Software for working with the network. Free software for working with the network. Network operating systems
The 2D vector CADE editor for Windows was developed by a CAD company. The program allows you to easily draw up a detailed network diagram. One of the most useful, in my opinion, features is the ability to sign the IP address, serial number and manufacturer's name for each device on the network. CADE includes all the templates necessary for drawing up a diagram and is distributed completely free of charge.
Concept Draw Pro is one of the most powerful business diagramming tools out there, not just online. It takes a minimum of time to master the program - all operations are carried out by simple drag and drop. Concept Draw Pro comes with a complete set of network symbols, and all aspects of the diagram can be personalized. The cost of the app is $ 249.

Dia is open source diagramming software, the main drawback of which is its outdated interface and primitive character set. But the program is very easy to use without being distracted by any extraneous tasks. Dia is free and works on almost all desktop Linux distributions.

Diagram Designer is another free utility with an outdated interface, but very easy to use, thanks to which many users will surely like it. Unlike Dia, the program offers a much wider selection of symbols and icons. The only thing I didn't like about Diagram Designer was the need to draw the connections between computers by hand, because the program uses an arbitrary shape for this. Except for this small flaw, DD is a decent solution.

eDraw Max is one of the best tools on this list, with the exception of, of course, Visio. The program is easy to learn, has a convenient and, moreover, the most modern user interface of all the options listed. eDraw Max is a fully featured business diagramming tool for any purpose, not just network diagrams. The solution costs $ 99.95 per license, and the more licenses, the cheaper each one costs.

There are some extremely unsuccessful programs, and the GoVisual Diagram Editor is one of them. It is a difficult tool to use and provides far from satisfactory results. Although it can still be used to draw up a network diagram, it will not be particularly readable since the GoVisual Diagram Editor lacks some useful features - in particular, icons for network devices. But if someone wants a free diagramming program for any purpose, GoVisual is the right choice because it is distributed free of charge.

LanFlow is one of the best. The program has an excellent interface, offers a rich selection of network objects and allows you to easily create local, telecommunication, external network diagrams, as well as computer diagrams. LanFlow even provides two different network diagram templates: 3D diagram and black and white. To create a diagram, just select a template and drag suitable objects onto it, which can be grouped, deleted, and so on. A single-user license for the program costs $ 89, so LanFlow can rightfully be called one of the best budget Visio alternatives.

Although NetProbe can also be used for mapping, the main purpose of the program is to monitor network devices in real time. But the main advantage of NetProbe as a diagramming tool is that network devices can be added to the diagram as needed, even in advance. It is not necessary to do this manually - the built-in NetProbe component automatically scans the network and makes a list of all devices available on the network. The Standard version is free, but can only track eight hosts. The Pro version is only $ 40 for 20 hosts, while the Enterprise version, which monitors 400 hosts, is priced at $ 295.

Network Notepad (literally "network notepad") is exactly what the name suggests - a notebook for drawing up network diagrams. But despite the seeming simplicity, the program has rich features, including interactive functions (Telnet, network browsing, ping, etc.). Network Notepad has a simple drag-and-drop interface and can automatically detect Cisco devices. The program is distributed free of charge.

Visio is, of course, the de facto standard in the Windows diagramming application market. The program makes it easy to create beautiful network diagrams and share them through a web browser. Visio includes a rich set of templates, including for data centers, helpdesks, network racks; for office consolidation, network planning for the enterprise, data center or home office; for troubleshooting trees, HVAC plans, and more Visio is the best solution for network diagrams and is therefore not cheap: $ 249.99 for the Standard edition, $ 559.99 for the Professional edition, and $ 999.99 for the Premium 2010. You can read more about the features of the versions on the official Visio page.

| Materials (edit) |
Today, on the forums, you can more and more often find such topics as "Prompt programs for sysadmins", "Which network programs are better", "Help choose programs for a grid consisting of N number of computers, servers and so many users", etc. .d. What is the meaning of the concept of "network programs" and what are they for?
Network programs- this software is responsible for the stable operation of the organization's computer park. I think there is no point in explaining that all computers in an organization must be part of a common local network, therefore programs of this kind are called network programs.
The network performs in the company two main functions... First, it allows the company's employees to work as a team. And, secondly, the network helps to make better use of available resources, helps to share limited or expensive resources between employees. For example, a printer for every workplace is expensive and inefficient. Sharing the printer on a network saves on equipment costs.
Network programs are designed to solve many problems and problems associated with the network, such as: arising problems with equipment, hardware and software, ensuring information security of the company, equipment inventory, organization of the common file system of the enterprise, and much more. And although the variety of computer networks is now enormous, the problems are about the same everywhere. Network programs are designed to deal with them as quickly as possible.
It is necessary to protect the network, first of all, from external threats: hacker attacks, viruses, sniffers, etc. Most importantly, the sysadmin sometimes has to protect the network from internal users as well. Some people think that since they were given a personal computer, provided with Internet access and access to documents, they can perform various actions without being subjected to any criticism or punishment. Well, for example, download a couple of movies. And what, the Internet in the organization is unlimited, more gigabytes, less gigabytes, what's the difference? Or take a brand new video card home and put your old one in place. All the same, after all, no one will see, which means that they will not know. Network programs will find out.
You can harm the system and unconsciously, without any ulterior motive. For example, bring infected files from home on a USB flash drive and drop them into a shared folder. Viruses have a dangerous property of spreading over a network at the speed of light, and protection against them appears, as a rule, a day or two later. Information security specialists have already understood that it is pointless to catch up with hacker technologies forever, computer cybercriminals are always one step ahead. Therefore, new techniques are increasingly based on the preventive detection of violations in information systems.
In order for an administrator to be aware of everything that happens in his computer park, network programs must respond to everything unusual on the network. For example, if the response time of any equipment is exceeded. this may indicate either its breakdown, or the fall of a service important for the operation of the equipment.
Network programs must respond to an excess of the traffic limit allocated to an organization or office, or to a drop in the speed of the Internet connection. There can be many reasons for these phenomena: from a not too conscientious employee who downloads movies and downloads a channel during the working day, and problems with network equipment, to a not too honest provider.
Most often, in organizations, network programs are designed to help the system administrator or IT manager to inventory and monitor equipment. In this case, when it comes to the intangible assets of the company, about its property, it is important to notify the system administrator about the problems that have arisen. After all, we are talking about the honesty and reliability of employees!
From all of the above, a completely obvious conclusion follows: network programs are designed not to prevent equipment breakdown or to solve all problems that arise in the network, but to warn the administrator about the problem in time - even before complaints from users that “ does not work ”,“ does not enter ”,“ slows down ”.
Built-in OS administration tools are not always convenient or often do not have sufficient functionality, therefore, the system administrator's arsenal is eventually replenished with useful utilities, add-ons and scripts that greatly simplify everyday tasks. It is doubly gratifying when the found solution not only helps to cope with a specific problem, but is also distributed free of charge.
Advanced IP Scanner
The sysadmin must know everything about the systems operating on the network and quickly access them. Advanced IP Scanner, designed for fast multithreaded scanning of a local network, helps to cope with this task. AIPS is provided completely free of charge, without any reservations. The program is very simple and straightforward to use. After starting AIPS, it checks the IP addresses of the network interfaces of the host on which it is installed and automatically assigns the IP range to the scan parameters; if the IP does not need to be changed, then it remains to start the scan operation. As a result, we will get a list of all active network devices. For each, all possible information will be collected: MAC address, network card manufacturer, network name, user registered in the system, available shared resources and services (shared folders, HTTP, HTTPS and FTP). Almost all scanning options can be configured, for example, change the speed or exclude scanning of a certain type of network resources (shared folders, HTTP, HTTPS and FTP). You can connect to any resource with one click, you just need to mark it in the list. AIPS is integrated with Radmin software and during scanning it finds all machines running Radmin Server. The scan result can be exported to a file (XML, HTML or CSV) or saved to Favorites (drag-and-drop supported). In the future, if you need to access the desired client computer, you do not need to scan the network again. If the remote device supports the Wake-on-LAN function, it can be turned on or off by selecting the appropriate menu item.
NetWrix, a company specializing in developing solutions for auditing changes in IT infrastructure, offers ten free and very useful utilities designed to significantly simplify administration of Windows. For example, NetWrix Inactive Users Tracker allows you to solve one of the pressing security problems - the presence of inactive accounts that no one uses for some time (dismissed employees, business trips, moving around the job, temporary registration, etc.). HR managers rarely warn the IT department about changes, and such an account can easily be exploited by an attacker. The utility periodically checks all accounts in the domains and reports on those that have not been accessed for a certain time. In the Free version, as actions, it is possible to specify only a warning by e-mail (it is enough to set the SMTP parameters), all other operations are performed manually by the administrator, although the warning in our case is sufficient. In the paid version, the following are available: automatic setting of a random password, deactivating an account and moving to another OU, an OU filter to search for accounts. The get-NCInactiveUsers PowerShell cmdlet is offered separately, which allows you to get a list of inactive users (the "lastLogon" attribute is checked) and to simplify the writing of the corresponding scripts.
WinAudit Freeware
WinAudit is a free utility from Parmavex Services that allows you to perform a complete system audit. Does not require installation, can be run in command line mode. The program has a simple and localized interface, it can run on all versions of Windows, including 64-bit. Collecting data takes about a minute (the duration of the process may vary depending on the operating system and computer configuration), the resulting report consists of 30 categories (configurable). As a result, the administrator can get data about the system, installed software and updates, indicating the version and vendor, connected devices; a list of open network ports (number, service, program, etc.) and open folders; active sessions; security installations; access rights to the periphery; information about accounts and groups; list of tasks / services; startup programs; log records and system statistics (uptime, memory usage, disk usage). You can also search for specific files by name. For example, to find music and video on a user's hard drives, just set the appropriate extensions (avi, mp3, and the like). The result can be opened as a web page, exported to a file of many popular formats (txt, XML, CSV, PDF) or to a database (using the wizard, all popular are supported: MS SQL, MS Access, MySQL, Oracle and others), send by e-mail and print.

Computer accounting with CheckCfg
The problem of accounting for office equipment and used software is acute in any organization. You can solve it in different ways, one of the options is offered by the developer Andrey TatukovCheckCfg. This solution periodically collects data about hardware, OS and programs, including CPU type, amount of RAM, disk space, S.M.A.R.T. state. etc. At the same time, CheckCfg easily copes with several hundred computers. The result is displayed in a convenient tree-like form, local directories are easy to access. Each PC can be assigned an inventory number, if necessary, it is easy to generate a report in RTF format.
CheckCfg is a whole complex of programs. For the direct collection of data about the computer, CheckCfg is responsible, which is launched at the start of the OS and writes the result to a file. Information is managed and archived using the Sklad accounting program, which processes the files created by CheckCfg and saves them to its database, after which reports can be generated. With the help of the Sklad_w program, you can conveniently view the current configurations of computers and basic data on office equipment (by IP addresses, CPU, Memory, software). To analyze changes in the PC configuration and notify the administrator about this, another utility is used - Doberman. Perhaps the setting will not seem entirely trivial, since you have to manually create the necessary configuration files, but the detailed description on the site and the available templates allow you to figure it out without any problems.
MailArchiva Open Source Edition
Some mail servers, such as MS Exchange, have mail archiving functions that allow you to find old messages if necessary, including to identify leakage of confidential information when investigating incidents. In other cases, you have to provide these functions yourself. A variant of the solution is the development of the MailArchiva company, which is compatible with most modern mail servers (Lotus Domino, MS Exchange, MDaemon, Postfix, Zimbra, Sendmail, Scalix, Google Apps). Archiving via SMTP, IMAP / POP3, WebDAV and Milter protocols is supported (the program has a built-in SMTP and Milter server, IMAP / POP client). To avoid collecting all mail, you can create any archiving rules. Three levels of access to saved data are implemented - user (only own mail), administrator (settings and own mail) and auditor (all mail, can be limited by rules). The Open Source version of MailArchiva also provides intuitive search functionality, including attachments (Word, PowerPoint, Excel, OpenOffice, PDF, RTF, ZIP, tar, gz). MailArchiva works on Windows, Linux, FreeBSD and Mac OS X.
Performance Analysis of Logs
In case of problems with system performance, it is rather difficult to detect a bottleneck using the standard Windows Performance Monitor without experience. In order to figure out which metrics need to be taken and how to correctly interpret the result, you will need to thoroughly go through the documentation. The PAL utility (Performance Analysis of Logs, pal.codeplex.com) makes finding the bottleneck much easier. Once launched, it scans the logs and analyzes them using built-in templates. Currently, there are settings for most of the popular MS products - IIS, MOSS, SQL Server, BizTalk, Exchange, Active Directory and others. After starting, the administrator activates the necessary counters in the PAL Wizard by simply selecting a template from the list of suggested ones, specifies the current server settings (number of CPUs and others), the analysis interval and the directory for saving the result. After a while, a detailed HTML and XML report will be issued with the description, counter name and metrics (Min, Avg, Max and Hourly Trend). The report can then be easily copied to any document. But you still have to figure out the collected parameters on your own. Although if the PAL shows that the characteristic is in the green sector, you should not worry. The request itself is saved in the PAL.ps1 PowerShell script, which can be saved for later use. Templates are XML files; taking any of them as an example, you can create your own version. The built-in PAL Editor is offered for editing parameters in the template.

Win7 is officially supported, but works on all MS OSs, starting with WinXP (32/64). To install, you need PowerShell v2.0 +, MS .NET Framework 3.5SP1 and MS Chart Controls for Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5.
Create an Access Point with Virtual Router
The situation when a computer with a Wi-Fi card needs to be turned into an access point is by no means rare today. For example, you need to quickly deploy a WLAN or expand your Wi-Fi coverage. Initially, the operation of a wireless card was provided only in one of two modes: point-to-point, when clients connect to each other, or as an access point. In Win7 / 2k8 (except for Win7 Starter Edition), it became possible to virtualize network connections (Virtual Wi-Fi technology), which allows you to create several Wi-Fi modules with their own settings using one physical Wi-Fi adapter. Thus, the computer can be connected to Wi-Fi and at the same time act as an access point (SAPoint, Software Access Point). The connection to this virtual hotspot is secured using WPA2. You can turn a PC running Win7 / 2k8R2 into an access point using the Netsh console utility, through the Network and Sharing Center, or using the Virtual Router application, which has an intuitive GUI and very simple settings. After starting Virtual Router, you just need to specify the SSD and the password to connect, and then activate the access point. If necessary, you can also stop the hot spot by pressing one button. Additionally, the window displays the current connections to the point, for each you can set its own icon and change some parameters.

RDC connection management - RDCMan
For remote control of servers and PCs running Windows, the Remote Desktop Connection snap-in is designed. If you need to establish many RDP connections with different settings, then it becomes inconvenient to work with it. Instead of methodically saving individual settings for each remote computer, you can use the free Remote Desktop Connection Manager RDCMan to automate this process. After starting, specify the RDP connection settings that will be used by default and inherited by all connections. Here we set general credentials, gateway, screen settings, security parameters and much more. Next, we create the required number of system groups (for example, by purpose, location, OS version), for each of them, you can specify specific connection settings. And the last step is filling the groups with systems. To add a server, you only need to enter the domain name; if any parameter differs from the group settings, you can immediately redefine it. If necessary, systems can be easily moved between groups by simply dragging and dropping. If there are many systems, it is easier to create a text file by specifying one name per line, and then feed the blank to the utility. Now, to connect, just select the required server and click on the "Connect" item in the context menu. You can simultaneously activate several connections and switch between them.
Free Active Directory Tools
Managing Active Directory parameters using standard tools is not always easy and convenient. In some situations, ManageEngine's Free Active Directory Tools will help. The kit consists of fourteen utilities, run from one shell. For convenience, they are divided into six groups: AD USer Report, SharePoint Report, User Management, Domain and DC Info, Diagnostic Tools, and Session Management. For example, launching Empty Password User Report will allow you to get a list of accounts with empty passwords, GetDuplicates - to get accounts with the same attributes, CSVGenerator - to save Active Directory account data to a CSV file. Other features: report last logon time, retrieve data from AD based on a query, report on SharePoint installations, manage local accounts, view and edit domain password policies, get a list of domain controllers and their roles, manage their replication, monitor them work (CPU load, RAM, hard drives, performance, etc.), terminal session management and much more.
Comodo Time Machine
The ability to restore the system using the System Restore component is incorporated in Windows, starting with XP, but its functionality, to put it mildly, is limited, so third-party applications are often used for backup. Free utility Comodo Time Machine (comodo.com) allows you to roll back the OS to any previous state. Moreover, it will work even if the OS has completely stopped loading. During the process, CTM creates restore points (manually or on a schedule), all modified system files, the registry, and user files are recorded in them. This is a big advantage over System Restore, which only saves and restores system files and the registry. The first copy has the maximum size, the rest of the copies store only changed files. In order to save free disk space, you should periodically create a new checkpoint, deleting old archives. To be able to restore the OS, information about CTM is written into the boot sector; to call up the corresponding menu, just press the "Home" key. You can also restore the OS state according to a schedule, for example, configure the utility's behavior so that each reboot automatically rolls back to a "clean" version of the system. This will be useful, for example, in Internet cafes, where users leave behind a lot of garbage in the system. In addition to full OS recovery, the utility provides the ability to get an earlier version of any file from the archive. Search has been implemented, so you can find the data you need without any problems.
Amanda
The task of centralized data backup from workstations and servers running Windows and * nix can be solved with the help of AMANDA Advanced Maryland Automatic Network Disk Archiver). Initially, the program was created to work with tape drives, but over time, developers have proposed a mechanism called "virtual tapes" (vtapes), which allows you to save the collected data to hard drives and CD / DVD. AMANDA is a convenient add-on to the standard Unix programs dump / restore, GNU tar and some others, so its main characteristics should be considered precisely in terms of the capabilities of these basic utilities. Works on a client-server basis. All available authentication methods are used to access computers: Kerberos 4/5, OpenSSH, rsh, bsdtcp, bsdudp or Samba password. To collect data from Windows systems, a special agent or, alternatively, Samba is used. Compression and encryption (GPG or amcrypt) of information can be performed both directly on the client and on the server. All settings of the backup parameters are made exclusively on the server, there are ready-made templates in the delivery, so it's quite easy to figure it out.
Core Configurator 2.0 for Server Core
The initial configuration of a server running Win2k8 / R2 in Server Core mode is performed in the console using commands. To make things easier, the OS developers have added an interactive script SCONFIG.cmd to R2, which allows you to configure the basic parameters of the system. An alternative is available on Codeplex - the wonderful Core Configurator. For its operation, you will need the NetFx2-ServerCore, NetFx2-ServerCore and PowerShell components. After starting Start_CoreConfig.wsf, we get a menu, in it we find several items that provide access to the main settings that would have to be managed from the command line: product activation, setting screen resolution, clock and time zone, network interface, setting permissions for remote RDP connections , managing local accounts, configuring Windows Firewall, enabling / disabling WinRM, changing the computer name, workgroup or domain, configuring the role, features, Hyper-V, and starting DCPROMO. If you select the "Load at Windows startup" checkbox, the program will be loaded along with the system.
Exchange 2010 RBAC Manager
Exchange 2010 introduces a new role-based access model that allows you to fine-tune the privilege level for users and administrators based on the tasks they perform. The only drawback is that the built-in management tools using PowerShell cmdlets may not seem convenient and understandable to everyone. More advanced is the free Exchange 2010 RBAC Manager (RBAC Editor GUI, rbac.codeplex.com), which offers a clean graphical interface for setting properties for all roles. Dealing with its features will not be difficult even for a beginner. The program is written in C # and uses PowerShell. To work, you need installed Exchange 2010 Management Tools.
PowerGUI
As soon as it appeared, the PowerShell command shell won the sympathy of Windows admins, who have long needed a tool to automate many tasks. With the first versions of PowerShell, Microsoft developers were unable to offer a more or less functional editor, so several third-party projects filled the niche. The best of these today is PowerGUI, which provides an easy-to-use graphical interface for efficiently creating and debugging PowerShell scripts. At the same time, the authors offer ready-made sets of scripts for solving many problems - they can be used in their developments.
Multi-Tabbed PuTTY
The free PuTTY client is well known for admins who need to connect to remote hosts using SSH, Telnet, or rlogin. This is a very handy program that allows you to save session settings for quick connection to the selected system. The only inconvenience is that with a large number of connections, the desktop is loaded with many open windows. This problem is solved by the Multi-Tabbed PuTTY add-on, which implements the tab system.
INFO
PuTTY was originally developed for Windows, but was later ported to Unix.Conclusion
Often there is no need to puzzle over a solution to a specific problem: most likely, other administrators have already encountered it and offered their own version - a specific utility or script that you don't even need to pay for.
Local networks are no longer something unusual, as it was at the dawn of their creation. The advantages of such networks are obvious. Users of computers united in a single local network will have access to shared files and folders and can quite easily exchange necessary information, edit documents, play games using command modes, etc. However, this only applies to computers that are connected to each other using wires and a fairly large amount of "iron" equipment. But what to do when computers are quite far from each other? This is where software products for creating virtual local area networks come to the rescue. Among them, quite often there are completely free programs. Downloading free programs for creating local networks and installing them on your computer is not a problem now. As they say, there would be a desire. Among the free burnouts for local networks, such applications can be divided into two main types. The first type allows you to create a virtual private network in such a way that one of the computers will play the role of a server. And this also includes programs that use computers alternately as the main server. In this case, data exchange is carried out using P2P (peer-to-peer) technologies, that is, using the universal BitTorrent protocol. The second type includes programs where the role of the central server is played by the remote server of the software manufacturer. Here you only need to register on the manufacturer's website. If we talk about free programs of this kind, then, in comparison with paid counterparts, they allow you to create networks with the connection of about a dozen computers or accounts. It is clear that paid counterparts can create networks with the connection of even several hundred computers. However, for home use or small offices, 15-20 users is perfectly sufficient. It must be said that networks created using such applications have all the capabilities of conventional wired networks. And the setting, in most cases, is very similar. The difference in such programs may also be that sometimes one computer is bound only to one specific IP address. In some other cases, an IP address may be assigned automatically. To work in such a network, only the program installed on the computer will be needed. Some free VPN software even allows you to use the credentials of many Internet pagers, such as Jabber accounts. However, the capabilities of such programs are quite similar to each other. Some additional features may differ, such as built-in chats or short text messaging capabilities. It seems that today, virtual networks are still preferable, since they allow computers to be combined into a single network that are even in different parts of the world. On our site you can download the most modern programs for creating local networks.
Network software Is software that allows you to organize the user's work on the network. It is represented by general, system and special software (Fig. 6.5).
Rice. 6.5.
General networking software includes:
- browser - a web browser (such as Internet Explorer). The browser contains the following tools: a program for working with e-mail (reading, creating, editing and sending mail messages); a program for working with a news server (subscribing to a news group, reading news, creating and forwarding messages), a text editor;
- HTML editors - editors designed to create web pages;
- graphic web tools - tools designed to optimize the graphic elements of web pages;
- machine translators - software for viewing web pages in various languages;
- antivirus network programs - programs used to prevent software viruses from entering the user's computer or spreading it over the company's local network.
TO system software include:
operating system - an indispensable part of the system software, guaranteeing effective
the functioning of the computer in various modes, organizing the execution of programs and the interaction of the user and external devices with the computer;
- service programs - programs that expand the capabilities of the OS, providing the user and his programs with a set of additional services;
- maintenance system - a system that facilitates diagnostics, equipment testing and troubleshooting in a PC.
Special network operating systems are designed for network management. According to its organization, this type of network operating system can be divided into peer-to-peer (Peer-To-Peer Network) and with dedicated server (Dedicated File Server Network).
Peer-to-peer network operating systems include NetWare Lite, Personal NetWare (Novell), Windows For Workgroups (Microsoft), LANtastic (Artisoft).
Network operating systems
V network OS there are several parts:
- WS Local Resource Management Tools - functions for distributing RAM between processes, scheduling and scheduling processes, controlling processors in multiprocessor machines, controlling peripheral devices and other functions for managing local OS resources;
- means of providing own resources and services for general use - the server side of the OS (server). These tools provide, for example, the locking of files and records, which is necessary for their sharing; maintaining directories of names of network resources; processing requests for remote access to your own file system and database; management of queues of requests of remote users to their peripheral devices;
- means of requesting access to remote resources and services and their use - the client side of the OS (redirector). This part recognizes and redirects requests to remote resources from applications and users to the network. In this case, the request comes from the application in a local form, and is transmitted to the network in a different form that meets the requirements of the server. The client part also receives responses from servers and converts them to a local format, so that for the application the execution of local and remote requests is indistinguishable;
- OS communication tools, through which messages are exchanged on the network. This part provides addressing and buffering of messages, selection of a message transmission route over the network, transmission reliability, i.e. is a means of transporting messages.
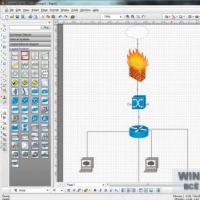 Free software for working with the network
Free software for working with the network How the password generator works
How the password generator works Recording video with sound from a computer screen: software overview Copying a computer screen program
Recording video with sound from a computer screen: software overview Copying a computer screen program Getting Started with Mozilla Firefox - Download and Install
Getting Started with Mozilla Firefox - Download and Install Best free hexadecimal editors (hex) Recover archives in WinRAR
Best free hexadecimal editors (hex) Recover archives in WinRAR A guide to file managers for Windows
A guide to file managers for Windows Free program to permanently delete files File Shredder screenshots File shredder 2
Free program to permanently delete files File Shredder screenshots File shredder 2