Software and technical means of protection. Protection of information on the Internet: Fixed assets and technologies Software protection software
Information security software is special programs and software complexes designed to protect information in the information system.
Software Tools include programs for user identification, access control, removal of residual (working) information of the type of temporary files, test control system and others. Advantages of software - versatility, flexibility, reliability, simplicity of installation, the ability to modify and develop.
Disadvantages - Using part of the file-server and workstations resources, high sensitivity to random or deliberate changes, a possible dependence on the types of computers (their hardware).
Software protection software includes:
· Built-in information security tools are tools that implement authorization and user authentication (logging in to the password), delimitation of access rights, copy protection, the correctness of data entry in accordance with the specified format and so on.
In addition, this group of funds includes the built-in tools for protecting the effect of the work of one program to work on the operation of another program when working in a computer in multiprogram mode, when several programs can simultaneously be in its implementation in its memory, alternately receiving management as a result of interrupts . Each such programs are likely to fail (errors) that may affect the performance of the functions by other programs. The operating system is engaged in processing interrupts and control multiprogram mode. Therefore, the operating system should ensure the protection of itself and other programs from such an influence using, for example, the memory protection mechanism and the distribution of program execution in a privileged or user mode;
· Managing protection system.
In order to form an optimal complex of software and technical information protection, it is necessary to go through the following steps:
· Determination of information and technical resources to be protected;
· Detection of a complete set of potentially possible threats and channel leakage channels;
· Conducting an assessment of vulnerability and risks of information with a variety of threats and leakage channels;
· Determining the requirements for protection system;
· Implementation of the selection of information security tools and their characteristics;
· Implementation and organization of the use of selected measures, methods and means of protection;
· Implementation of monitoring and managing protection system.
Information today is expensive and it needs to be protected. Information own and use all people without exception. Each person decides for himself what information he needs to get what information should not be available to others. To prevent information loss and are developed by various methods of its technical protection, which are used at all stages of working with it, protecting against damage and external influences.
Information protection tools - This is a combination of engineering, electrical, electronic, optical and other devices and devices, devices and technical systems, as well as otherware items used to solve various information protection tasks, including leakage warnings and ensuring the security of protected information.
In general, the means of ensuring information protection in terms of preventing intentional actions depending on the method of implementation can be divided into groups:
- Technical (hardware. These are different in the type of device (mechanical, electromechanical, electronic, etc.), which hardware solve information protection tasks. They either prevent physical penetration, or if the penetration still took place, access to information, including with the help of its disguise. The first part of the task solve locks, lattices on windows, protective alarm, etc. The second - noise generators, network filters, scanning radio and many other devices, "overlapping" potential channel leakage channels or allow them to be detected. The advantages of technical means are associated with their reliability, independence from subjective factors, highly resistant to modification. Weaknesses are insufficient flexibility, relatively large volume and weight, high cost.
- Software Tools include programs to identify users, access control, encryption information, deleting residual (working) information such as temporary files, test control of the protection system, etc. Benefits of software - versatility, flexibility, reliability, simplicity of installation, the ability to modify and develop. Disadvantages - limited network functionality, use of part of the resource server and workstations, high sensitivity to random or deliberate changes, possible dependence on computers (their hardware).
- Mixed Hardware and software implements the same functions that hardware and software are separately and have intermediate properties.
- Organizational The means fold out of the organizational and technical (preparation of premises with computers, laying the cable system, taking into account the requirements for restricting access to it, etc.) and organizational and legal (national legislation and the rules of work established by the management of a particular enterprise). The advantages of organizational funds are that they allow you to solve many heterogeneous problems, easy to implement, quickly respond to unwanted actions on the network, have unlimited possibilities of modification and development. Disadvantages - high dependence on subjective factors, including from a general organization of work in a particular unit.
According to the degree of distribution and availability, software is allocated, other means apply in cases where additional level of information protection is required.
Information security software
- Built-in information security tools
- Antivirus Program (Antivirus) - a program for detecting computer viruses and treating infected files, as well as for prevention - prevent file infection or malicious system operating system.
- Ahnlab - South Korea
- Alwil Software (Avast!) - Czech Republic (free and paid version)
- AOL Virus Protection As part of AOL Safety and Security Center
- Arcavir - Poland.
- Authentium - United Kingdom
- AVG (GRISOFT) - Czech Republic (free and paid version, including firewall)
- Avira - Germany (there is a free version of Classic)
- AVZ - Russia (free); missing Real-Time Monitor
- BitDefender - Romania
- Bullguard - Denmark
- ClamAV - GPL license (free, open source); missing Real-Time Monitor
- Computer Associates - USA
- Dr.Web - Russia
- ESET NOD32 - Slovakia
- Fortinet - USA
- FRISK SOFTWARE - Iceland
- F-PROT - Iceland
- F-Secure - Finland (multivine product)
- G-DATA - Germany (multi-modified product)
- GECAD - Romania (company purchased Microsoft in 2003)
- Ikarus - Austria
- H + BedV - Germany
- Hauri - South Korea
- Microsoft Security Essentials - Free Antivirus from Microsoft
- MicroWorld Technologies - India
- MKS - Poland.
- Moonsecure - GPL license (free, open source), based on ClamAV code, but has a REAL-TIME monitor
- Norman - Norway
- Nuwave Software - Ukraine (use engines from AVG, Frisk, Lavasoft, Norman, Sunbelt)
- Outpost - Russia (two antimalware engines are used: Anti-virus from Virusbuster and Antispy, former Tauscan, own development)
- PANDA SOFTWARE - Spain
- Quick Heal Antivirus - India
- Rising - China
- Rose Swe - Germany
- Safe`n`sec - Russia
- SIMPLE Antivirus - Ukraine
- Sophos - United Kingdom
- Spyware Doctor - Anti-virus utility
- Stiller Research.
- Sybari Software (company purchased Microsoft in early 2005)
- Trend Micro - Japan (nominally Taiwan / USA)
- Trojan Hunter - Anti-virus utility
- Universal Anti Virus - Ukraine (free)
- Virusbuster - Hungary
- Zonealarm Antivirus - USA
- Zillya! - Ukraine (free)
- Kaspersky Anti-Virus - Russia
- VirusBokka (VBA32) - Belarus
- Ukrainian National Antivirus - Ukraine
- Specialized software protection software from unauthorized access is generally the best possible features and characteristics than the built-in funds. In addition to encryption programs and cryptographic systems, there are many other available external information protection tools. Of the most frequently mentioned solutions, the following two systems should be noted, allowing to limit and control information flows.
- Firewater screens (also called firewalls or firewalls - from it. Brandmauer., eng. firewall - "Fire Wall"). A special intermediate servers are created between local and global networks, which inspected and filter the entire network / transport level traffic through them. This allows you to drastically reduce the threat of unauthorized access from outside to corporate networks, but does not eliminate this danger completely. A more secure method of the method is the MasqueraDing method, when the entire traffic from the local network is sent on behalf of the Firewall server, making the local network with almost invisible.
| Firewater screens | ||
|---|---|---|
| Free | Ashampoo Firewall Free Comodo Core Force (Eng.) Online Armor PC Tools Peerguardian (English) Sygate (English) ZoneAlarm | |
| Proprietary | Ashampoo Firewall Pro AVG Internet Security Ca Personal Firewall Jetico (English) Kaspersky Microsoft Isa Server Norton Outpost Trend Micro (English) WINROUTE (English) Windows Firewall Sunbelt | |
| Hardware | FORTINET CISCO JUNIPER CHECK POINT (English) | |
| FreeBSD. | Ipfw ipfilter. | |
| Mac Os. | NetBarrier X4 (English) | |
| Linux. | NetFilter (Iptables Firestarter Iplist Nufw Shorewall) | |
- Proxy-Servers (Proxy - Power of Attorney, Trustee). All network / transport level traffic between local and global networks is prohibited completely - routing as such is missing, and circulation from the local network to the global occur through special intermediary servers. Obviously, with this appeal from the global network to local becomes impossible in principle. This method does not provide sufficient protection against attacks at higher levels - for example, at the application level (viruses, Java and JavaScript code).
- A VPN (Virtual Private Network) allows you to transmit secret information through networks in which there may be a traffic audition by foreign people. Used technologies: PPTP, PPPOE, IPSec.
Hardware tools for information protection
Hardware protection includes various electronic, electron-mechanical, electron-optical devices. To date, a significant number of hardware has been developed for various purposes, but the most common is the following:
- special registers for storing security details: passwords identifying codes, vultures or secrecy levels;
- devices for measuring individual characteristics of a person (voice, prints) in order to identify it;
- interruption circuits of information transmission in line in order to periodically check the data issuing address.
- devices for encryption information (cryptographic methods).
Technical means of information protection
To protect the perimeter of the information system, the security and fire alarm systems are created; digital video surveillance systems; Access Control and Access Control Systems. Protection of information from its leakage by technical communication channels is provided by the following means and activities: using shielded cable and laying of wires and cables in shielded structures; installation on high-frequency filter communication lines; construction of shielded premises ("capsules"); Use of shielded equipment; Installation of active sleeve systems; Creating controlled zones.
Financial vocabulary
Technical, cryptographic, software and other means intended to protect information constituting the state secret, funds in which they are implemented, as well as means of controlling the effectiveness of information protection. Edwart. ... ... Dictionary rapid situations
Information protection tools - Technical, cryptographic, software and other means intended to protect information that make up the state secret, funds in which they are implemented, as well as means of controlling the effectiveness of information protection.
Today, no concern, consisting of enterprises performing part of the general production cycle, the trading network or the accounting system cannot do without exchanging data via the Internet.
It can be or traffic information between individual processing points, or the creation of a single storage center.
In each case, carefully thought-out protection of information on the Internet, which is able to get rid of many troubles and financial losses.
Risks arising with not protected use of the Internet
List which hazards may arise if the protection of information on the Internet is not organized or is organized poorly - almost impossible.
Each individual case is usually a totality, often the most unpleasant combination of several factors.
Their brief list can be formulated as follows:
- obtaining unauthorized access to information;
- theft of critical data;
- substitution or intentional changing information in the repository or directly during transmission;
- malicious removal of important data;
- disclosure of confidential information after receiving access to it by various methods;
- intentional data encryption in order to follow the next blackmail, extortion.
When organizing a system for preserving data, which will carefully read all laws on the protection of information on the Internet - it is worth understanding the existing problem areas.

Preservation of corporate information by its redemption by intruders
One of them relates to the human factor, the other concerns the transmission techniques, the third formulates a storage management scheme.
Who needs information protection
It is worth understanding that everyone without exception is needed to protect information on the Internet.
Kidnapping or access to personal data to unauthorized persons - can cause a variety of consequences.
For example, cases of constructing a fictitious personality dealing with criminal activities on the Internet and constantly operating the identification information of another individual.
Another danger is the intentional damage to reputation, material losses by selling personal real estate, loan design and so on.
Therefore, the protection of personal information on the Internet today is regulated by legislative acts.

But this does not mean that each person should not personally follow the rules for handling data, their transfer and storage.
However, the most information system in the Internet is needed by manufacturing and commercial companies.
With unauthorized access to data, their abduction, intentional change can occur a wide variety of dangerous cases:
- Damage to the quality of the product as a result of changing the key parameters of the production process or the feedstock.
- Violation of the obligations assumed due to violation of the logistics of supplies, quality changes, disruptions of contractual terms.
- Direct damage due to industrial espionage, direct sale of developing competitors.
- Indirect damage due to the disclosure of development plans and other strategic data.
- Integrated damage in stealing, data encryption with the purpose of blackmail, extortion, which leads to direct financial losses, is fraught with the consequences of industrial espionage, impairment of workflows and many others.
The listed list, although not complete - gives a sufficient idea of \u200b\u200bwhy the problems of protecting information on the Internet large companies are valued very seriously. To reduce the predictable minimum potential damage, sufficiently deployed complexes of countermeasure measures are developed and implemented.
Basic methods and means of information security on the Internet
A specific list of measures taken and selected information protection technologies in Internet networks depends on the set of factors.

This may be the nature of the information, the method of its separation and storage, the format of the used technical means and much more. However, in practice, all decisions are conditionally formalized and divided into large categories.
Hardware
Hardware applied at all organizational levels. However, it is especially important to properly organize information storage.
The task of hardware at the same time:
- provide the desired data access speed;
- guarantee the proper speed of calculation systems;
- ensure the integrity of the data and the guarantee of their conservation upon failure of individual storage facilities;
- organize backup, quick recovery of information in case of failures;
- ensure interaction with communications;
- react and minimize damage in emergency situations (fire, flooding);
- keep the performance of the main equipment during the disconnection of the main source of energy (generators, uninterrupted power sources).
- process requests for connected users.
In the data warehouses, servers equipped with RAID arrays are used to solve the tasks assigned tasks.
It is imperative to one way or another, the principle of duplication of key systems is implemented. Network controllers, switchgear and much more are used.

Picture showing the work of the firewall (Firewall)
Hardware information security technologies on the Internet also include firewalls, software controlled equipment, identification systems, access control and much more.
Software
The area of \u200b\u200bsoftware is the most extensive. The choice of a specific list of packages depends on the platforms used and operating systems adopted by the access mechanic.
The average list of protective measures includes:
- the system of detection of network attacks and attempts to unauthorized access to the node as part of software managed equipment;
- encryption complexes (software or hardware);
- authentication tools, electronic keys and systems for working with them;
- access controls that may include hardware.
In practice, the correctly selected software package can virtually exclude a direct attack on the repository or a separate data processing unit.

Protection measures also include standard encrypted information transfer protocols.
Mixed
Mixed protection measures are developed for the storage and processing network in the case when the nature of the data actions differs for different user groups.
The list of funds used may include software complexes in separate workplaces, systems of separation of rights and access levels within one sector and the overall structure of responsibility.
Popular application of various schemes of interaction between performers among themselves, as well as methods of control and monitoring.

The simplest case of mixed security measures can be attributed to the mandatory use of antiviruses, standard encrypted transmission protocols, identification systems (including hardware) with multi-level access to working with information.
Organizational
Organizational information protection measures include the development of optimal staff interaction schemes with information and society.
This refers here:
- development of instructions, prescriptions, clear schemes for working with data for employed personnel;
- providing personnel with a limited set of certified, reliable software;
- mandatory application of the principles of responsibility for disclosing confidential information;
- separation of the responsibility zones of each labor unit, ranking areas of available data, the formulation of the amount of available actions;
- creating funds to prevent accidental, intentional deletion of information;
- application of software that fully eliminate direct access to data;
- formulation in the form of instructions, rules of action of employees, protection - systems of work with internal information carriers, regulations of the detailed documentation;
- the use of authentication tools and authentication (electronic keys).
In close to the ideal scheme of working with staff, there are constant checks of the actions of each labor unit.

At the same time, the employee is provided with a standardized workplace where the set of programs is regulated for its level of access.
Computer housings and other electronic technology, parts of which can serve as carriers of important information - are sealing and are under constant control.
At enterprises where work is constantly underway, it is recommended to introduce personnel identification system to access a network (premises), based on periodically changing and under strict taking into account electronic passes and other labels.
Conclusion
To protect data on the Internet using hardware and software solutions offered in the market - you can build an effective and fault-toeble complex.
But it is worth remembering: All famous hackers received access to this by working with people and using their errors.
Therefore, the freedom of personnel is limited at the enterprise for security purposes to the limit.
All that can prevent leakage, as well as the separation of access and responsibility - can help keep important data and avoid serious trouble.
Video: "Cognitive film": information protection
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted by http://www.allbest.ru/
Introduction
1. Problems of information protection in computer systems
2. Ensuring information security in networks
3. Safety mechanisms
3.1 Cryptography
3.2 Electronic signature
3.3 Authentication
3.4 Network Protection
4. Requirements for modern information protection tools
Conclusion
Literature
Introduction
In the computing technology, security concept is quite wide. It implies the reliability of the computer, and the safety of valuable data, and the protection of information from making changes to unauthorized persons, and preserving the secrets of correspondence in electronic communications. Of course, in all civilized countries guarding citizens' security are laws, but in the field of computational technology, law enforcement practice is not yet developed, and the legislative process does not have time for the development of computer systems, it is largely based on self-defense measures.
There is always a problem of choosing between the necessary level of protection and the efficiency of the network. In some cases, users or consumers security measures may be regarded as measures to limit access and efficiency. However, such as, for example, cryptography, allow you to significantly increase the degree of protection without limiting user access to the data.
1. Problems of information protection incomputersystems
The widespread use of computer technologies in automated information processing systems and management has led to the exacerbation of the problem of protecting information circulating in computer systems, from unauthorized access. Protection of information in computer systems has a number of specific features related to the fact that the information is not a rigidly associated media, can be easily and quickly copied and transmitted over communication channels. A very large number of threats of information that can be implemented both by external intruders and on the part of the internal violators are known.
The radical solution to the problems of protection of electronic information can be obtained only on the basis of the use of cryptographic methods that allow you to solve the most important problems of protected automated processing and data transmission. At the same time, modern high-speed methods of cryptographic transformation allow you to maintain the original performance of automated systems. Cryptographic data transformations are the most effective means of providing data confidentiality, their integrity and authenticity. Only their use in conjunction with the necessary technical and organizational events can provide protection against a wide range of potential threats.
Problems arising from the security of information transmission when working in computer networks can be divided into three main types:
· interception of information - the integrity of the information is maintained, but its confidentiality is violated;
· Modification of information - the source message varies either completely replaced by another and is sent to the addressee;
· substitution of certificate of information. This problem may have serious consequences. For example, someone can send a letter from your name (this kind of deception is called a spoofing) or a Web server can pretend to electronic store, receive orders, credit card numbers, but not send any goods.
The needs of modern practical informatics led to the emergence of unconventional tasks of protecting electronic information, one of which is the authentication of electronic information in conditions when the parties shakes do not trust each other. This problem is related to the creation of electronic digital signature systems. The theoretical basis for solving this problem was the discovery of two-specific cryptography by the American researchers Diffy and Heemiman in the mid-1970s, which was the brilliant achievement of the centuries-old evolutionary development of cryptography. The revolutionary ideas of bunk cryptography led to a sharp increase in the number of open research in the field of cryptography and showed new ways to develop cryptography, its new opportunities and the unique importance of its methods in modern mass use of electronic information technologies.
The technical basis for the transition to the information society are modern microelectronic technologies that provide a continuous increase in the quality of computing equipment and serve as a basis for maintaining the main trends of its development - miniaturization, reduction of electric consumption, increasing the volume of RAM (OP) and capacity of built-in and removable drives, productivity growth and reliability, expansion of spheres and applications. These trends in the development of computational equipment led to the fact that at the present stage, the protection of computer systems from unauthorized access is characterized by an increase in the role of software and cryptographic protection mechanisms compared to hardware.
The increase in the role of software and cryptographic drugs is sewn manifested in the fact that emerging new problems in the field of protection of computing systems from unauthorized access, require the use of mechanisms and protocols with a relatively high computational complexity and can be effectively solved by using computer resources.
One of the important social and ethical problems generated by the increasing application of the methods of cryptographic protection of information is a contradiction between the desire of users to protect their information and transferring reports and the desire of special public services to be able to access the information of some other organizations and individuals in order to prevent illegal activities. . In developed countries, there has been a wide range of opinions on approaches to the issue of regulating the use of encryption algorithms. Proposals are made from a complete ban on the widespread use of cryptographic methods to complete freedom of their use. Some proposals refer to permission to use only weakened algorithms or to establish the procedure for mandatory registration of encryption keys. It is extremely difficult to find the optimal solution to this problem. How to estimate the ratio of loss of law-abiding citizens and organizations from the illegal use of their information and state losses from the impossibility of gaining access to encrypted information of individual groups that hide their illegal activities? How can I be guaranteed to prevent the illegal use of cryptal farms by persons who violate other laws? In addition, there are always hidden storage and information transfer methods. These questions have yet to solve sociologists, psychologists, lawyers and politicians.
The emergence of global Internet type information networks is an important achievement of computer technologies, however, the mass of computer crimes is associated with the Internet.
The result of the experience of using the Internet network is the identified weakness of traditional information protection mechanisms and lagging in the application of modern methods. Cryptography provides an opportunity to ensure the security of information on the Internet and now work is actively under the introduction of the necessary cryptographic mechanisms into this network. Not a refusal of progress in informatization, and the use of modern achievements of cryptography is a strategically correct decision. The possibility of wide use of global information networks and cryptography is an achievement and a sign of a democratic society.
The ownership of cryptography in the information society objectively cannot be the privilege of individual public services, but is an urgent need for the widest layers of scientific and technical workers who apply computer processing of data or developing information systems, security services and managerial staff of organizations and enterprises. This can only be the basis for the effective implementation and operation of information security.
One separately taken organization cannot provide sufficiently complete and effective control over information flows within the total state and ensure the proper protection of the national information resource. However, individual government bodies can create conditions for the formation of a market of qualitative means of protection, the preparation of a sufficient number of specialists and mastering the funds of cryptography and the protection of information from mass users.
In Russia and other CIS countries, in the early 1990s, the tendency to advance advanced expansion of the scope and regions of the application of information technologies on the development of data protection systems was clearly traced. Such a situation was to a certain extent, and is typical and for developed capitalist countries. This is natural: first there should be a practical problem, and then decisions will be found. The beginning of the restructuring in the situation of the strong lag of the CIS countries in the field of informatization in the late 1980s created fertile soil for sharp overcoming the established break.
Example of developed countries, the possibility of acquiring system software and computer equipment inspired domestic users. The inclusion of a mass consumer interested in operational processing of data and other advantages of modern information and computing systems, in solving the problem of computerization led to a very high pace of development of this area in Russia and other CIS countries. However, the natural joint development of the means of automating information processing and information protection tools has largely violated, which caused mass computer crimes. It's no secret that computer crimes currently make up one of very topical problems.
The use of foreign production systems cannot be fixed this breakdown, since the products entering the Russian market do not comply with the requirements due to existing export restrictions adopted in the United States - the main manufacturer of information security tools. Another aspect of paramount importance is that this type of product should undergo an established certification procedure in authorized organizations.
Certificates of foreign firms and organizations, no way be a substitute for domestic. The fact of the use of foreign system and applied software creates an increased potential threat to information resources. The use of foreign remedies without proper analysis of the compliance with the functions and the level of protection provided can many times complicate the situation.
Forcing the informatization process requires adequate to provide consumers with means of protection. The absence of a sufficient number of information protection tools in computer systems in the domestic market, has not allowed a considerable time in the required scale to carry out data protection measures. The situation was exacerbated by the lack of a sufficient number of specialists in the field of information protection, since the latter, as a rule, were prepared only for special organizations. The restructuring of the latter, associated with changes in Russia, led to the formation of independent organizations specializing in the field of information that switched the released personnel, and as a result of the spirit of competition, which currently led to the appearance of a sufficiently large number of certified funds for the protection of domestic developers.
One of the important features of the mass use of information technologies is that in order to effectively solve the problem of protecting the state information resource, it is necessary to disperse data protection measures among mass users. The information must be protected primarily where it is created, is going, processed by both organizations that are direct damage with unauthorized access to data. This principle is rational and effective: protection of the interests of individual organizations is the component of the realization of the protection of the interests of the state as a whole.
2. Ensuring the protection of information innetworks
In the Armed Forces, information is focused, the exclusive right to use which belongs to certain persons or groups of persons acting in the order of a personal initiative or in accordance with official duties. Such information should be protected from all types of extraneous intervention: reading by persons who do not have access to information and deliberate information change. In addition, measures should be taken to protect network computing resources from their unauthorized use, i.e. Access to the network of persons who do not have rights to it should be excluded. Physical protection of the system and data can be carried out only with respect to working computer and communication nodes and it is impossible for means of transmission having a greater length. For this reason, funds that exclude unauthorized data access and ensuring their secrecy should be used.
Studies of the functioning of data processing systems and computing systems have shown that there are quite many possible directions of information leakage and unauthorized access paths in systems and networks. Among them:
· reading residual information in the system's memory after executing authorized requests;
· copying media and information files with overcoming protection measures;
· disguise under a registered user;
· disguise under the request of the system;
· use of software traps;
· use of deficiencies of the operating system;
· illegal connection to equipment and communication lines;
· The malicious conclusion is due to protection mechanisms;
· The introduction and use of computer viruses.
Ensuring the safety of information in the aircraft and in autonomously working PEVM is achieved by a complex of organizational, organizational and technical, technical and software measures.
To organizational measures to protect informationrelate:
· restriction of access to the premises in which the information is prepared and processing;
· admission to the processing and transfer of confidential information only proven officials;
· storage of magnetic media and registration logs in closed for access of unauthorized persons in safes;
· Exception of viewing by unauthorized persons of the material being processed through the display, printer, etc.;
· the use of cryptographic codes when transmitting valuable information on channels;
· The destruction of coloring tapes, paper and other materials containing fragments of valuable information.
Organizational and technical measures to protect informationinclude:
· the power supply of equipment processing valuable information from an independent power source or through special network filters;
· Installation on the doors of the rooms of code locks;
· Use to display information when entering a liquid crystal or plasma displays, and to obtain solid copies - inkjet printers and thermal printers, since the display gives such high-frequency electromagnetic radiation that the image from its screen can be taken at a distance of several hundred kilometers;
· the destruction of information stored in the ROM and the NGMD, when writing or sending PCP to repair;
· Installing the keyboard and printers on soft gaskets in order to reduce the possibility of removing information by an acoustic way;
· Restricting electromagnetic radiation by screening of rooms where information is processed, sheets of metal or from special plastics.
Technical means of information protection- These are the protection systems of territories and premises by shielding machine rooms and the organization of check-in systems. Protection of information in networks and computing means using technical means is implemented on the basis of the organization of access to memory using:
· access control to different memory levels of computers;
· blocking data and input keys;
· Allocation of check bits for entries for the purpose of identification, etc.
Architecture of information security softwareincludes:
· security control, including control of registration of entry into the system, fixing in the system log, user actions;
· reaction (including sound) on a violation of a system for protecting access control to network resources;
· control of access mandates;
· formal control of the protection of operating systems (basic system-wide and network);
· control of protection algorithms;
· Check and confirm the correctness of the functioning of technical and software.
To ensure the protection of information and detecting cases of unauthorized actions, registration of the system is carried out: special diaries and protocols are created, which are recorded all actions related to the protection of information in the system. The time of receipt of the application is recorded, its type, username and terminal from which the application is initialized. When selecting events to be registered, it is necessary to keep in mind that with an increase in the number of registered events it makes it difficult to view the diary and the detection of attempts to overcome protection. In this case, software analysis can be applied and fixed dubious events. Special programs for testing protection system are also used. Periodically or in randomly chosen moments of time, they check the performance of hardware and software protection.
A separate group of measures to ensure the safety of information and identifying unauthorized requests includes programs for detecting violations in real time. The programs of this group form a special signal when registering actions that can lead to unlawful actions with respect to protected information. The signal may contain information on the nature of the violation, the place of its occurrence and other characteristics. In addition, programs may prohibit access to secure information or simulate such a mode of operation (for example, instant loading of I / O devices), which will allow you to identify the intruder and detain it with the relevant service. Information Computer Authentication Protection
One of the common protection methods is a clear indication of the secrecy of the displayed information. In systems that support multiple levels of secrecy, outputting the terminal screen or the printing device of any unit of information (for example, file, records and tables) is accompanied by a special vulture indicating the level of secrecy. This requirement is implemented using relevant software.
A separate group highlighted means of protection against unauthorized use of software. They acquire particular importance due to the wide distribution of PCs.
3. Fur.security anisms
3.1 Cryptography
To ensure secrecy, encryption is applied, or cryptography, which allows you to transform data into an encrypted form, from which it is possible to extract initial information if there is a key.
Encryption systems as many years as the written exchange of information.
"Cryptography" translated from the Greek language means "Tynsopcript", which fully reflects its initial destination. Primitive (from the standpoint of today) cryptographic methods are known from ancient times and for a very long time they were considered rather as some tricks than strict scientific discipline. The classical task of cryptography is the reversible transformation of some clear source text (open text) to the seemingly random sequence of some characters, called the ciphertext or cryptogram. At the same time, the cipher package may contain both new and available signs in the open message. The number of signs in the cryptogram and in the source text in the general case may vary. An indispensable requirement is that using some logical change of symbols in the ciphertext, you can definitely restore the source text in full. The reliability of the conservation of information in the mystery was determined in the distant times by the fact that the conversion method itself was held in the secret.
Many centuries passed, during which the cryptography was the subject of the elect - priests, rulers, major military leaders and diplomats. Despite the lowest prevalence, the use of cryptographic methods and methods for overcoming enemy ciphers have had a significant impact on the outcome of important historical events. It is known not one example of how the revaluation of the ciphers used led to military and diplomatic lesions. Despite the use of cryptographic methods in important areas, the episodic use of cryptography could not even close it to the role and the meaning it in modern society. For its transformation into a scientific discipline, cryptography is obliged to the needs of practice generated by electronic information technology.
The awakening of considerable interest in cryptography and its development began with the XIX century, which is associated with the emergence of telecommunications. In the 20th century, the secret services of most developed countries belongs to this discipline as a mandatory tool for their activities.
The basis of encryption is two basic concepts: the algorithm and key. Algorithm - This is a way to encode the source text, resulting in an encrypted message. Enpreated message can be interpreted only with key
Obviously, to encrypt the message, the algorithm is enough.
Dutch cryptographer Kerkhoff (1835 - 1903) for the first time formulated the rule: cipher resistance, i.e. Cryptosystems - a set of procedures managed by some secret information of a small amount must be provided in the case when the opponent's cryptanalytics is known for the entire encryption mechanism with the exception of the secret key - information controlling the cryptographic transformation process. Apparently, one of the tasks of this requirement was awareness of the need to test the cryptosham developed in the conditions of more rigid compared to the conditions in which a potential intruder could act. This rule stimulated the emergence of better ciphering algorithms. It can be said that it contains the first element of standardization in the field of cryptography, since it is planned to develop open transformation methods. Currently, this rule is interpreted more widely: all long-term elements of the protection system must be assumed to be a well-known potential attacker. The last wording of the cryptosystem includes as a special case of protection systems. In this formulation, it is assumed that all elements of protection systems are divided into two categories - long-term and easily replaced. Long-term elements include those elements that relate to the development of protection systems and to change require the intervention of specialists or developers. Elements of the system that are intended for arbitrary modification or modification of a predetermined rule are elements, based on the randomly selected initial parameters, relate to easily connected elements. Easily changeable elements include, for example, key, password, identification, etc. The rule under consideration reflects the fact that the proper level of secrecy can only be ensured with respect to easily connected elements.
Despite the fact that, according to modern cryptosystem requirements, they must withstand cryptoanalysis based on a well-known algorithm, a large amount of well-known text and the corresponding ciphertectust, ciphers used by special services are preserved in the Security. This is due to the need to have an additional safety margin, since currently the creation of cryptosystems with proven resistance is the subject of a developing theory and is a rather complicated problem. To avoid possible weaknesses, the encryption algorithm can be built on the basis of well-studied and tested principles and transformation mechanisms. No serious modern user will always rely only on reliability of preservation in the secret of its algorithm, since it is extremely difficult to guarantee a low probability that information about the algorithm will become a well-known attacker.
Information secrecy is ensured by the introduction of special keys (codes) into algorithms. The use of a key in encryption provides two significant advantages. First, you can use one algorithm with different keys to send messages to different addressees. Secondly, if the key secrecy is broken, it can be easily replaced without changing the encryption algorithm. Thus, the safety of encryption systems depends on the secrecy of the key used, and not on the secrecy of the encryption algorithm. Many encryption algorithms are publicly available.
The number of possible keys for this algorithm depends on the number of bits in the key. For example, an 8-bit key admits 256 (28) key combinations. The greater the possible combinations of keys, the harder it is to choose the key, the religious message is encrypted. For example, if you use a 128-bit key, you will need to take out 2128 keys, which is currently not at least the most powerful computers. It is important to note that the growing performance of the technique leads to a decrease in the time required to open the keys, and security systems have to use more and longer keys, which, in turn, leads to an increase in encryption costs.
Since such an important place in encryption systems is paid to key secrecy, the main problem of such systems is generation and key transmission. There are two main encryption schemes: symmetrical encryption (It is also sometimes called traditional or encryption with a secret key) and open key encryption (Sometimes this type of encryption is called asymmetric).
For symmetric encryptionthe sender and the recipient own the same key (secret), with which they can encrypt and decipher the data. After symmetrical encryption, small length keys are used, so you can quickly encrypt large data volumes. Symmetrical encryption is used, for example, some banks in ATM networks. However, symmetric encryption has several shortcomings. First, it is very difficult to find a safe mechanism with which the sender and the recipient will be able to secretly select the key. There is a problem of safe proliferation of secret keys. Secondly, a separate secret key must be stored for each destination. Thirdly, in the symmetric encryption scheme it is impossible to guarantee the identity of the sender, since two users own one key.
In the scheme open key encryption Two different keys are used to encrypt the message. With the help of one of them, the message is encrypted, and with the second - deciphered. Thus, the required security can be achieved by making the first key with publicly available (open), and the second key is stored only at the recipient (closed, personal key). In this case, any user can encrypt the message using an open key, but only the owner of a personal key is capable of decrypting the message. At the same time, there is no need to take care of the security of the open key, and in order for users to exchange secret messages, it is enough to have the open keys of each other.
The disadvantage of asymmetric encryption is the need to use longer than with symmetrical encryption, keys to ensure an equivalent security level, which affects the computational resources required to organize the encryption process.
3.2 Electronic signature
If the message whose security we want to ensure is properly encrypted, it still remains the possibility of modifying the source message or the substitution of this message to others. One of the ways to solve this problem is the user's transfer to the recipient of a short presentation of the transmitted message. A similar brief view is called a checksum, or a digest message.
Check sums are used when creating a fixed-length summary to represent long messages. Algorithms for calculating checksums are designed so that they are unique to each message if possible. Thus, the possibility of replacing one message to others is eliminated with the preservation of the same checksum value.
However, when using checksums, the problem of transmitting them to the recipient arises. One of the possible ways to solve it is the inclusion of the checksum in the so-called electronic signature.
With the help of electronic signatures, the recipient may make sure that the message received by the message is sent not by a third-party person, but having certain rights by the sender. Electronic signatures are created by encrypting the checksum and additional information using the Personal Key of the sender. Thus, anyone can decipher the signature using the public key, but only the owner of the personal key can correctly create a signature. To protect against interception and reuse, the signature includes a unique number - the sequence number.
3.3 Authentication
Authenticationit is one of the most important components of organizing information protection in the network. Before the user will be given the right to receive one or another resource, it is necessary to make sure that he is really the one for whom it gives out.
When you receive a request for the use of a resource on behalf of a user, the server that provides this resource transmits the authentication server management. After receiving the positive response of the authentication server, the user is provided with a requested resource.
When authentication is used, as a rule, the principle called "What He knows," is used - the user knows some secret word, which he sends the authentication server in response to his request. One of the authentication schemes is the use of standard passwords. Password- The set of characters known to the subscriber connected to the network is entered at the beginning of the network interaction session, and sometimes at the end of the session (in particularly responsible cases, the password for normal output from the network may differ from the input). This scheme is the most vulnerable in terms of security - the password can be intercepted and used by another person. Schemes are most often used using disposable passwords. Even being intercepted, this password will be useless for the next registration, and get the next password from the previous one is extremely difficult task. To generate disposable passwords, both software and hardware generators are used, which are devices inserted into the computer slot. Knowledge of the secret word is necessary to the user to bring this device into action.
One of the most simple systems that do not require additional costs of equipment, but at the same time providing a good level of protection, is S / KEY, on the example of which you can demonstrate the procedure for representing disposable passwords.
In the process of authentication using S / KEY, two parties are involved - client and server. When registering in the system using the S / KEY authentication scheme, the server sends an invitation to the client machine that contains the grain transmitted over the network in the open form, the current value of the iteration meter and the request to enter a disposable password, which must comply with the current value of the iteration meter. After receiving the answer, the server checks it and transmits the management of the server required by the user.
3.4 Network protection
Recently, corporate networks are increasingly included in the Internet or even use it as their basis. Considering what damage can bring an illegal invasion of a corporate network, it is necessary to develop protection methods. Firewalls are used to protect corporate information networks. Firewalls- this is a system or combination of systems, allowing to divide the network into two or more parts and implement a set of rules that determine the conditions for passing packets from one part to another. As a rule, this border is carried out between the local network of the enterprise and the internetom, although it can be carried out inside. However, protecting individual computers is unprofitable, therefore usually protect the entire network. Firewall misses all traffic through itself and for each passing package makes a decision - to skip it or discard. In order for the firewall to make these decisions, a set of rules is defined for it.
The firewall can be implemented as hardware (that is, both a separate physical device) and as a special program running on the computer.
As a rule, the Operational System, under the control of which the firewall is running, changes are made, the purpose of which is to increase the protection of the firewall itself. These changes affect both the OS kernel and the corresponding configuration files. On the firewall itself, it is not allowed to have partitions of users, and therefore potential holes - only the administrator section. Some firewalls work only in single-user mode, and many have a system for checking the integrity of program codes.
Firewall usually consists of several different components, including filters or screens that block the transmission of part of traffic.
All firewalls can be divided into two types:
· batch filters that are filtered by IP packets with filter routers;
· Applied level servers that block access to specific services on the network.
Thus, the firewall can be defined as a set of components or a system that is located between two networks and has the following properties:
· All traffic from the internal network to the external and out of the external network should go through this system;
· Only traffic defined by a local defense strategy can go through this system;
· the system is reliably protected from penetration.
4. Requirements for modern fundsprotection informanations
According to the requirements of the State Commission of Russia, the means of protecting information from unauthorized access (SHI NSD) that meet the high level of protection must provide:
· discretionary and mandatory access control principle;
· memory cleaning;
· insulation modules;
· labeling documents;
· protection of input and output to the alienated physical storage medium;
· mapping a user with the device;
· identification and authentication;
· design guarantees;
· registration;
· user interaction with a set of protection tools;
· reliable recovery;
· the integrity of the protection equipment complex;
· Modification control;
· monitoring distribution;
· architecture guarantees;
Comprehensive SHI NSDs must be accompanied by a packet of the following documents:
· SZI manual;
· user's manual;
· Test documentation;
· Design (project) documentation.
Thus, in accordance with the requirements of the State General Commission of Russia, comprehensive SHI NSDs should include a basic set of subsystems. The specific possibilities of these subsystems on the implementation of information protection functions determine the level of security of computing equipment. The real efficacy of SZI NSD is determined by the functional capabilities of not only basic, but also additional subsystems, as well as the quality of their implementation.
Computer systems and networks are subject to a wide range of potential threats to information, which necessitates providing a large list of functions and protection subsystems. It is advisable primarily to ensure the protection of the most informative channel leakage channels, which are as follows:
· Ability to copy data from machine media;
· data channels;
· The embezzlement of computer or built-in drives.
The problem of overlapping these channels is complicated by the fact that data protection procedures should not lead to a noticeable reduction in the performance of computing systems. This task can be effectively solved based on the global encryption technology discussed in the previous section.
The modern mass protection system should be ergonomic and have such properties conducive to widespread use as:
· the complexity is the ability to install various modes of protected data processing, taking into account specific requirements of various users and provide a wide range of possible actions of the intended violator;
· Compatibility - the system must be compatible with all programs written for this operating system, and must provide a protected mode of operation of the computer in the computing network;
· Portability - the ability to install the system to various types of computer systems, including portable;
· Ease of operation - the system should be easy to operate and should not change the usual technology of users;
· Working in real time - information transformation processes, including encryption, must be performed at high speed;
· high level of information security;
· Minimum system cost.
Conclusion
Following the massive use of modern information technologies, the cryptography invade the life of a modern person. On cryptographic methods, the use of electronic payments is based, the ability to transfer secret information on open communication networks, as well as solving a large number of other information protection tasks in computer systems and information networks. The needs of the practice led to the need for mass use of cryptographic methods, and therefore the need to expand open studies and developments in this area. The ownership of cryptography becomes important for scientists and engineers specializing in the development of modern means of information protection, as well as in areas of operation and design information and telecommunication systems.
One of the current problems of modern applied cryptography is the development of high-speed software blocks of block type, as well as high-speed encryption devices.
Currently, a number of encryption methods protected by patents of the Russian Federation and based on ideas are used:
· Flexible Sampling Connection Sampling;
· generation of an encryption algorithm for a secret key;
· Forces depending on the transformed data.
Literature
1. Ostreykovsky V.A. Informatics: studies. Manual for studies environments prof. studies. establishments. - M.: Higher. Shk., 2001. - 319С.: IL.
2. Economics / Ed. P.V. Konyukhovsky and D.N. Wheel. - SPb.: Peter, 2000. - 560s.: Il.
3. Informatics: Basic Course / S.V. Simonovich et al. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2002. - 640С.: IL.
4. Moldova A.A., Moldova N.A., Soviets B.Ya. Cryptography. - St. Petersburg: Publisher "Lan", 2001. - 224С., IL. - (textbooks for universities. Special literature).
Posted on Allbest.ru.
Similar documents
The problem of choosing between the necessary level of protection and the efficiency of the network. Information protection mechanisms in networks: cryptography, electronic signature, authentication, network protection. Requirements for modern information security tools.
course work, added 01/12/2008
Problem to protect information. Features of information protection in computer networks. Threats, attacks and channel leakage channels. Classification of methods and safety equipment. Network architecture and its protection. Network security methods.
thesis, added 16.06.2012
Methods and means of protecting information from unauthorized access. Features of information protection in computer networks. Cryptographic protection and electronic digital signature. Methods of protecting information from computer viruses and from hacker attacks.
abstract, Added 10/23/2011
The concept of protecting intentional threats to the integrity of information in computer networks. Characteristics of information security threats: compromising, dysfunction. Characteristics of NPO LLC "Mehinstrument", Main methods and methods of information protection.
thesis, added 16.06.2012
The main provisions of the theory of information protection. The essence of the basic methods and means of information protection in networks. The overall characteristics of the activities and corporate network of the enterprise "Velvet", analysis of its information protection techniques in telecommunication networks.
thesis, added 30.08.2010
Problems of information protection in information and telecommunication networks. Studying threats to information and ways of their impact on information protection objects. Concept of information security of the enterprise. Cryptographic methods for the protection of information.
thesis, added 08.03.2013
Ways of unauthorized access, classification of methods and means of information protection. Analysis of information protection methods in LAN. Identification and authentication, logging and auditing, access control. The concepts of security of computer systems.
thesis, added 04/19/2011
Methods and means of protecting information data. Protection against unauthorized access to information. Features of protecting computer systems by cryptography methods. Criteria for assessing the safety of information computer technologies in European countries.
examination, added 06.08.2010
The main properties of information. Data operations. Data is a dialectical component of the information. Types of intentional threats to the safety of information. Classification of malicious programs. Basic methods and information security tools in computer networks.
coursework, added 02/17/2010
Essence of the problem and task of protecting information in information and telecommunication networks. Threats of information, ways to influence objects. Concept of information security of the enterprise. Cryptographic methods and means of information protection.
Ensuring security in computer networks is the basic condition for the protection of confidential data from various types of threats, such as espionage, destroy files and other unauthorized actions. Each of the listed factors can negatively affect the correct operation of the local and global network, which, in turn, often leads to disclosure or loss of confidential information. One of the common networks [...]
Ensuring security in computer networks is the basic condition for the protection of confidential data from various types of threats, such as espionage, destroy files and other unauthorized actions.
Each of the listed factors can negatively affect the correct operation of the local and global network, which, in turn, often leads to disclosure or loss of confidential information.

One of the common network threats is unauthorized access from outside, and not only intentional, but also random. Also in this case, the risk of access to information constituting the medical, commercial, bank or state mystery is great.
The next nuisance with which users often encounter all over the world are different software malfunctions, including provoked by viruses infecting the system at the time of accessing the Internet.
The incorrect work of office equipment may be due to lack of power, as well as the presence of some problems in the server, auxiliary devices and systems. It is impossible to exclude the human factor, as the illiterate manipulations of employees of the enterprise can cause a lot of damage to the office equipment and the information contained in it.
Unfortunately, there is no single solution that can cope with all listed threats, but today some technical and administrative techniques are available today, reducing the likelihood of such problems.
Types of information protection
Progressive methods for the protection of information when using computer networks are mostly aimed at preventing all sorts of factors, inevitably leading to the loss or theft of confidential information. In the field of computer technologies, there are three main categories of such protection:
- installing special software;
- physical means;
- administrative events.
Effective protection tools include administration, the use of anti-virus programs, akud and UPS, as well as a competent distribution of powers between employees. In order to prevent unauthorized access to secret files, cryptographic protection methods are used, implying encryption of file content using electronic keys.

Computer network security tools
According to many years of research, more than half of the violations in the network is associated with network cable faults and connecting elements, the reason for which the wires can be broken, their mechanical damage or closure. Also, do not forget about electromagnetic radiation, provoked by household appliances, which delivers a lot of problems.
As a rule, special scanners are used to establish the cause and location of the damaged cable, which are based on the supply of electrical pulses with subsequent control of the reflected signal. Modern scanning systems allow you to specify the nominal signal propagation parameters and display the results of diagnostics on the peripheral devices.
The next reliable measure that impede the loss of important information due to the power supply interruption is the installation of the UPS, which is selected taking into account the technical requirements and standards. A competently selected device can provide for a certain time the nutrition of a local network or separate equipment.
The physical protection tools include the system archiving and reproduction of information. For large-scale corporate networks, it is recommended to organize a separate archiving server.
Of course, the most reliable are the integrated methods of protecting computer networks, combining a set of security measures, and what they are more, the better. In this case, specialists along with the provision of standard solutions are developing special action plans in case of emergency situations.
Among other things, the company managers are recommended to clearly share the powers of employees with the obligatory control of access to technical resources. It must be remembered that in the modern world of kiberataki takes a threatening scale, and only a serious approach to the organization of proper security measures will protect confidential information from criminal encroachment, entailing the image and financial loss of the enterprise.
 Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference
Cellular - what it is on the iPad and what's the difference Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare?
Go to digital television: What to do and how to prepare? Social polls work on the Internet
Social polls work on the Internet Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments
Savin recorded a video message to the Tyuments Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens
Menu of Soviet tables What was the name of Thursday in Soviet canteens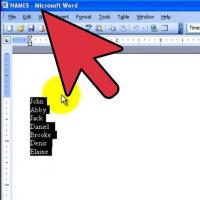 How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips
How to make in the "Word" list alphabetically: useful tips How to see classmates who retired from friends?
How to see classmates who retired from friends?