Windows 8 disk is write protected. Proven ways to remove protection from the drive. Using command line
It happens that the data carrier “does not allow itself to be formatted”, and the system reports that it is write-protected, although the card or flash drive does not have a corresponding switch at all (or the protection is disabled). You can read the data stored on the media, but you will not be able to delete it in any way. In other cases, the system supposedly deletes files without problems, but, in fact, they do not disappear.
Below are two methods that should help you unlock the protected media and format it. Keep in mind, however, that they may not bring the expected result.
In the case of damaged media, any formatting attempts may not be effective. Then it remains only to purchase a new medium and copy all the resources to it.
Protected media - unlock via registry
If within the section control there is no "StorageDevicePolicies" subkey, create it by right clicking and select Create → Chapter. Make sure you enter the correct name. Select the created partition with the right mouse button, select the item Create → DWORD parameter. Name the new value WriteProtect and assign it the number 0 in the Value Data. Confirm with the OK button, close the Registry Editor and reboot the system.
If this method doesn't work, try the next tip.
Removing a lock with Diskpart
Connect a USB drive to the USB connector, then call up the console. Enter for this cmd.exe in the start menu search box, right-click the found item and select command Run as administrator. Administrator rights will allow you to avoid the message Access denied.

Then enter the following commands in sequence, confirming each by pressing the Enter key.
diskpart
list disk
select disk x(x is the drive number assigned to the USB memory being used - determine this number from the capacity of the listed media)
attributes disk clear readonly
create partition primary
format fs=fat32(you can use the option ntfs instead of fat32 if you intend to use the media only on Windows computers)
Question from user
Hello. I'm trying to write one Word document to a USB flash drive from a hard drive, but an error appears that the disk is write-protected. This has never happened before, I didn’t hit the flash drive, I didn’t drop it, I didn’t do anything with it ...
Interestingly, I tried to delete some file from the flash drive - exactly the same error appeared, there was no access. Those. in fact, I can only copy previously recorded data from a USB flash drive. Can you tell me how to remove this error?
PS Windows 7, 8 GB Kingston USB stick (most common)
Hello.
Such an error can be caused by several reasons: a hardware malfunction of the flash drive (for example, if you accidentally dropped it before), a virus infection, a “manual” write protection setting, etc.
In this article, I will consider in sequence all the popular causes (causing this error) and how to fix them. I think that by presenting the article in a similar format, it will be easier and easier for you and other users with the same error to solve the problem.

Typical error when deleting a folder from an SD card // example
Reasons blocking writing to a flash drive
Eliminate consistently!
1) Check if there is a write lock on the hardware level
Experienced users probably remember that earlier on floppy disks there was a small lever, thanks to which it was possible to protect the information on it from unwanted deletion (or change). And in my opinion, the thing was extremely useful!
Now on most USB flash drives there is no such protection, one part of the manufacturers (mainly Chinese) produces such flash drives. Therefore, some users do not attach much importance to some "locks" on the body of the flash drive. Meanwhile, if protection is enabled, then you will not write anything to such a flash drive (see photo below).
Well, SD cards (used in cameras, for example) have a small switch on the side. If you move it to the Lock position (blocked), then the flash drive becomes read-only.

The moral of the last sentences: first of all, check if there is a mechanical write protection, if the lever is set correctly (and in general, if it is on your device).
2) Is the flash drive (computer) infected with a virus?
I remember my student days... When it was necessary to bring and connect a USB flash drive to computers "infected" with viruses quite often (and deliberately and knowing it in advance) - otherwise it was problematic (or even impossible) to print materials. After such a connection, I had to check the flash drive for viruses and clean the "infection".

If you do not have an antivirus on your computer, I recommend choosing one from the list:
3) Is there a place on the flash drive?
I understand that this question is somewhat banal, but still. If the size of the recorded file is larger than the remaining free space on the flash drive, you can get a recording error.
To find out how much free space is left on the flash drive: open "My Computer", then right-click on the flash drive, and open it properties. In the tab general- will indicate how much space is occupied, and how much is free.

4) Is it worth it to write protection in the registry
First you need to open the registry editor as an administrator. You can do this, for example, through the task manager: to launch it, press the key combination Ctrl+Shift+Esc(or Ctrl+Alt+Del ).
Next click file/new task and in line open enter the command regedit(note that the task will be run as an administrator).

By the way, you may find the article on how to open the registry editor helpful.-
(for Windows XP branch: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\USBSTOR )
Important! If branches StorageDevicePolicies will not be in the registry - it means you do not have a record lock in the registry. Just in case, you can create a branch (a branch in the registry is an analogue of a folder in Explorer) and then the Write Protect string parameter with the value "0". Creating branches and options is like working in a regular explorer, it's like creating a simple folder.


5) Check the file system of the flash drive for errors
A similar error can also pop up due to errors in the file system of the flash drive. For example, while copying a file, you removed the USB flash drive from the USB port or simply turned off the light - errors could well appear on it (by the way, the file system can be marked as RAW in such cases).
To check the flash drive for errors, open "My computer", then open properties flash drives, and in the section service press the button (checking the disk for errors, see screenshot below).
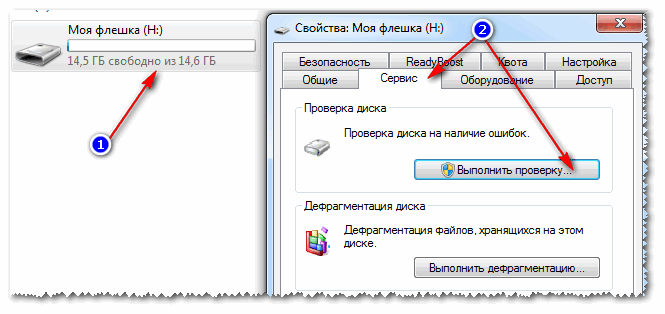

6) Is there a read-only attribute on the flash drive?
Another reason why Windows may give an error when writing a file to a USB flash drive is read-only attribute (if it is installed on a flash drive). There is nothing wrong with this attribute, it only tells the system that this disk is read-only, so it does not write data to it.
By the way, this happens quite often if you have picked up some types of viruses, or, for example, downloaded something from torrents (the uTorrent program often creates files with a read-only attribute).
And so, we will remove this attribute.

7) Check if there is any protection in the group policy editor
Writing to a flash drive can be disabled through the Group Policy Editor. Therefore, I also recommend checking if there is a treasured parameter there ...
Note: Windows Starter and Home users will not be able to open the Group Policy Editor.
To open the Group Policy Editor:
- press button combination Win+R;
- enter the command gpedit.msc;
- click Enter .

It should have the "Removable drives: disable recording" option. Open it up and see if it's enabled...

By default, the parameter should be set to "Not set" (see screenshot below). If not, switch it to this position, save the settings and restart your computer.

Parameter responsible for prohibiting recording
8) Formatting a flash drive
Perhaps this is the last thing that can be done if all other advice turned out to be in vain and did not lead to anything. Formatting the media helps in many cases, including our error discussed in this article.
Note: copy all the necessary data from the flash drive, when formatting from the flash drive, everything will be deleted (just in case, I warn you ☺)!
In most cases, to format a flash drive, just go to "My computer", select the flash drive among the disks, right-click on it and select the command in the context menu "Format" .

If it is not possible to format the media: errors will come out, the computer will freeze, etc., then you need to use special utilities to format it. One of those that I would recommend is HDD LLF Low Level Format Tool.
HDD LLF Low Level Format Tool
A small utility used for low-level formatting of disks, flash drives. It helps in the most difficult situations when it is not possible to format the media through Windows. Interfaces supported: S-ATA (SATA), IDE (E-IDE), SCSI, USB, Firewire.
The utility is distributed in several versions: there is also a portable one that does not need to be installed.
Because there is no Russian in the program, I will show with an example how the media is formatted.
After launching the utility, click the button "Continue for Free".


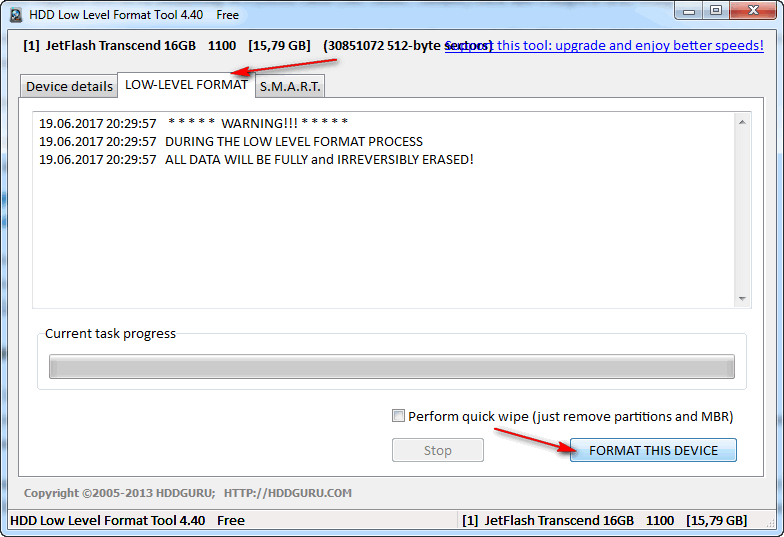
When it is over, Windows will prompt you to format the flash drive (you can format it in the usual way through "My Computer"). As a rule, after low-level formatting, the flash drive is easily and without errors formatted in Windows.
By the way, if your flash drive still does not work, I recommend trying to restore it. Here is another way described in this article:
That's all I wanted to say! For additions on the topic - I would be grateful.
Floppy disks are a thing of the past after they were successfully replaced by flash drives. But a modern person, when trying to write something to such a flash drive, can sometimes encounter a situation that has been familiar since the time of using those very floppy disks (floppy disks). It happens that a removable drive is locked and cannot be used for its intended purpose, that is, to write any files. How to solve such a problem? We will consider this issue in detail in this article.
So, you are faced with a situation: you need to write some information to a removable drive, and when you try to do this, you see a message like “ The disc is write-protected, remove the protection or insert another disc to".

Such a problem can be eliminated quite quickly, and we will talk about this a little later, but now it’s worth saying a couple of words about why protection is set against writing any information to a USB flash drive.
Please note that most often such an operation is performed solely for the sole purpose of protecting the flash drive from malware (viruses), which can themselves be copied to various removable media without the user's knowledge.
Ways to remove write protection from a flash drive
There are two most important options for removing protection from a removable drive: hardware and software.Hardware way
You need to set the lock switch, which is available on some models of USB flash drives, as well as on SD cards. Often, such a switch is located on the side edge of a drive. Therefore, you need to carefully consider from all sides the drive that you have and find on it the icon of an open and closed lock or the inscription Lock.
Please note that in fact, the protection is not difficult to remove - you just need to move the lock lever in the right direction. After such a simple maneuver, it often turns out that the write protection has already been removed. It remains only to install a removable drive (flash drive) in the appropriate slot and repeat the entire file recording operation.
Programmatic way
This method involves software interaction between the OS and the flash drive controller, which is responsible for the ability to record any information. It is possible to remove write protection using this method, using the command line, the registry editor, or the local group policy of the Windows 7/8/10 operating system. Let's now look at all of these options in more detail.Unprotect with regedit

Removing protection with Diskpart
If it was not possible to unlock the flash drive using the registry, you can try to do this using the command interpreter diskpart. The latter makes it possible to manage disks and partitions using commands that the user enters directly at the command line.
Removing Protection Using the Local Group Policy Editor
 If all the methods listed in this article did not help solve the difficulties with the impossibility of writing to a USB flash drive, you can still try to go to the official website of the manufacturer of your particular flash drive and find branded original utilities there for working with your particular drive. In addition, a situation is possible when the flash drive has already exhausted its resource (some manufacturers set a limit on the number of repeated writes, after a certain number of which the drive itself is transferred to a special read-only mode). In this case, you will have to purchase a new flash drive.
If all the methods listed in this article did not help solve the difficulties with the impossibility of writing to a USB flash drive, you can still try to go to the official website of the manufacturer of your particular flash drive and find branded original utilities there for working with your particular drive. In addition, a situation is possible when the flash drive has already exhausted its resource (some manufacturers set a limit on the number of repeated writes, after a certain number of which the drive itself is transferred to a special read-only mode). In this case, you will have to purchase a new flash drive. Flash drives and memory cards have almost completely occupied the niche of portable storage media for several years now. Sometimes it gets to the point that a blank disc in some places is almost impossible to buy. Agree, it is much more convenient to buy a small accessory once, on which you can overwrite various data a huge number of times without worrying that if you suddenly write something wrong, you will have to write everything over again. In addition, using flash drives, you practically protect yourself from the situation when a disc recorded on one computer may not play correctly on another. Well, you don’t always stock up on clean disks either.
Despite its durability and almost indestructibility, from time to time various errors may occur in the operation of a flash drive or memory card. One of the most annoying is write protection. You can copy information from portable media, but if you want to write something to it or change the location of files already placed on it, the system displays a window with the inscription: "The disk is write-protected." The first thought that comes to the mind of almost every user is that the accessory is broken. In some cases, this is exactly what it is, but very often the reasons lie elsewhere. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with all the possible reasons why write protection can be installed on a flash drive or memory card, and we will also analyze all possible ways to remove this protection.
Method 1. Hardware switch
This method is the simplest and can be really effective for older USB flash drives, as well as almost all SD memory cards. What is its essence? On the case of the drive there is a small button in the form of a slider, with which you can manually activate the write protection mode. If you are using a microSD memory card, then you are probably using a standard-sized SD card adapter to connect directly to your computer. It is on this adapter that the slider will be located. Look at it carefully, and you will see the inscription Lock or the image of a padlock, as well as an arrow indicating the direction in which you need to move the slider to activate the write protection. Since in most cases the problem does not occur on its own, it is likely that the last time you just accidentally touched the switch with your finger. Slide it in the opposite direction and try again to write the file you need. It is very likely that the problem will be solved already at this stage.

Next, we list the software ways to remove write protection. Thus, you act on the controller responsible for the operation of the drive chip. Choose one, since each of them leads to the same result, only the sequence of actions and the tools involved differ.
Method 2. Format the flash drive
A very simple and at the same time effective method in almost 100% of cases. The flash drive is formatted in two ways: through Windows Explorer or through the command execution utility. Let's analyze each of them in more detail.
Through Windows Explorer.
- In Explorer, depending on the version of Windows, open the My Computer, Computer or This Computer tab, find your USB flash drive in the list of drives and devices.
- Right click and select Format.
- In the window that opens, select the file system (we recommend choosing FAT32) and click the "Start" button. After a few seconds, the formatting will be completed.
We would like to draw your attention to the fact that if the flash drive is write-protected, then in this way you are unlikely to succeed. Better use the command execution utility.
- In Explorer, look under which letter the flash drive or memory card is defined in the system.
- Press the key combination Win + R, then in the window that opens, enter the command
format<буква_диска>: /q
format<буква_диска>: /q /fs:fat32
- After the command prompt opens, wait until the window is automatically closed, and then try again to write some .

Method 3. Through the registry editor
If for some reason the previous method did not help, let's try to dig deeper into the system. To do this, we will use the regedit utility - the Windows registry editor. You will need to change some settings.
- Click on the search button, located either in the Start menu, or, if you have Windows 10, in the lower left corner near the Start button, and type regedit, then find the utility in the search results and run it as an administrator.
- Navigate to the following branch: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\StorageDevicePolicies.
- If there is no StorageDevicePolicies folder, create it by clicking Options - Create - Section in the top menu and name it StorageDevicePolicies without spaces or quotes.
- Right-click on the created partition, select New - DWORD (32-bit) Value and name it WriteProtect.
- In the right part of the window, right-click on the name of the created parameter and select Change, after which you need to set the value to 0.
- Remove the flash drive, close the utility and restart your computer.
- Repeat writing the file to your drive, everything should work.

Method 4. Through the command line
To unlock a portable drive using the command line, you will need to run it as an administrator, and then enter a few commands that will help you remove the write protection. To achieve the desired result, take the following steps:
- Click the Start button and in the search bar type "command prompt" or cmd, right-click on the utility that appears in the search results and select run as administrator. If you are using Windows 10, right-click on the Start button and select "Command Prompt (Admin)".
- Enter the following commands in sequence:
diskpart
list disk
- The system will offer a list of disks connected to the computer, indicating the serial number. Based on the size, determine the number of your flash drive, then select it by entering the command select disk 3, where instead of 3, specify the number of your drive.
- After the utility notifies you that the disk has been successfully selected, you need to remove the write protection with the following command:
attributes disk clear readonly
- If you need to format the flash drive, do it with one of the commands:
format fs = ntfs
format fs = fat
- After a few seconds, everything will work, try again to copy something to the USB flash drive.

Method 5: Using the Local Group Policy Editor
- To open the local group policy editor, hold down the Win + R button combination, then type gpedit.msc in the line that opens and confirm the entry with the Enter button.
- In the utility window that opens, go to Computer Configuration - Administrative Templates - System - Access to Removable Storage Devices.
- See if the option "Removable drives: Deny reading" is activated. If the checkbox is "Enabled", select "Disabled", then click Apply - OK.
- Check if writing files to the flash drive works.
Method 6. Using proprietary utilities
If for some reason none of the methods helps, try using the proprietary flash drive troubleshooting utility from the device manufacturer. To do this, go to the official website, on the support page, look for software for external drives. The most famous utilities are HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool, JetFlash Recovery Tool and Transcend JetFlash Online Recovery.
If this does not help, then most likely your removable disk has become unusable. Perhaps the maximum rewrite cycles have simply been exhausted, which will make it impossible to write something. It's easier to buy a new flash drive, their price today is completely affordable for everyone.
Conclusion
We hope that our guide will help you remove the write protection from your flash drive or memory card and you can use it for a long time. We invite you to write in the comments what exactly helped you get rid of the problem.
Now let's try to remove the write lock from your flash drive, having considered the main options:
1. Using the registry editor.
- We go to "Start", in the search engine we write regedit and open the found file;
- Next, follow the branch HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Control \ StorageDevicePolicies;
- Select StorageDevicePolicies (if this item is not present, see below how to create it) and right-click on the WriteProtect parameter in the editor window;
- Then select "Change ..." and change the value to 0, save the changes "OK";

- In a safe way, we take out the USB flash drive and reboot the PC. Checking the performance of the drive.
If the StorageDevicePolicies item is missing, create it. For this:
- We click on the Control section, then we create, by right-clicking on an empty space, a section and name it StorageDevicePolicies;
- We select it and right-click on the empty space of the right half of the window to create a DWORD / QWORD parameter (depending on the bit depth installed on your PC system);
- We call this parameter WriteProtect and check its value, which should be equal to 0;
- Well, then we take out the drive, restart the computer and check for an error.
2. Using the command line.
Be sure to open it as an administrator by doing the following:

We close all windows and try to write something to a USB flash drive or format it.
3. Using the local group policy editor. We do the following:

Similar actions must be done in the "User Configuration" group in the same editor.
Now let's try to format the flash drive. Surely, the system will not issue a warning that the disk is protected.
We hope that this article helped you answer your question about why a flash drive is write-protected and how to format it. But, once again I want to remind you that safely removing the drive and treating it with care will protect you from such problems, and your flash drive will serve you for a long period of time. Good luck!
 How to Fix Windows Update Installation Errors Using Built-in Component Repair
How to Fix Windows Update Installation Errors Using Built-in Component Repair Free programs for Windows free download
Free programs for Windows free download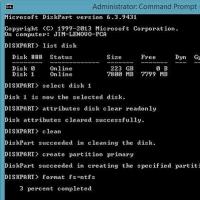 Proven ways to remove protection from the drive
Proven ways to remove protection from the drive how to change windows startup ringtone how to set windows ringtone
how to change windows startup ringtone how to set windows ringtone Nokia lumiya blacklist in classmates
Nokia lumiya blacklist in classmates How to get a replacement phone under warranty
How to get a replacement phone under warranty Sony Xperia Tablet S - Specifications
Sony Xperia Tablet S - Specifications