diode in a 3.0 × 1.4 mm package is one of the new options. Model medium power with good heat dissipation. Options:
A diode in a 3.0 × 1.4 mm package is one of the new options. Model medium power with good heat dissipation. Options:
- voltage - 2.7-3.3 V;
- current - up to 0.3 A;
- glow - 9-11 lm.
Devices give all shades of white light.
SMD 3528
 One of the most popular and inexpensive chips. The length of its sides is 3.5 × 2.8 mm. The working platform is round, a layer of phosphor is applied on it. Characteristics:
One of the most popular and inexpensive chips. The length of its sides is 3.5 × 2.8 mm. The working platform is round, a layer of phosphor is applied on it. Characteristics:
- operating current - 0.2-0.25 A;
- voltage - 3-3.2 V;
- luminous flux - up to 7 Lm.
The brightness of the model depends on temperature, increasing the parameter leads to accelerated degradation of the crystal. At 75-80 ° the device shines weaker by 25%.
Application and connection requirements
The scope of LED-devices includes domestic, commercial and street lighting. Depending on the size of the smd, the LEDs are placed in lamps or strip lights. Several chips placed on the board replace standard incandescent and energy-saving fluorescent lamps. Devices with a wide angle of illumination are used in spotlights. LED matrices have replaced lamps in flashlights, headlights, pointers, traffic lights and signboards.
 Compact Bluetooth Amplifier What you need
Compact Bluetooth Amplifier What you need Overview Highscreen Zera S Power
Overview Highscreen Zera S Power FAT32 or NTFS: which file system to choose for a USB flash drive or external hard drive
FAT32 or NTFS: which file system to choose for a USB flash drive or external hard drive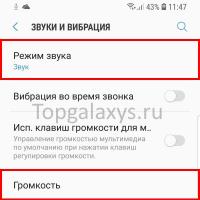 Missing sound on Galaxy S9?
Missing sound on Galaxy S9? Update flash player to new version
Update flash player to new version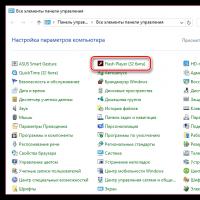 Update flash player to new version
Update flash player to new version Daemon Tools Lite Virtual drive for disk images
Daemon Tools Lite Virtual drive for disk images